- Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome
-
Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome Classification and external resources OMIM 218030 DiseasesDB 12740 MeSH D043204 Apparent mineralocorticoid excess (AME) is an autosomal recessive[1] disorder causing hypertension (high blood pressure) and hypokalemia (abnormally low levels of potassium). The condition responds to glucocorticoid treatment. It results from mutations in the HSD11B2 gene, which encodes the kidney isozyme of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. In an unaffected individual, this isozyme inactivates circulating cortisol to the less-active metabolite cortisone. The inactivating mutation leads to elevated local concentrations of cortisol in the kidney. Cortisol at high concentrations can cross-react and activate the mineralocorticoid receptor, leading to aldosterone-like effects in the kidney. This is what causes the hypokalemia, hypertension, and hypernatremia associated with the syndrome.
Other conditions such as Liddle's Syndrome can mimic the clinical features of AME, so diagnosis can be made by calculating the ratio of free urinary cortisol to free urinary cortisone. Since AME patients create less cortisone, the ratio will much be higher than non-affected patients.[2] Alternatively, one could differentiate between the two syndromes by administering a potassium-sparing diuretic. Patients with Liddle's syndrome will only respond to a diuretic that binds the ENaC channel, whereas those with AME will respond to a diuretic that binds to ENaC or the mineralcorticoid receptor.
AME is exceedingly rare, with less than 100 cases recorded worldwide.[2]
Liquorice consumption may also cause a temporary form of AME due to its ability to block 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2, in turn causing increased levels of cortisol.[3] Cessation of licorice consumption will reverse this form of AME.
Contents
Genetics
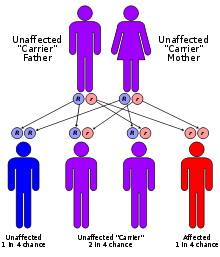 Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
AME is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.[1] This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
See also
References
- ^ a b Levtchenko, E. N.; Deinum, J.; Knoers, N. V.; Hermus, A. R.; Monnens, L. A.; Lenders, J. W. (Mar 2007). "From gene to disease; 'apparent mineralocorticoid excess' syndrome, a syndrome with an apparent excess of mineral corticoids". Nederlands tijdschrift voor geneeskunde 151 (12): 692–694. PMID 17447595.
- ^ a b Palermo M, Quinkler M, Stewart PM. (Oct 2004). "Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome: an overview.". Epub 48 (5): 687–696. doi:10.1590/S0004-27302004000500015. PMID 15761540.
- ^ Weizmann Institute of Science > GeneCards > hydroxysteroid (11-beta) dehydrogenase 2 Retrieved on Feb 27, 2010. Cite: Consumption of large amounts of liquorice can lead to apparent mineralocorticoid excess and hypertension
External links
- Apparent mineralocorticoid excess at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
Inborn error of steroid metabolism Mevalonate pathway To cholesterol 7-Dehydrocholesterol path: Hydrops-ectopic calcification-moth-eaten skeletal dysplasia · CHILD syndrome · Conradi-Hünermann syndrome · Lathosterolosis · Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
desmosterol path: DesmosterolosisSteroids aldosterone: Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism
cortisol/cortisone: CAH 17α hydroxylase · CAH 11β hydroxylase
both: CAH 3β dehydrogenase · CAH 21α hydroxylase · Apparent mineralocorticoid excess syndrome/11β dehydrogenaseTo androgensTo estrogensAromatase deficiencyOtherCategories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Syndromes
- Genetic disorder stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
