- Tyrosinase
-
monophenol monooxygenase Identifiers EC number 1.14.18.1 CAS number 9002-10-2 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles Tyrosinase also known as monophenol monooxygenase is an enzyme that catalyses the oxidation of phenols (such as tyrosine) and is widespread in plants and animals. Tyrosinase is a copper-containing enzyme present in plant and animal tissues that catalyzes the production of melanin and other pigments from tyrosine by oxidation, as in the blackening of a peeled or sliced potato exposed to air. It is found inside melanosomes. In humans, the tyrosinase enzyme is encoded by the TYR gene.[1]
Contents
Clinical significance
A mutation in the tyrosinase gene resulting in impaired tyrosinase production leads to type I oculocutaneous albinism, a hereditary disorder that affects one in every 17,000 people.[2]
Catalyzed reaction
Tyrosinase carries out the oxidation of phenols such as tyrosine and dopamine using dioxygen (O2). In the presence of catechol, benzoquinone is formed (see reaction below). Hydrogens removed from catechol combine with oxygen to form water.
The substrate specificity becomes dramatically restricted in mammalian tyrosinase which utilizes only L-form of tyrosine or DOPA as substrates, and has restricted requirement for L-DOPA as cofactor.[3]
Tyrosinase structure
Tyrosinases have been isolated and studied from a wide variety of plant, animal and fungal species. Tyrosinases from different species are diverse in terms of their structural properties, tissue distribution and cellular location.[4] It has been suggested that there is no common tyrosinase protein structure occurring across all species.[5] The enzymes found in plant, animal and fungal tissue frequently differ with respect to their primary structure, size, glycosylation pattern and activation characteristics. However, all tyrosinases have in common a binuclear type 3 copper centre within their active site. Here two copper atoms are each coordinated with three histidine residues.
Common central domain of tyrosinase Identifiers Symbol Tyrosinase Pfam PF00264 InterPro IPR002227 PROSITE PDOC00398 SCOP 1hc2 Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Transmembrane protein and sorting
Human tyrosinase is a single membrane spanning transmembrane protein.[6] In humans, tyrosinase is sorted into melanosomes[7] and the catalytically active domain of the protein resides within melanosomes. Only a small enzymatically non-essential part of the protein extends into the cytoplasm of the melanocyte.
Active site
The two copper atoms within the active site of tyrosinase enzymes interact with dioxygen to form a highly reactive chemical intermediate that then oxidizes the substrate. The activity of tyrosinase is similar to catechol oxidase, a related class of copper oxidase. Tyrosinases and catechol oxidases are collectively termed polyphenol oxidases.
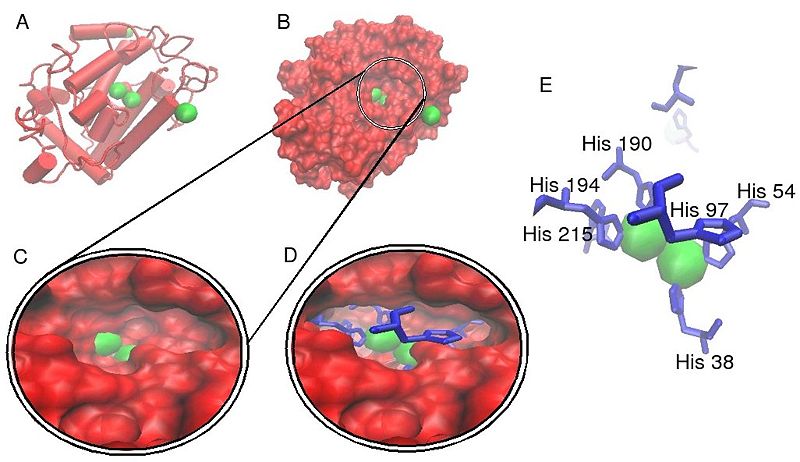
Crystallographic structure of a Streptomyces derived tyrosinase in complex with a so called "caddie protein".[8] In all models only the tyrosinase molecule is shown, copper atoms are shown in green and the molecular surface is shown in red. In models D and E histidine amino acids are shown as a blue line representation. From model E it can be clearly seen that each copper atom within the active site is indeed complexed with three histidine residues, forming a type 3 copper center. It can also be seen from models C and D that the active site for this protein sits within a pillus formed on the molecular surface of the molecule.
Gene regulation
The gene for tyrosinase is regulated by the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor.[9][10]
References
- ^ Barton DE, Kwon BS, Francke U (July 1988). "Human tyrosinase gene, mapped to chromosome 11 (q14----q21), defines second region of homology with mouse chromosome 7". Genomics 3 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(88)90153-X. PMID 3146546.
- ^ Witkop CJ (October 1979). "Albinism: hematologic-storage disease, susceptibility to skin cancer, and optic neuronal defects shared in all types of oculocutaneous and ocular albinism". Ala J Med Sci 16 (4): 327–30. PMID 546241.
- ^ Hearing VJ, Ekel TM, Montague PM, Nicholson JM (February 1980). "Mammalin tyrosinase. Stoichiometry and measurement of reaction products". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 611 (2): 251–68. PMID 6766744.
- ^ Mayer, AM (2006). "Polyphenol oxidases in plants and fungi: Going places? A review". Phytochemistry 67 (21): 2318–2331. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.08.006. PMID 16973188.
- ^ Jaenicke, E and Decker, H. (2003). "Tyrosinases from crustaceans form hexamers". Biochem. J. 371 (Pt 2): 515–523. doi:10.1042/BJ20021058. PMC 1223273. PMID 12466021. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1223273.
- ^ Kwon BS, Haq AK, Pomerantz SH, Halaban R (November 1987). "Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for human tyrosinase that maps at the mouse c-albino locus". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (21): 7473–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.21.7473. PMC 299318. PMID 2823263. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=2823263.
- ^ Theos AC, Tenza D, Martina JA, Hurbain I, Peden AA, Sviderskaya EV, Stewart A, Robinson MS, Bennett DC, Cutler DF, Bonifacino JS, Marks MS, Raposo G (November 2005). "Functions of adaptor protein (AP)-3 and AP-1 in tyrosinase sorting from endosomes to melanosomes". Mol. Biol. Cell 16 (11): 5356–72. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-07-0626. PMC 1266432. PMID 16162817. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1266432.
- ^ PDB 1WX3; Matoba Y, Kumagi, T. et al. (2006). "Crystallographic evidence that the dinuclear copper center of tyrosinase is flexible during catalysis". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (13): 8981–8990. doi:10.1074/jbc.M509785200. PMID 16436386.
- ^ Hou L, Panthier JJ, Arnheiter H (2000). "Signaling and transcriptional regulation in the neural crest-derived melanocyte lineage: interactions between KIT and MITF". Development 127 (24): 5379–89. PMID 11076759.
- ^ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, Widmer DS, Praetorius C, Einarsson SO, Valgeirsdottir S, Bergsteinsdottir K, Schepsky A, Dummer R, Steingrimsson E (2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21 (6): 665–76. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971.
External links
Oxidoreductases: dioxygenases, including steroid hydroxylases (EC 1.14) 1.14.11: 2-oxoglutarate 1.14.13: NADH or NADPH Flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO1, FMO2, FMO3, FMO4, FMO5) - Nitric oxide synthase (NOS1, NOS2, NOS3) - Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase - Methane monooxygenase - 3A4 - Lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase1.14.14: reduced flavin or flavoprotein 1.14.15: reduced iron-sulfur protein 1.14.16: reduced pteridine (BH4 dependent) 1.14.17: reduced ascorbate 1.14.18-19: other Tyrosinase - Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-11.14.99 - miscellaneous Metabolism: amino acid metabolism · synthesis and catabolism enzymes (essential in CAPS) K→acetyl-CoA (see below)G →alpha-ketoglutarate→TCAOther→succinyl-CoA→TCAG→fumarateasparagine→aspartate→Categories:- Human proteins
- Enzymes
- EC 1.14.18
- Copper enzymes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.