- Sulfatase
Pfam_box
Symbol = Sulfatase
Name =
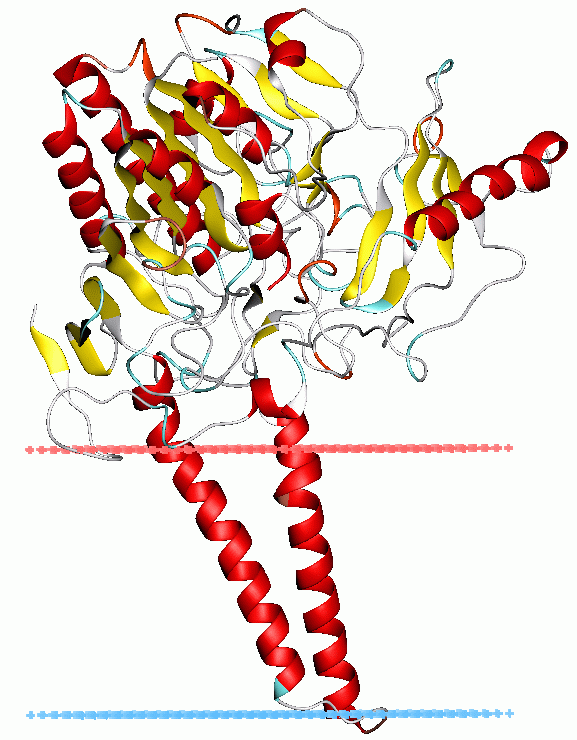
width =200
caption =Steryl-sulfatase
Pfam= PF00884
InterPro= IPR000917
SMART=
PROSITE = PDOC00117
SCOP = 1auk
TCDB =
OPM family= 24
OPM protein= 1p49
PDB=PDB3|1fsu :43-486 PDB3|1hdhB:3-501 PDB3|1p49A:25-514PDB3|1n2kA:19-440 PDB3|1e3cP:19-440 PDB3|1e2sP:19-440PDB3|1e1zP:19-440 PDB3|2aikP:68-74 PDB3|1e33P:19-440PDB3|1auk :19-440 PDB3|1n2lA:19-440Sulfatases EC number|3.1.6. are
enzyme s of theesterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis ofsulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates.Sulfatases play important roles in the cycling of sulfur in the environment, in the degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids in the lysosome, and in remodelling sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the extracellular space. Together with
sulfotransferase s, sulfatases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of sulfate esters.Occurrence and importance
Sulfatases are found in lower and higher organisms. In higher organisms they are found in intracellular and extracellular spaces. A large number of sulfatases are localized in the lysosome, an acidic digestive organelle found within the cell. Lysosomal sulfatases cleave a range of sulfated carbohydrates including sulfated glycosaminoglycans and glycolipids. Genetic defects in sulfatase activity can arise through mutations in individual sulfatases and result in certain lysosomal storage disorders with a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from defects in physical and intellectual development.
Three-dimensional structure
The following sulfatases have been shown to be structurally related based on their
sequence homology :cite journal |author=von Figura K, Vingron M, Schmidt B, Meyer HE, Peters C, Rommerskirch W, Rupp K, Pohlmann R, Zuhlsdorf M |title=Phylogenetic conservation of arylsulfatases. cDNA cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase B |journal=J. Biol. Chem. |volume=265 |issue=6 |pages=3374–3381 |year=1990 |pmid=2303452] cite journal |author=Wilson PJ, Morris CP, Anson DS, Occhiodoro T, Bielicki J, Clements PR, Hopwood JJ |title=Hunter syndrome: isolation of an iduronate-2-sulfatase cDNA clone and analysis of patient DNA |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=87 |issue=21 |pages=8531–8535 |year=1990 |pmid=2122463 |doi=10.1073/pnas.87.21.8531] cite journal |author=Grossman AR, de Hostos EL, Schilling J |title=Structure and expression of the gene encoding the periplasmic arylsulfatase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii |journal=Mol. Gen. Genet. |volume=218 |issue=2 |pages=229–239 |year=1989 |pmid=2476654 |doi=10.1007/BF00331273]
*cerebroside-sulfatase
*steryl-sulfatase
*arylsulfatase A EC number|3.1.6.8 (ASA), a lysosomal enzyme which hydrolyzescerebroside sulfate ;
*arylsulfatase B EC number|3.1.6.12 (ASB) which hydrolyzes the sulfate ester group fromN-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate residues ofdermatan sulfate ;
*arylsulfatase C (ASD) and E (ASE); steryl-sulfatase EC number|3.1.6.2 (STS), a membrane bound enzyme which hydrolyzes 3-beta-hydroxysteroid sulfate s;
*iduronate 2-sulfatase EC number|3.1.6.13 (IDS), a lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyzes the 2-sulfate groups fromiduronic acid s indermatan sulfate andheparan sulfate ;
*N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase EC number|3.1.6.4, which hydrolyzes the 6-sulfate groups of theN-acetyl-D-galactosamine ofchondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units ofkeratan sulfate ;
*N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase EC number|3.10.1.1, the lysosomal enzyme that hydrolysesN-sulfo-D-glucosamine intoglucosamine andsulfate ;
*glucosamine-6-sulfatase EC number|3.1.6.14 (G6S), which hydrolyzes the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate;
*N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase EC number|3.10.1.1, the lysosomal enzyme that hydrolysesN-sulfo-D-glucosamine intoglucosamine andsulfate ;
*sea urchin embryoarylsulfatase EC number|3.1.6.1;
*green algaearylsulfatase EC number|3.1.6.1, which plays a role in themineralization of sulfates; and
*arylsulfatase EC number|3.1.6.1 from "Escherichia coli ", "Klebsiella aerogenes " and "Pseudomonas aeruginosa ".Human proteins containing this domain
ARSA ;ARSB ;ARSD ;ARSE ;ARSF ;ARSG ;ARSH ;ARSI ;ARSJ ;ARSK ;GALNS ;GNS ;IDS ;PIGG ;SGSH ;STS ;SULF1 ;SULF2 ;References
External links
*
* [http://www.rndsystems.com/molecule_group.aspx?g=954&r=6 Overview at rndsystems.com]
* [http://www.mad-cow.org/00/annotation_frames/tools/genbrow/sulfatases/sulfatases.html "Annotation of the sulfatase gene family" at mad-cow.org]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
