- Adrenocortical carcinoma
Infobox_Disease
Name = Adrenocortical carcinoma
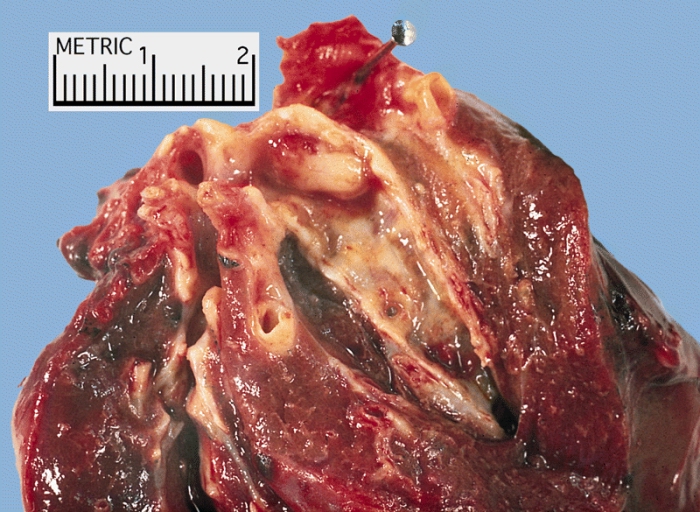
Caption = Metastasis of an adrenocortical carcinoma to the lung
DiseasesDB =
ICD10 = ICD10|C|74|0|c|73
ICD9 = ICD9|194
ICDO = 8370/3
OMIM =
MedlinePlus =
eMedicineSubj = ped
eMedicineTopic = 41
MeshID = D018268Adrenocortical carcinoma, also adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC) and adrenal cortex cancer, is an aggressive
cancer originating in the cortex (steroid hormone -producing tissue) of theadrenal gland . Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare tumor, with incidence of 1-2 per million population annually.cite book |author=edited by Vincent T. DeVita, Samuel Hellman, Steven A. Rosenberg |title=Cancer: principles & practice of oncology |publisher=Lippincott-Raven |location=Philadelphia |year=2005 |pages= |isbn=0-7817-4865-8 |oclc= |doi=] cite web | last =Savarese | first =Diane MF | coauthors =Lynnette K Nieman| title =Clinical presentation and evaluation of adrenocortical tumors| work =UpToDate Online v. 15.1| publisher =UpToDate| date = 2006-08-08| url =http://www.uptodateonline.com/utd/content/topic.do?topicKey=adrenal/17707&type=A&selectedTitle=1~16 | accessdate =2007-06-05] Adrenocortical carcinoma has a bimodal distribution by age, with cases clustering in children under 6, and in adults 30-40 years old. Adenocortical carcinoma is remarkable for the many hormonal syndromes which can occur in patients with steroid hormone-producing ("functional") tumors, includingCushing's syndrome ,Conn syndrome ,virilization , and feminization. Adrenocortical carcinoma has often invaded nearby tissues or metastasized to distant organs at the time of diagnosis, and the overall 5-year survival rate is only 20-35%.Signs and Symptoms
Adrenocortical carcinoma may present differently in children and adults. Most tumors in children are functional, and
virilization is by far the most common presenting symptom, followed byCushing's syndrome andprecocious puberty . Among adults presenting with hormonal syndromes, Cushing's syndrome alone is most common, followed by mixed Cushing's and virilization (glucocorticoid andandrogen overproduction).Feminization andConn syndrome (mineralcorticoid excess) occur in less than 10% of cases. Rarely,pheochromocytoma -like hypersecretion ofcatecholamine s has been reported in adrenocortical cancers.cite book |author=Richard Cote, Saul Suster, Lawrence Weiss, Noel Weidner (Editor) |title=Modern Surgical Pathology (2 Volume Set) |publisher=W B Saunders |location=London |year= |pages= |isbn=0-7216-7253-1 |oclc= |doi=] Non-functional tumors (about 40%, authorities vary) usually present with abdominal or flank pain, or they may be asymptomatic and detected incidentally.All patients with suspected adrenocortical carcinoma should be carefully evaluated for signs and symptoms of hormonal syndromes. For Cushing's syndrome (
glucocorticoid excess) these includeweight gain ,muscle wasting , purple lines on the abdomen, a fatty "buffalo hump" on the neck, a "moonlike" face, and thinning, fragile skin. Virilism (androgen excess) is most obvious in women, and may produce excess facial and body hair,acne , enlargement of theclitoris , deepening of the voice, coarsening of facial features, and cessation of menstruation.Conn syndrome (mineralcorticoid excess) is marked byhigh blood pressure , which can result inheadache , andhypokalemia (low serum potassium), which can produce muscle weakness, confusion, andpalpitations . low plasmarenin activity, and high serumaldosterone .Feminization (estrogen excess) is most readily noted in men, and includes breast enlargement, decreasedlibido andimpotence . [Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Jameson JL. "Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine". New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005. ISBN 0-07-139140-1]Diagnosis
Laboratory findings
Hormonal syndromes should be confirmed with laboratory testing. Laboratory findings in Cushing syndrome include increased
serum glucose (blood sugar) and increased urinecortisol . Adrenal virilism is confirmed by the finding of an excess of serumandrostenedione anddehydroepiandrosterone . Findings inConn syndrome include low serum potassium, low plasmarenin activity, and high serumaldosterone . Feminization is confirmed with the finding of excess serumestrogen Radiology
Radiological studies of the
abdomen , such asCT scan s andmagnetic resonance imaging are useful for identifying the site of the tumor, differentiating it from other diseases, such asadrenocortical adenoma , and determining the extent of invasion of the tumor into surrounding organs and tissues. CT scans of thechest andbone scan s are routinely performed to look for metastases to thelung s andbone s respectively. These studies are critical in determining whether or not the tumor can be surgically removed, the only potentialcure at this time.Pathology
Adrenal tumors are often not biopsied prior to surgery, so diagnosis is confirmed on examination of the surgical specimen by a pathologist. Grossly, adrenocortical carcinomas are often large, with a tan-yellow cut surface, and areas of
hemorrhage andnecrosis . On microscopic examination, the tumor usually displays sheets of atypical cells with some resemblance to the cells of the normaladrenal cortex . The presence ofinvasion and mitotic activity help differentiate small cancers fromadrenocortical adenoma s.cite book |author=Richard Cote, Saul Suster, Lawrence Weiss, Noel Weidner (Editor) |title=Modern Surgical Pathology (2 Volume Set) |publisher=W B Saunders |location=London |year= |pages= |isbn=0-7216-7253-1 |oclc= |doi=] There are several relatively rare variants of adrenal cortical carcinoma: Oncocytic adrenal cortical carcinoma, Myxoid adrenal cortical carcinoma, Carcinosarcoma, Adenosquamous adrenocortical carcinoma, Clear cell adrenal cortical carcinoma.Differential diagnosis includes:
Adrenocortical adenoma ,Renal cell carcinoma ,Adrenal medullary tumors ,Hepatocellular carcinoma .Treatment
The only curative treatment is complete surgical excision of the tumor, which can be performed even in the case of invasion into large blood vessels, such as the
renal vein orinferior vena cava . The 5-year survival rate after successful surgery is 50-60%, but unfortunately, a large percentage of patients are not surgical candidates.Radiation therapy andradiofrequency ablation may be used for palliation in patients who are not surgical candidates.Chemotherapy regimens typically include the drugmitotane , an inhibitor ofsteroid synthesis which is toxic to cells of theadrenal cortex ,cite book |author=Laurence L. Brunton, editor-in-chief;John S. Lazo and Keith L. Parker, Associate Editors |title=Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 11th Edition |publisher=The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. |location=United States of America |year=2006 |pages= |isbn=0-07-142280-3 |oclc= |doi= ] as well as standard cytotoxic drugs. One widely used regimen consists ofcisplatin ,doxorubicin ,etoposide ) and mitotane. The endocrine cell toxinstreptozotocin has also been included in some treatment protocols. Chemotherapy may be given to patients with unresectable disease, to shrink the tumor prior to surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy ), or in an attempt to eliminate microscopic residual disease after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy ).Hormonal therapy with steroid synthesis inhibitors such as
aminoglutethimide may be used in a palliative manner to reduce the symptoms of hormonal syndromes.Prognosis
ACC, generally, carries a poor prognosiscite journal | author = Allolio B, Fassnacht M | title = Clinical review: Adrenocortical carcinoma: clinical update | journal = J Clin Endocrinol Metab | volume = 91 | issue = 6 | pages = 2027–37 | year = 2006 | pmid = 16551738 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2005-2639 [http://jcem.endojournals.org/cgi/content/full/91/6/2027 Free Full Text] .] and is unlike most tumours of the adrenal cortex, which are
benign (adenoma s) and only occasionally causeCushing's syndrome . Five-year disease-free survival for a complete resection of a stage I-III ACC is approximately 30%.The most important prognostic factors are age of the patient and stage of the tumor.Poor prognostic factors: mitotic activity, venous invasion, weight of 50g+; diameter of 6.5 cm+, Ki-67/MIB1 labeling index of 4%+, p53+.References
External links
* [http://www.endotext.org/adrenal/adrenal22/adrenalframe22.htm www.endotext.org article]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
