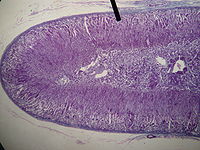
- Adrenal cortex
-
Adrenal cortex 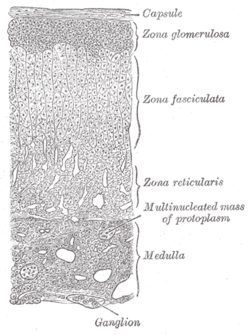
Layers of cortex. Latin cortex glandulae suprarenalis Gray's subject #277 1278 Precursor mesoderm[1] Situated along the perimeter of the adrenal gland, the adrenal cortex mediates the stress response through the production of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, including aldosterone and cortisol respectively. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis.
Contents
Layers
Layer Name Primary product Most superficial cortical layer zona glomerulosa mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone) Middle cortical layer zona fasciculata glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol) Deepest cortical layer zona reticularis weak androgens (e.g., dehydroepiandrosterone, adrenosterone) Notably, the reticularis in all animals is not always easily distinguishable and dedicated to androgen synthesis. In rodents, for instance, the reticularis also generates corticosteroids (specifically corticosterone, not cortisol). The two layers are collectively referred to as the fasciculo-reticularis. Female rodents also exhibit another cortical layer called the "X zone" whose function is not yet clear.
Hormone synthesis
All adrenocortical hormones are synthesized from cholesterol. Cholesterol is transported into the adrenal gland. The steps up to this point occur in many steroid-producing tissues. Subsequent steps to generate aldosterone and cortisol, however, primarily occur in the adrenal cortex:
- Progesterone → (hydroxylation at C21) → 11-Deoxycorticosterone → (two further hydroxylations at C11 and C18) → Aldosterone
- Progesterone → (hydroxylation at C17) → 17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone → (hydroxylation at C21) → 11-Deoxycortisol → (hydroxylation at C11) → Cortisol
Production
The adrenal cortex produces a number of different corticosteroid hormones.
Mineralocorticoids
Main article: MineralocorticoidsThey are produced in the zona glomerulosa. The primary mineralocorticoid is aldosterone. Its secretion is regulated by the oligopeptide angiotensin II (angiotensin II is regulated by angiotensin I, which in turn is regulated by renin). Aldosterone is secreted in response to high extracellular potassium levels, low extracellular sodium levels, and low fluid levels and blood volume. Aldosterone affects metabolism in different ways:
- It increases urinary excretion of potassium ions
- It increases interstitial levels of sodium ions
- It increases water retention and blood volume
Glucocorticoids
Main article: GlucocorticoidsThey are produced in the zona fasciculata. The primary glucocorticoid released by the adrenal gland in the human is cortisol and corticosterone in many other animals. Its secretion is regulated by the hormone ACTH from the anterior pituitary. Upon binding to its target, cortisol enhances metabolism in several ways:
- It stimulates the release of amino acids from the body
- It stimulates lipolysis, the breakdown of fat
- It stimulates gluconeogenesis, the production of glucose from newly-released amino acids and lipids
- It increases blood glucose levels in response to stress, by inhibiting glucose uptake into muscle and fat cells
- It strengthens cardiac muscle contractions
- It increases water retention
- It has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects
Androgens
Main article: AndrogensThey are produced in the zona reticularis. The most important androgens include:
- Testosterone: a hormone with a wide variety of effects, ranging from enhancing muscle mass and stimulation of cell growth to the development of the secondary sex characteristics.
- Dihydrotestosterone (DHT): a metabolite of testosterone, and a more potent androgen than testosterone in that it binds more strongly to androgen receptors.
- Androstenedione (Andro): an androgenic steroid produced by the testes, adrenal cortex, and ovaries. While androstenediones are converted metabolically to testosterone and other androgens, they are also the parent structure of estrone.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA): It is the primary precursor of natural estrogens. DHEA is also called dehydroisoandrosterone or dehydroandrosterone. The reticularis also produces DHEA-sulfate due to the actions of a sulfotransferase, SULT2A1.[2]
Pathology
- Adrenal insufficiency (e.g. due to Addison's disease)
- Cushing's syndrome
- Conn's syndrome
- Adrenal Virilism
See also
References
- ^ "Embryology of the adrenal gland". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=endocrin.box.466. Retrieved 2007-12-11.
- ^ Rainey WE, Nakamura Y (February 2008). "Regulation of the adrenal androgen biosynthesis". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 108 (3-5): 281–6. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.09.015. PMC 2699571. PMID 17945481. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2699571.
External links
- SUNY Labs 40:04-0203 - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Blood Supply to the Suprarenal Glands"
- Mnemonic at medicalmnemonics.com 180 2201 412
- Histology at BU 14502loa
- Anatomy Atlases - Microscopic Anatomy, plate 15.292 - "Adrenal Gland"
- Adrenal Cortex Medical Notes on rahulgladwin.com
Human anatomy, endocrine system: endocrine glands (TA A11, TH H3.08, GA 11.1269) Islets of pancreas Hypothalamic/
pituitary axes
+parathyroidPituitaryPars intermedia · Pars tuberalis · Pars distalis
Acidophil cell (Somatotropic cell, Prolactin cell) · Basophil cell (Corticotropic cell, Gonadotropic cell, Thyrotropic cell) · Chromophobe cellThyroid isthmus · Lobes of thyroid gland · Pyramidal lobe of thyroid gland
Follicular cell · Parafollicular cellCortexPineal gland Other Enteroendocrine cell · ParagangliaCategories:- Glands
- Abdomen
- Endocrine system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.