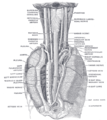
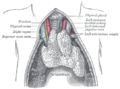
- Human right lung
-
Human right lung 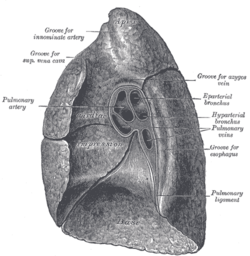
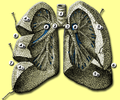
Mediastinal surface of right lung. 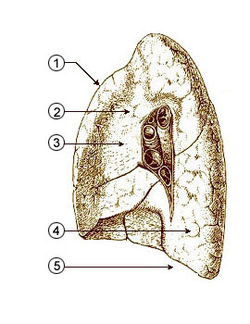
1. Anterior border
2. Mediastinal part
3. Medial surface
4. Inferior lobe
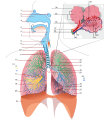
5. Base of lungLatin pulmo dexter Gray's subject #240 1096 The human right lung is divided into three lobes (as opposed to two lobes on the left), superior, middle, and inferior, by two interlobular fissures:
Contents
Fissures
- One of these, the oblique fissure, separates the inferior from the middle and superior lobes, and corresponds closely with the fissure in the left lung. Its direction is, however, more vertical, and it cuts the lower border about 7.5 cm. behind its anterior extremity.
- The other fissure, the horizontal fissure, separates the superior from the middle lobe. It begins in the previous fissure near the posterior border of the lung, and, running horizontally forward, cuts the anterior border on a level with the sternal end of the fourth costal cartilage; on the mediastinal surface it may be traced backward to the hilum.
Lobes
The middle lobe, the smallest lobe of the right lung, is wedge-shaped, and includes the lower part of the anterior border and the anterior part of the base of the lung. (There is no middle lobe on the left lung, though there is a lingula.)
The superior and inferior lobes are similar to their counterparts on the left lung.
Difference in size
The right lung, although shorter by 5 cm. than the left, in consequence of the diaphragm rising higher on the right side to accommodate the liver, is broader, owing to the inclination of the heart to the left side. Consequently, the volume, the total capacity and the weight of the right lung is higher than that of the left.
Impressions
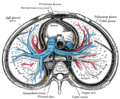
On the mediastinal surface, immediately above the hilum, is an arched furrow which accommodates the azygos vein; while running upward, and then arching lateralward some little distance below the apex, is a wide groove for the superior vena cava and right innominate vein; behind this, and nearer the apex, is a furrow for the innominate artery.
Behind the hilum and the attachment of the pulmonary ligament is a vertical groove for the esophagus; this groove becomes less distinct below, owing to the inclination of the lower part of the esophagus to the left of the middle line.
In front and to the right of the lower part of the esophageal groove is a deep concavity for the extrapericardiac portion of the thoracic part of the inferior vena cava.
Additional images
See also
External links
- Lung Lobes
- 00458 at CHORUS
- SUNY Figs 19:05-01 - "Mediastinal surface of the right lung."
- Diagram and quiz at cancer.gov
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 02101.002-1
- Cross section at univie.ac.at
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Anatomy: Lower RT respiratory system (TA A06.3–5, TH H3.05.02, GA 11.1084) TB tree main bronchus (right, left) · lobar/secondary bronchi (eparterial bronchus) · segmental/tertiary bronchiLungs GeneralLeft lung/Right lung · Base/Apex · Root/Hilum
Superior lobe · Lingula of left lung/Middle lobe of right lung · Inferior lobe
borders: Anterior border (Cardiac notch) · Posterior border · Inferior border
surfaces: Costal surface · Mediastinal surface (Cardiac impression) · Diaphragmatic surface
fissures: Oblique fissure · Horizontal fissureBronchiole: Conducting zone (Terminal bronchiole) · Respiratory zone (Respiratory bronchiole · Alveolar duct · Alveolus · Blood-air barrier)CellsCategories:- Lung anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.