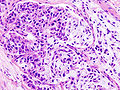
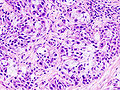
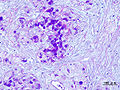
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
-
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Classification and external resources 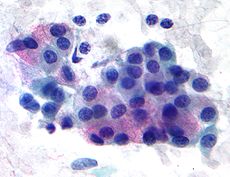
Micrograph of a mucoepidermoid carcinoma. FNA specimen. Pap stain.ICD-O: 8430/3 OMIM 607536 MeSH C04.557.470.200.025.340 Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most common type of salivary gland malignancy in children. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma can also be found in other organs, as bronchi, lacrimal sac [1] and thyroid.
Mucicarmine staining is one stain used by pathologist for detection.[2]
Contents
Epidemiology
Occurs in adults, with peak incidence from 20–40 years of age. A causal link with cytomegalovirus (CMV) has been strongly implicated in a 2011 research.[3]
Clinical Features
Presents as painless, slow-growing mass that is firm or hard. Most appear clinically as mixed tumors.
Histology
This tumor is not encapsulated and is characterized by squamous cells, mucus-secreting cells, and intermediate cells.
Molecular biology
Mucoepidermoid carcinomas of the salivary and bronchial glands are characterized by a recurrent t(11;19)(q21;p13) chromosomal translocation resulting in a MECT1-MAML2 fusion gene. The CREB-binding domain of the CREB coactivator MECT1 (also known as CRTC1, TORC1 or WAMTP1) is fused to the transactivation domain of the Notch coactivator MAML2 (PMID:16444749).
Prognosis
Generally, there is a good prognosis for low-grade tumors, and a poor prognosis for high-grade tumors.
Additional images
References
- ^ Elsevier Article Locator
- ^ Modern Pathology - Primary Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma and Sclerosing Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma with Eosinophilia of the Thyroid Gland: A Report of Nine Cases
- ^ "Melnick M., Sedghizadeh P. S., Allen C. M., Jaskoll T.". Experimental and Molecular Pathology. 10 November 2011. doi:doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.10.011. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014480011001869.
External links
- -489684982 at GPnotebook
- Overview at usc.edu
- Slide at jhu.edu
- mucoepidermoid carcinoma at humpath.com
- salivary mucoepidermoid carcinoma images at humpath.com
Glandular and epithelial neoplasms (ICD-O 8010-8589) Epithelium Small cell carcinoma · Combined small cell carcinoma · Verrucous carcinoma · Squamous cell carcinoma · Basal cell carcinoma · Transitional cell carcinoma · Inverted papillomaGlands Other/multipleAdnexal and
skin appendage (8390-8429)Cystic, mucinous,
and serous (8440-8499)Cystic generalSignet ring cell carcinoma (Krukenberg tumor) · Mucinous cystadenoma/Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma (Pseudomyxoma peritonei) · Mucoepidermoid carcinomaSerousOvarian serous cystadenoma/Pancreatic serous cystadenoma/Serous cystadenocarcinoma/Papillary serous cystadenocarcinomaDuctal, lobular,
and medullary (8500-8549)Lobular carcinoma in situ · Invasive lobular carcinomaAcinar cell (8550-8559)Other Complex epithelial (8560-8589)see also Template:Epithelium and epithelial tissueTumors of lip, oral cavity and pharynx / head and neck cancer (C00–C14/D10–D11, 140–149/210) Oral cancer malignant epithelial tumors (Acinic cell carcinoma, Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, Adenoid cystic carcinoma, Salivary duct carcinoma, Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma)benign epithelial tumors (Pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin's tumor)Categories:- Salivary gland neoplasia
- Oncology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.