- Warthin's tumor
-
Warthin's tumor Classification and external resources 
This Warthin's tumor presented as a parotid mass in a middle-aged male, who underwent superficial parotidectomy. The tumor, at the right of the image, is well-demarcated from the adjacent parotid tissue and tends to shell out from it.ICD-10 D11 ICD-9 210.2 ICD-O: 8561/0 DiseasesDB 31941 eMedicine plastic/371 MeSH D000235 - Not to be confused with Wharton's duct (submandibular duct)
Warthin's tumor or Warthin tumour, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum or adenolymphoma, is a type of benign tumor of the salivary glands.
Contents
Etiology
Its etiology is unknown, but there is a strong association with cigarette smoking. Smokers are at 8 times greater risk of developing Warthin's tumor than the general population.[1]
Locations
The gland most likely affected is the parotid gland. Though much less likely to occur than pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin's tumor is the second most common benign parotid tumor.
Characteristic
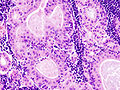
 Low magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor arising from the parotid gland.
Low magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor arising from the parotid gland.
Warthin's tumor primarily affects older individuals (age 60–70 years). There is a slight female predilection according to recent studies, but historically it has been associated with a strong male predilection. This change is possibly due to the tumor's association with cigarette smoking and the growing use of cigarettes by women. The tumor is slow growing, painless, and usually appears in the tail of the parotid gland near the angle of the mandible. In 5–14% of cases, Warthin's tumor is bilateral, but the two masses usually are at different times. Warthin's tumor is highly unlikely to become malignant.
Histology
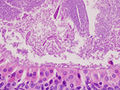
The appearance of this tumor under the microscope is unique. There are cystic spaces surrounded by two uniform rows of cells with centrally placed pyknotic nuclei. The cystic spaces have epithelium referred to as papillary infoldings that protrude into them. Additionally, the epithelium has lymphoid stroma with germinal center formation.
The differential diagnosis includes sebaceous lymphadenoma and oncocytoma.
Treatment
Most of these tumors are treated with surgical removal. It is non recurrent .
Additional images
-
Intermediate magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor.
-
High magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor showing the characteristic bilayered epithelium.
See also
References
Additional sources
- Kahn, Michael A. Basic Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Volume 1. 2001.
External links
Glandular and epithelial neoplasms (ICD-O 8010-8589) Epithelium Small cell carcinoma · Combined small cell carcinoma · Verrucous carcinoma · Squamous cell carcinoma · Basal cell carcinoma · Transitional cell carcinoma · Inverted papillomaGlands Other/multipleAdnexal and
skin appendage (8390-8429)Cystic, mucinous,
and serous (8440-8499)Cystic generalSerousOvarian serous cystadenoma/Pancreatic serous cystadenoma/Serous cystadenocarcinoma/Papillary serous cystadenocarcinomaDuctal, lobular,
and medullary (8500-8549)Lobular carcinoma in situ · Invasive lobular carcinomaAcinar cell (8550-8559)Other Complex epithelial (8560-8589)Warthin's tumor · Thymomasee also Template:Epithelium and epithelial tissueTumors of lip, oral cavity and pharynx / head and neck cancer (C00–C14/D10–D11, 140–149/210) Oral cancer malignant epithelial tumors (Acinic cell carcinoma, Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, Adenoid cystic carcinoma, Salivary duct carcinoma, Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma)benign epithelial tumors (Pleomorphic adenoma, Warthin's tumor)Categories:- Salivary gland neoplasia
- Benign neoplasms
- Oncology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.