- Germinal center
Infobox Anatomy
Name = Germinal centre
Latin =
GraySubject = 175
GrayPage = 689
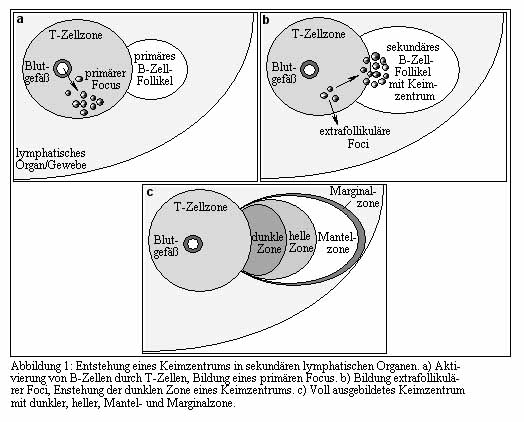
Caption = Image labeled in German, but "Keimzentrum" visible in upper right.
Caption2 =
Precursor =
System =
Artery =
Vein =
Nerve =
Lymph =
MeshName =
MeshNumber =
DorlandsPre = c_20
DorlandsSuf = 12226657Germinal centres (GC) are areas within
lymph nodes whereB lymphocytes rapidly divide, and are an important part of the humoral immune response. They develop dynamically after the activation ofB-cell s by T-dependentantigen .
Histologically, the GCs describe microscopically distinguishable parts inlymphoid tissues.Process
1. Activated B-cells migrate into the
follicular system and beginmonoclonal expansion in the environment offollicular dendritic cell s (FDC).2. After three days of expansion the B cells mutate their
antibody -encodingDNA and thus generate a diversity of clones in the germinal centre. This involves random substitutions, deletions and insertions due tosomatic hypermutation .3. Upon some unidentified stimulus from the FDC, the B cells start to expose their antibody to their surface and in this stage are referred to as
centrocyte s. The centrocytes are in a state of activatedapoptosis and compete for survival signals from FDCs that present the antigen. This rescue process is believed to be dependent on theaffinity of the antibody to the antigen.4. The functional B-cells have then to interact with helper T cells to get final differentiation signals. This also involves
isotype switching for example fromIgM toIgG .The interaction with T cells is believed to prevent the generation of autoreactive antibodies. [cite journal | author=Thorbecke GJ, Amin AR, Tsiagbe VK| title=Biology of germinal centers in lymphoid tissue| journal=FASEB | volume=8 | year=1994 | pages=832–840 | pmid=8070632]5. The B cells become either a
plasma cell spreading antibodies or amemory B cell that will be activated in subsequent contacts with the same antigen. They may also restart the whole process ofproliferation ,mutation andselection according to the recycling hypothesis.Morphology at different stages
The morphology of GCs is very specific and shows properties which are characteristic for different stages of the reaction.
* In an early state of the reaction a network of FDCs is fully filled with proliferating B cells.
* Later at day 4 of the reaction GCs show a separation of two zones, the dark and the light zone. [cite journal | author=Meyer-Hermann ME|title=A Mathematical Model for the Germinal Center Morphology and Affinity Maturation |journal=J. theor. Biol. |volume=216|year=2002|pages=273–300 | pmid=12183119|doi=10.1006/jtbi.2002.2550] The former still contains dominantly proliferating cells while the latter one is the area of B cells selection.
* These zones dissolve after 10 days of GC development which ends after about 3 weeks.References
ee also
*
Lymph node External links
*
* - "Lymphoid Tissues and Organs: lymph node, germinal center"
* [http://www.bio.davidson.edu/courses/immunology/hyperhuman/Lymphnode/medula/node40_0.html Hyperlinked Human Histology]
* [http://www.owlnet.rice.edu/~bios423/Lecture%20outlines/BCELLSH.htm Summary of lecture on B-cell development] with Q'n'A collection
*
* [http://www.cvm.okstate.edu/instruction/mm_curr/histology/HistologyReference/HRLym.htm Overview at okstate.edu]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
