- Phosphofructokinase
-
- "PFK" redirects here. PFK (Poulet Frit Kentucky) is also the name for KFC in French-speaking Quebec, Canada. For the Polish hip-hop group, see Paktofonika.
Phosphofructokinase Identifiers Symbol Ppfruckinase Pfam PF00365 InterPro IPR000023 PROSITE PDOC00336 Available protein structures: Pfam structures PDB RCSB PDB; PDBe PDBsum structure summary Phosphofructokinase is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose 6-phosphate in glycolysis.
The enzyme-catalysed transfer of a phosphoryl group from ATP is an important reaction in a wide variety of biological processes[1]. One enzyme that utilises this reaction is phosphofructokinase (PFK), which catalyses the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6- bisphosphate, a key regulatory step in the glycolytic pathway[2][3]. PFK exists as a homotetramer in bacteria and mammals (where each monomer possesses 2 similar domains) and as an octomer in yeast (where there are 4 alpha- (PFK1) and 4 beta-chains (PFK2), the latter, like the mammalian monomers, possessing 2 similar domains[3]).
PFK is about 300 amino acids in length, and structural studies of the bacterial enzyme have shown it comprises two similar (alpha/beta) lobes: one involved in ATP binding and the other housing both the substrate-binding site and the allosteric site (a regulatory binding site distinct from the active site, but that affects enzyme activity). The identical tetramer subunits adopt 2 different conformations: in a 'closed' state, the bound magnesium ion bridges the phosphoryl groups of the enzyme products (ADP and fructose-1,6- bisphosphate); and in an 'open' state, the magnesium ion binds only the ADP[4], as the 2 products are now further apart. These conformations are thought to be successive stages of a reaction pathway that requires subunit closure to bring the 2 molecules sufficiently close to react[4].
Deficiency in PFK leads to glycogenosis type VII (Tarui's disease), an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by severe nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps and myoglobinuria in response to bursts of intense or vigorous exercise[3]. Sufferers are usually able to lead a reasonably ordinary life by learning to adjust activity levels[3].
There are two types of the enzyme:
Type Synonyms EC number Substrate Product Subunit genes Phosphofructokinase 1 6-phosphofructokinase
phosphohexokinaseEC 2.7.1.11 
Fructose 6-phosphate
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatePFKL, PFKM, PFKP Phosphofructokinase 2 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase EC 2.7.1.105 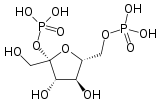
Fructose-2,6-bisphosphatePFKFB1, PFKFB2, PFKFB3, PFKFB4 See also
References
- ^ Evans PR, Hellinga HW (1987). "Mutations in the active site of Escherichia coli phosphofructokinase". Nature 327 (6121): 437–439. doi:10.1038/327437a0. PMID 2953977.
- ^ Wegener G, Krause U (2002). "Different modes of activating phosphofructokinase, a key regulatory enzyme of glycolysis, in working vertebrate muscle". Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30 (2): 264–270. PMID 12023862.
- ^ a b c d Raben N, Exelbert R, Spiegel R, Sherman JB, Nakajima H, Plotz P, Heinisch J (1995). "Functional expression of human mutant phosphofructokinase in yeast: genetic defects in French Canadian and Swiss patients with phosphofructokinase deficiency". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 56 (1): 131–141. PMC 1801305. PMID 7825568. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1801305.
- ^ a b Shirakihara Y, Evans PR (1988). "Crystal structure of the complex of phosphofructokinase from Escherichia coli with its reaction products". J. Mol. Biol. 204 (4): 973–994. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(88)90056-3. PMID 2975709.
External links
This article includes text from the public domain Pfam and InterPro IPR000023
Transferases: phosphorus-containing groups (EC 2.7) 2.7.1-2.7.4:
phosphotransferase/kinase
(PO4)Hexo- · Gluco- · Fructo- (Hepatic) · Galacto- · Phosphofructo- (1, Liver, Muscle, Platelet, 2) · Riboflavin · Shikimate · Thymidine (ADP-thymidine) · NAD+ · Glycerol · Pantothenate · Mevalonate · Pyruvate · Deoxycytidine · PFP · Diacylglycerol · Phosphoinositide 3 (Class I PI 3, Class II PI 3) · Sphingosine · Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate synthase2.7.6: diphosphotransferase
(P2O7)2.7.7: nucleotidyltransferase
(PO4-nucleoside)DNA-directed DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase I · DNA polymerase II · DNA polymerase III holoenzyme
DNA nucleotidylexotransferase/Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
RNA-directed DNA polymerase: Reverse transcriptase (Telomerase)RNA nucleotidyltransferaseRNA polymerase/DNA-directed RNA polymerase: RNA polymerase I · RNA polymerase II · RNA polymerase III · RNA polymerase IV · Primase · RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
PNPaseUridylyltransferaseGuanylyltransferasemRNA capping enzymeOther2.7.8: miscellaneous PhosphatidyltransferasesCDP-diacylglycerol—glycerol-3-phosphate 3-phosphatidyltransferase · CDP-diacylglycerol—serine O-phosphatidyltransferase · CDP-diacylglycerol—inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase · CDP-diacylglycerol—choline O-phosphatidyltransferaseGlycosyl-1-phosphotransferase2.7.10-2.7.13: protein kinase
(PO4; protein acceptor)see tyrosine kinasessee serine/threonine-specific protein kinasessee serine/threonine-specific protein kinasesCategories:- EC 2.7.1
- Moonlighting proteins
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
