- Parathyroid gland
Infobox Anatomy
Name = Parathyroid gland
Latin = glandula parathyroidea inferior, glandula parathyroidea superior, Phillip.Hungerford. Daniel.Mart
GraySubject = 273
GrayPage = 1271

Caption = Endocrine system. (Parathyroid gland not pictured, but are present on surface of thyroid gland, as shown below.)
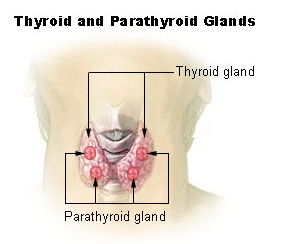
Caption2 = Thyroid and parathyroid.
Precursor =neural crest mesenchyme and third and fourthpharyngeal pouch endoderm
System =
Artery =superior thyroid artery ,inferior thyroid artery ,
Vein =superior thyroid vein ,middle thyroid vein ,inferior thyroid vein ,thyreoidea ima
Nerve =middle cervical ganglion ,inferior cervical ganglion
Lymph =
MeshName = Parathyroid+Glands
MeshNumber = A06.407.560
DorlandsPre = g_06
The parathyroid glands are small endocrine
gland s in the neck, usually located behind thethyroid gland , which produceparathyroid hormone . In rare cases the parathyroid glands are located within thethyroid glands. Most often there are four parathyroid glands, but some people have six or even eight.Anatomy
The parathyroid glands are four or more small glands located on the posterior surface of the
thyroid gland . Histologically they are quite easily recognizable from the thyroid as they have densely packed cells in contrast with the follicle structure of thethyroid . [BUHistology|15001ooa] However at surgery they are harder to differentiate from the thyroid or fat.They distinguish themselves from the
thyroid gland histologically as they contain two types of cells: [BUHistology|15002loa]History
The parathyroid glands were discovered by Ivar Viktor Sandström (1852-1889), a Swedish medical student, in
1880 . [cite journal | author = Eknoyan G.. | title = A history of the parathyroid glands | journal = Am J Kidney Dis | volume = 26 | issue =5| pages = 801–7 | year =1995 | pmid = 7485136 | doi = 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90447-6] It was the last major organ to be recognized in humans.Physiology
The sole function of the parathyroid glands is to maintain the body's
calcium level within a very narrow range, so that the nervous andmuscular system s can function properly.When blood
calcium levels drop below a certain point,calcium-sensing receptor s in the parathyroid gland are activated to release hormone into the blood.Parathyroid hormone (PTH, also known as parathormone) is a smallprotein that takes part in the control ofcalcium and phosphatehomeostasis , as well as bone physiology.Parathyroid hormone has effects antagonistic to those ofcalcitonin . It increases bloodcalcium levels by stimulatingosteoclast s to break down bone and releasecalcium . It also increases gastrointestinalcalcium absorption by activatingvitamin D , and promotescalcium uptake by thekidney s.Role in disease
Hyperparathyroidism and related conditionsThe single major disease of parathyroid glands is overactivity of one or more of the parathyroid lobes, which make too much
parathyroid hormone causing a potentially seriouscalcium imbalance. This is calledhyperparathyroidism ; it leads tohypercalcemia andosteitis fibrosa cystica . Sincehyperparathyroidism was first described in 1925, the symptoms have become known as "moan s,groan s, stones, and bones." The primary treatment for this disease is the surgical removal of the faulty gland.Modern high frequency ultrasound can see
parathyroid masses, even before they cause highcalcium . They are called parathyroid incidentalomas. If a patient has elevatedcalcium , the ultrasound can be used to locate the abnormal glands. The use of ultrasound guided FNA, andparathyroid hormone washings can confirm the abnormal glands. A blood calcium 15-30 minutes after the biopsy can help determine if the disease is caused by a single abnormal gland or multiple glands.A drop in serum
calcium suggests a single source, and no drop suggests multiple glands. This, with a non-localizing Sestamibi scan would point toward a neck exploration, rather than a minimally invasive method aimed a single gland disease.A
Sestamibi scan is often used to determine which parathyroid gland(s) are responsible for overproduction of parathyroid hormone.Another related condition is called secondary hyperparathyroidism, or secondary HPT - common in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis. In secondary HPT, the parathyroid glands make too much parathyroid hormone (PTH), and the kidneys do not produce enough vitamin D, and calcium and phosphorus are out of balance. Even though one may not have any symptoms, treating secondary HPT is important. Cinacalcet (Sensipar) is a medicine that can help treat such dialysis patients and is available by prescription only.
Hypoparathyroidism and related conditions*
Hypoparathyroidism
*Pseudohypoparathyroidism
*Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
* Disorders of theparathyroid hormone receptor have been associated withJansen's metaphyseal chondroplasia andBlomstrand's chondroplasia .Embryology and Evolution
The parathyroid glands originate from the interaction of
neural crest mesenchyme and third and fourthbranchial pouch endoderm .Genetically,
Eya-1 (transcripitonal co-activator),Six-1 (a homeobox transcription factor), andGcm-2 (a transcription factor) have been associated with the development of the parathyroid gland, and alterations in these genes alters parathyroid gland development.The conserved homology of genes and
calcium sensing receptors in fish gills with those in the parathryroid glands of birds and mammals is recognized byevolutionary developmental biology as evolution using genes and gene networks in novel ways to generate new structures with some similar functions and novel functions.
=AdditionalReferences
External links
* [http://www.endocrineweb.com/parathyroid.html Endocrine Web at endocrineweb.com]
* [http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/101/51/17716 The origin of the parathyroid gland at pnas.org]
* [http://www.pandasthumb.org/archives/2004/12/human_gland_pro.html Human Gland Probably Evolved From Gills at pandasthumb.org]
* [http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00472.x The role of the endoderm in the development and evolution of the pharyngeal arches at blackwell-synergy.com]
* [http://www.parathyroid.com Parathyroid disease and treatments discussed in layman's terms at Parathyroid.com]
* [http://scienceblogs.com/pharyngula/2006/06/deep_homologies_in_the_pharyng.php Deep homologies in the pharyngeal arches at scienceblogs.com]
*
*
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
