- Parotid gland
Infobox Anatomy
Name = PAGENAME
Latin = glandula parotidea
GraySubject = 177
GrayPage = 693
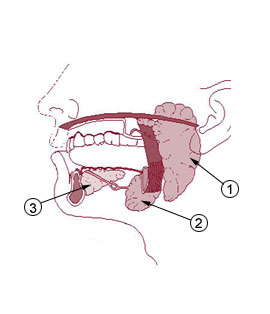
Caption =Salivary gland s:
#1 isParotid gland
#2 isSubmandibular gland
#3 isSublingual gland
Caption2 =
Precursor =
System =
Artery =
Vein =
Nerve =otic ganglion
Lymph =preauricular deep parotid lymph nodes
MeshName = Parotid+Gland
MeshNumber = A03.556.500.760.464
DorlandsPre = g_06
DorlandsSuf = 12392553
"For the toad wart, seeparotoid gland ."The parotid gland is the largest of the
salivary gland s. It is found wrapped around themandibular ramus , and it secretes saliva throughStensen's duct into the oral cavity, to facilitatemastication and swallowing.Anatomy
Location
The parotid gland is found in the
subcutaneous tissue of theface , overlying themandibular ramus and anterior and inferior to theexternal ear . The gland occupies the parotid fascial space, an area posterior to the mandibular ramus, anterior and inferior to the ear. The gland extends irregularly from the zygomatic arch to the angle of the mandible. This gland is effectively palpated bilaterally. Start anterior to each ear and move to the cheek area and then inferior to the angle of the mandible ("Illustrated Head and Neck Anatomy", Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2007, p. 170-1).The
facial nerve and its branches pass through the parotid gland, as does theexternal carotid artery , which gives off its two terminal branches, themaxillary artery and thesuperficial temporal artery , inside the gland.Posteriorly, it is related to the posterior belly of the
digastric , thestylohyoid , and thesternocleidomastoid .The parotid gland resembles a three sided pyramid. The apex of the pyramid is directed downwards. the gland has four surfaces: (1) superior (2) superficial (3) anteromedial & (4) posteromedial. The surfaces are separated by three borders: (1) anterior (2) posterior &(3) medial.
Excretory portion
The duct to this
gland (also known asStensen's duct ) empties within thebuccal cavity (the inside of the cheek) opposite the upper second molar. The parotid papilla is a small elevation of tissue that marks the opening of the parotid duct on the inner surface of the cheek ("Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy", Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2006, p. 166).Serous fluid (as opposed to mucous fluid) is produced by the parotid gland.Innervation
Although the
facial nerve (CN VII) runs "through" this gland, it does "not" control it.Secretion ofsaliva by the parotid gland is controlled by postsynapticparasympathetic fibres originating in theinferior salivatory nucleus ; these leave the brain via thetypanic nerve (branch ofglossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), travel through thetympanic plexus (located in themiddle ear ), and then form thelesser petrosal nerve until reaching theotic ganglion . After synapsing in theOtic ganglion , thepostganglionic (postsynaptic) fibers travel as part of theauriculotemporal nerve (a branch of themandibular nerve (V3)) to reach the parotid gland.Sympathetic nerves originating fromSuperior Cervical Ganglion reach the gland by traveling along the internal carotid artery through the neck and then via smaller blood vessels to the parotid gland.Parasympathetic stimulation produces a water rich,serous saliva .Sympathetic stimulation leads to the production of a low volume,enzyme -rich saliva. This is done by vasoconstricting to blood supply to the parotid gland reducing the potential for water collection. There is no inhibitory nerve supply to the gland.Vascularization
Branches of the
external carotid artery traverse the glandular tissue and supply the parotid gland with oxygenated blood. The main branch to supply the gland is thetransverse facial artery , whereas numerous local veins drain the organ. These veins drain into tributaries of external andinternal jugular vein s.The maxillary vein and superficial temporal vein meet to form the retromandibular vein within the parotid gland, but are not responsible for draining it.
Lymphatics mainly comprise
pre-auricular lymph nodes .Pathology
Inflammation of one or both parotid glands is known as
parotitis . The most common cause of parotitis ismumps . Widespread vaccination against mumps has markedly reduced the incidence of mumps parotitis. Other infections such as bacterial infections can cause parotitis as may blockage of the duct, whether fromsalivary duct calculi or external compression. Stones mainly occur within the main confluence of the ducts and within the main parotid duct. The patient usually complains of intense pain when salivating and tends to avoid foods which produce this symptom. In addition the parotid gland may become enlarged upon trying to eat. The pain can be reproduced in clinic via squirting lemon juice into the patient's mouth. Surgery depends upon the situation of the stone, if within the anterior aspect of the duct a simple incision into the buccal mucosa with sphinterotomy may allow removal, however if further posterior within the main duct, complete gland excision may be necessary.The most common of tumors in the parotid gland are benign and only affect the superficial gland. These include
pleomorphic adenoma andadenolymphoma . Their importance is in relation to their anatomical position. The tumorous growth can also change the consistency of the gland and cause facial pain on the involved side since the facial nerve travels through the gland ("Illustrated Head and Neck Anatomy", Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2007, p. 172). Critically, the relationship of the tumor to the branches of thefacial nerve (CN VII) must be defined because resection may damage the nerves, resulting in paralysis of the muscles of facial expression. If the tumor is deep within the gland, the patient should give consent for potential damage of the facial nerve.ecretion
The parotid gland secretes alpha-amylase which is the first step in the digestion of starches during mastication. It breaks down amylose (straight chanin starch) and amylopectin (branched starch) by hydrolyzing alpha 1,4 bonds.
=Additionalee also
*
Parotitis
*Sjögren's syndrome
*John Leonora External links
* [http://www.yoursurgery.com/procedures/parotidectomy/images/ParotidAnat1.jpgIllustration at yoursurgery.com]
*
* [http://www.usc.edu/hsc/dental/ohisto/Cards/sal/02_tns.html Histology at usc.edu]
*
* [http://www.breitbart.com/article.php?id=071207145613.hnkq6bin&show_article=1 Israeli study says regular mobile use increases (parotid gland) tumour risk]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
