- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2b
-
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2b Classification and external resources 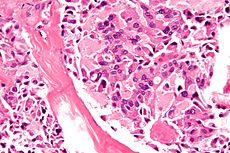
Micrograph of medullary thyroid carcinoma, as may be seen in MEN 2b. H&E stain.OMIM 162300 DiseasesDB 22784 MeSH D018814 Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 3 (also known as "Mucosal neuromata with endocrine tumors", "Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B", "MEN2B", "Multiple mucosal neuroma syndrome", "Williams Syndrome", and "Wagenmann–Froboese syndrome"[1]) is a genetic disease that causes multiple tumors on the mouth, eyes, and endocrine glands. It is the most severe type of multiple endocrine neoplasia,[2] differentiated by the presence of oral and submucosal tumors in addition to endocrine tumors. It was first described by Wagenmann in 1922.[3]
MEN 2B typically manifests before a child is 10 years old. Affected individuals tend to be tall and lanky, with an elongated face and protruding, blubbery lips. Benign tumors (neoplasms) develop in the mouth, eyes, and submucosa of almost all organs in the first decade of life,[4] followed by adrenal and thyroid tumors after puberty. Medullary thyroid cancer almost always occurs, and cancer of the adrenal glands (pheochromocytoma) occurs in 50% of cases. In MEN 2b, the medullary cancer is very aggressive with most patients dying before developing either a phaeochromocytoma or hyperparathyroidism.
A variety of eponyms have been proposed for MEN 2B, such as Williams-Pollock syndrome, Gorlin-Vickers syndrome, and Wagenmann-Froboese syndrome. However, none ever gained sufficient traction to merit continued use, and are no longer used in the medical literature.[5]
It has an estimated prevalence of 1 in 40.000.[6]
Contents
Causes
2A]], MEN 2B is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, which means affected people have one affected parent, and possibly-affected siblings and children. However, about half of the cases appear to be spontaneous mutations.[4] 95% of patients with MEN 2B have a single-point mutation of the RET proto-oncogene allele, which suppresses cancer formation.[7] The mutation - a single methionine to threonine substitution in the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain - alters the substrate specificity of intracellular signal transduction,[8] conferring dominant cancer-causing activity.
Fifty percent of MEN 2B cases appear to be from a de novo mutation, a copying error that occurs in either the sperm or ovum prior to fertilization. Like many de novo mutations, children born to older parents have an increased risk of spontaneous MEN 2B.[2] The mutated gene is almost exclusively paternal,[8] particularly from older fathers. The sex ratio is also uneven: sons are twice as likely to develop MEN 2B as daughters.[8]
Symptoms
Patients are tall and lanky, with a "marfanoid" body type and occasional muscle wasting.[4] Mucosal neuromas are the most consistent and distinctive feature, appearing in 100% of patients.[9] Usually there are numerous yellowish-white, sessile, painless nodules on the lips or tongue, with deeper lesions having normal coloration. There may be enough neuromas in the body of the lips to produce enlargement and a "blubbery lip" appearance. Similar nodules may be seen on the sclera and eyelids, sometimes causing th=
Findings at postmortem evaluation indicate that symptoms can be attributed to neuroma formation: a characteristic adventitious plaque of tissue composed of hyperplastic, interlacing bands of Schwann cells and myelinated fibers overlay the posterior columns of the spinal cord.[10] Mucosal neuromas are made up of nerve cells, often with thickened perineurium, intertwined with one another in a plexiform pattern. This tortuous pattern of nerves is seen within a background of loose endoneurium-like fibrous stroma.
Differential Diagnosis
DNA testing is now the preferred method of establishing a diagnosis for MEN 2B. Identifying a mutated RET proto-oncogene indicates a greater than 90% probability of developing multiple mucosal neuromata.[7]
In the absence of DNA testing, Luxol fast blue staining identifies myelin sheathing of some fibers, and lesional cells react immunohistochemically for S-100 protein, collagen type IV, vimentin, NSE, and neural filaments. More mature lesions will react also for EMA, indicating a certain amount of perineurial differentiation. Early lesions, rich in acid mucopolysaccharides, will stain positively with alcian blue. When medullary thyroid cancer is present, levels of the hormone calcitonin are elevated in serum and urine.[7] When adrenal cancer is present, serum levels of vanillylmandelic acid are increased and the ratio of epinephrine to norepinephrine is skewed.
Under the microscope, tumors may closely resemble traumatic neuroma, but the streaming fascicles of mucosal neuroma are usually more uniform and the intertwining nerves of the traumatic neuroma lack the thick perineurium of the mucosal neuroma.[11] Inflammatory cells are not seen in the stroma and dysplasia is not present in the neural tissues.
Treatment and Prognosis
The mucosal neuromas of this syndrome are asymptomatic and self limiting, and present no problem requiring treatment. They may, however, be surgically removed for aesthetic purposes or if they are being constantly traumatized.
Almost all patients develop medullary thyroid cancer, in a more aggressive form than MEN 2A. Complete thyroidectomy is often recommended at a young age, before malignant tumors develop.[7][12] The ideal age for surgery is 4 years old or younger, since cancer may metastasize before age 10.[8] Pheochromocytoma - cancer of the adrenal glands - is also present in 50% of cases.[8] Affected individuals are encouraged to get yearly screenings for thyroid and adrenal cancer, and it is strongly suggested that other family members also be evaluated for MEN 2B.
Abraham Lincoln controversy
In 2007, Dr. John Sotos proposed that President Abraham Lincoln suffered from MEN2B.[13] This theory suggests Lincoln had all the major features of the disease: a marfan-like body shape, large, bumpy lips, constipation, muscular hypotonia, a history compatible with cancer and a family history of the disorder - his sons Eddie, Willie, and Tad, and probably his mother. The "mole" on Lincoln's right cheek, the asymmetry of his face, his large jaw, his drooping eyelid, and "pseudo-depression" are also suggested as manifestations of MEN2B. Lincoln's longevity is the principal challenge to the MEN2B theory, which could be proven by DNA testing.[14][15] (Lincoln's reputed muscular strength does not contradict hypotonia; resting muscle tone is distinct from maximal muscle tension.)
See also
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2a
- Multiple mucosal neuromata
References
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 858. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ a b Carlson KM, Bracamontes J, Jackson CE, et al. (December 1994). "Parent-of-origin effects in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 55 (6): 1076–82. PMC 1918453. PMID 7977365. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1918453.
- ^ Wagenmann A. (1922), "Multiple neurome des Auges und der Zunge", Ber Dtsch Opthalmol Ges: 282–5
- ^ a b c Fryns JP, Chrzanowska K (October 1988). "Mucosal neuromata syndrome (MEN type IIb (III))". J. Med. Genet. 25 (10): 703–6. doi:10.1136/jmg.25.10.703. PMC 1051565. PMID 2906373. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1051565.
- ^ Schimke RN, Hartmann WH, Prout TE, Rimoin DL (1968). "Syndrome of bilateral pheochromocytoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma and multiple neuromas. A possible regulatory defect in the differentiation of chromaffin tissue". N. Engl. J. Med. 279 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1056/NEJM196807042790101. PMID 4968712.
- ^ Martino Ruggieri (2005). Neurocutaneous Disorders : The Phakomatoses. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-211-21396-1. - Chapter: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2B by Electron Kebebew, Jessica E. Gosnell and Emily Reiff. Pages 695-701. [1]
- ^ a b c d Sperling, Mark A. (2008), Pediatric Endocrinology (3 ed.), Elsevier Health Sciences, pp. 246–7, ISBN 1416040900, http://books.google.com/books?id=jIxXJCxGNvAC&pg=PT264&lpg=PT264
- ^ a b c d e Morrison PJ, Nevin NC (September 1996). "Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B (mucosal neuroma syndrome, Wagenmann-Froboese syndrome)". J. Med. Genet. 33 (9): 779–82. doi:10.1136/jmg.33.9.779. PMC 1050735. PMID 8880581. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1050735.
- ^ Pujol RM, Matias-Guiu X, Miralles J, Colomer A, de Moragas JM (August 1997). "Multiple idiopathic mucosal neuromas: a minor form of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B or a new entity?". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 37 (2 Pt 2): 349–52. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(97)70025-2. PMID 9270546.
- ^ Dyck, PJ (October 1979), "Multiple endocrine neoplasia, type 2b: phenotype recognition; neurological features and their pathological basis", Annals of Neurology (4): 302–314, PMID 554522
- ^ R. L. Miller, N. J. Burzynski, B. L. Giammara (1977), "The ultrastructure of oral neuromas in multiple mucosal neuromas, pheochromocytoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma syndrome", Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine: 253–63, doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.1977.tb01647.x, http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/119632940/abstract
- ^ Lester W. Burket, Martin S. Greenberg, Michaël Glick, Jonathan A. Ship (2008), Burket's oral medicine (11 ed.), PMPH-USA, pp. 141, ISBN 1550093452, http://books.google.com/books?id=Q2SP8cOZPvkC&pg=PA141&lpg=PA141
- ^ Sotos, JG (2008). The Physical Lincoln: Finding the Genetic Cause of Abraham Lincoln's Height, Homeliness, Pseudo-Depression, and Imminent Cancer Death. Mount Vernon, VA: Mt. Vernon Book Systems. http://www.physical-lincoln.com/.
- ^ Scientist Wants to Test Abraham Lincoln’s Bloodstained Pillow for Cancer Discover Magazine April 20, 2009
- ^ Lincoln's Shroud of Turin, Philadelphila Inquirer, April 13, 2009
External links
- The Association for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Disorders (AMEND)
- A Personal Blog (Thyroid Cancer and Pheochromocytoma, MEN 2B)
Tumors: endocrine gland neoplasia (C73–C75/D34–D35, 193–194/226–227) Pancreas/
islets of LangerhansHypothalamic/
pituitary axes
+parathyroidPituitaryThyroidThyroid cancer (malignant): epithelial cell /carcinoma (Papillary, Follicular/Hurthle cell) · parafollicular cell (Medullary) · AnaplasticBenign: Thyroid adenoma · Struma ovariiParathyroidGonadssee genital neoplasiaPinealoma Pinealoblastoma · PineocytomaMEN Categories:- Hereditary cancers
- Endocrine neoplasia
- Endocrine-related cutaneous conditions
- Autosomal dominant disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
