- Histology
-
 A stained histologic specimen, sandwiched between a glass microscope slide and coverslip, mounted on the stage of a light microscope.
A stained histologic specimen, sandwiched between a glass microscope slide and coverslip, mounted on the stage of a light microscope.
Histology (compound of the Greek words: ἱστός "tissue", and -λογία -logia) is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining a thin slice (section) of tissue under a light microscope or electron microscope. The ability to visualize or differentially identify microscopic structures is frequently enhanced through the use of histological stains. Histology is an essential tool of biology and medicine.
Histopathology, the microscopic study of diseased tissue, is an important tool in anatomical pathology, since accurate diagnosis of cancer and other diseases usually requires histopathological examination of samples. Trained medical doctors, frequently board-certified as pathologists, are the personnel who perform histopathological examination and provide diagnostic information based on their observations.
The trained scientists who perform the preparation of histological sections are histotechnicians, histology technicians (HT), histology technologists (HTL), medical scientists, medical laboratory technicians, or biomedical scientists. Their field of study is called histotechnology.
Contents
Histology
Fixing
Chemical fixation with formaldehyde or other chemicals
Chemical fixatives are used to preserve tissue from degradation, and to maintain the structure of the cell and of sub-cellular components such as cell organelles (e.g., nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria). The most common fixative for light microscopy is 10% neutral buffered formalin (4% formaldehyde in phosphate buffered saline). For electron microscopy, the most commonly used fixative is glutaraldehyde, usually as a 2.5% solution in phosphate buffered saline. These fixatives preserve tissues or cells mainly by irreversibly cross-linking proteins. The main action of these aldehyde fixatives is to cross-link amino groups in proteins through the formation of CH2 (methylene) linkage, in the case of formaldehyde, or by a C5H10 cross-links in the case of glutaraldehyde. This process, while preserving the structural integrity of the cells and tissue can damage the biological functionality of proteins, particularly enzymes, and can also denature them to a certain extent. This can be detrimental to certain histological techniques. Further fixatives are often used for electron microscopy such as osmium tetroxide or uranyl acetate
Formalin fixation leads to degradation of mRNA, miRNA and DNA in tissues. However, extraction, amplification and analysis of these nucleic acids from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues is possible using appropriate protocols.[1]
Frozen section fixation
Frozen section is a rapid way to fix and mount histology sections. It is used in surgical removal of tumors, and allow rapid determination of margin (that the tumor has been completely removed). It is done using a refrigeration device called a cryostat. The frozen tissue is sliced using a microtome, and the frozen slices are mounted on a glass slide and stained the same way as other methods. It is a necessary way to fix tissue for certain stain such as antibody linked immunofluorescence staining. It can also be used to determine if a tumour is malignant when it is found incidentally during surgery on a patient.
Processing - dehydration, clearing, and infiltration
The aim of Tissue Processing is to remove water from tissues and replace with a medium that solidifies to allow thin sections to be cut. Biological tissue must be supported in a hard matrix to allow sufficiently thin sections to be cut, typically 5 μm (micrometres; 1000 micrometres = 1 mm) thick for light microscopy and 80-100 nm (nanometre; 1,000,000 nanometres = 1 mm) thick for electron microscopy. For light microscopy, paraffin wax is most frequently used. Since it is immiscible with water, the main constituent of biological tissue, water must first be removed in the process of dehydration. Samples are transferred through baths of progressively more concentrated ethanol to remove the water. This is followed by a hydrophobic clearing agent (such as xylene) to remove the alcohol, and finally molten paraffin wax, the infiltration agent, which replaces the xylene. Paraffin wax does not provide a sufficiently hard matrix for cutting very thin sections for electron microscopy. Instead, resins are used. Epoxy resins are the most commonly employed embedding media, but acrylic resins are also used, particularly where immunohistochemistry is required. Thicker sections (0.35μm to 5μm) of resin-embedded tissue can also be cut for light microscopy. Again, the immiscibility of most epoxy and acrylic resins with water necessitates the use of dehydration, usually with ethanol.
Embedding
After the tissues have been dehydrated, cleared, and infiltrated with the embedding material, they are ready for external embedding. During this process the tissue samples are placed into molds along with liquid embedding material (such as agar, gelatine, or wax) which is then hardened. This is achieved by cooling in the case of paraffin wax and heating (curing) in the case of the epoxy resins. The acrylic resins are polymerised by heat, ultraviolet light, or chemical catalysts. The hardened blocks containing the tissue samples are then ready to be sectioned.
Because Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues may be stored indefinitely at room temperature, and nucleic acids (both DNA and RNA) may be recovered from them decades after fixation, FFPE tissues are an important resource for historical studies in medicine.
Embedding can also be accomplished using frozen, non-fixed tissue in a water-based medium. Pre-frozen tissues are placed into molds with the liquid embedding material, usually a water-based glycol, OCT, TBS, Cryogel, or resin, which is then frozen to form hardened blocks.
Sectioning
Sectioning can be done in limited ways. Vertical sectioning perpendicular to the surface of the tissue is the usual method. Horizontal sectioning is often done in the evaluation of the hair follicles and pilosebaceous units. Tangential to horizontal sectioning is done in Mohs surgery and in methods of CCPDMA.
For light microscopy, a steel knife mounted in a microtome is used to cut 10-micrometer-thick tissue sections which are mounted on a glass microscope slide. For transmission electron microscopy, a diamond knife mounted in an ultramicrotome is used to cut 50-nanometer-thick tissue sections which are mounted on a 3-millimeter-diameter copper grid. Then the mounted sections are treated with the appropriate stain.
Frozen tissue embedded in a freezing medium is cut on a microtome in a cooled machine called a cryostat.
Staining
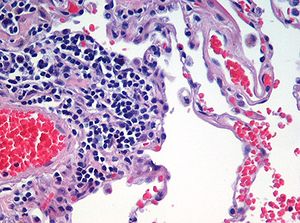
Biological tissue has little inherent contrast in either the light or electron microscope. Staining is employed to give both contrast to the tissue as well as highlighting particular features of interest. Where the underlying mechanistic chemistry of staining is understood, the term histochemistry is used. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E stain) is the most commonly used light microscopical stain in histology and histopathology. Hematoxylin, a basic dye, stains nuclei blue due to an affinity to nucleic acids in the cell nucleus; eosin, an acidic dye, stains the cytoplasm pink. Uranyl acetate and lead citrate are commonly used to impart contrast to tissue in the electron microscope.
Special staining: There are hundreds of various other techniques that have been used to selectively stain cells and cellular components. Other compounds used to color tissue sections include safranin, oil red o, Congo red, fast green FCF, silver salts, and numerous natural and artificial dyes that were usually originated from the development dyes for the textile industry.
Histochemistry refers to the science of using chemical reactions between laboratory chemicals and components within tissue. A commonly performed histochemical technique is the Perls Prussian blue reaction, used to demonstrate iron deposits in diseases like hemochromatosis.
Histology samples have often been examined by radioactive techniques. In historadiography, a slide (sometimes stained histochemically) is X-rayed. More commonly, autoradiography is used to visualize the locations to which a radioactive substance has been transported within the body, such as cells in S phase (undergoing DNA replication) which incorporate tritiated thymidine, or sites to which radiolabeled nucleic acid probes bind in in situ hybridization. For autoradiography on a microscopic level, the slide is typically dipped into liquid nuclear tract emulsion, which dries to form the exposure film. Individual silver grains in the film are visualized with dark field microscopy.
Recently, antibodies have been used to specifically visualize proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. This process is called immunohistochemistry, or when the stain is a fluorescent molecule, immunofluorescence. This technique has greatly increased the ability to identify categories of cells under a microscope. Other advanced techniques, such as nonradioactive in situ hybridization, can be combined with immunochemistry to identify specific DNA or RNA molecules with fluorescent probes or tags that can be used for immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked fluorescence amplification (especially alkaline phosphatase and tyramide signal amplification). Fluorescence microscopy and confocal microscopy are used to detect fluorescent signals with good intracellular detail. Digital cameras are increasingly used to capture histological and histopathological image
Common laboratory stains
Stain Common use Nucleus Cytoplasm Red blood cell (RBC) Collagen fibers Specifically stains Haematoxylin General staining when paired with eosin (i.e. H&E) Blue N/A N/A N/A Nucleic acids—blue ER (endoplasmic reticulum)—blue
Eosin General staining when paired with haematoxylin (i.e. H&E) N/A Pink Orange/red Pink Elastic fibers—pink Collagen fibers—pink Reticular fibers—pink
Toluidine blue General staining Blue Blue Blue Blue Mast cells granules—purple Masson's trichrome stain Connective tissue Black Red/pink Red Blue/green Cartilage—blue/green Muscle fibers—red
Mallory's trichrome stain Connective tissue Red Pale red Orange Deep blue Keratin—orange Cartilage—blue Bone matrix—deep blue Muscle fibers—red
Weigert's elastic stain Elastic fibers Blue/black N/A N/A N/A Elastic fibers—blue/black Heidenhain's AZAN trichrome stain Distinguishing cells from extracellular components Red/purple Pink Red Blue Muscle fibers—red Cartilage—blue Bone matrix—blue
Silver stain Reticular fibers, nerve fibers, fungi N/A N/A N/A N/A Reticular fibers—brown/black Nerve fibers—brown/black
Wright's stain Blood cells Bluish/purple Bluish/gray Red/pink N/A Neutrophil granules—purple/pink Eosinophil granules—bright red/orange Basophil granules—deep purple/violet Platelet granules—red/purple
Orcein stain Elastic fibres Deep blue [or crazy red] N/A Bright red Pink Elastic fibres—dark brown Mast cells granules—purple Smooth muscle—light blue
Periodic acid-Schiff stain (PAS) Basement membrane, localizing carbohydrates Blue N/A N/A Pink Glycogen and other carbohydrates—magenta Table sourced from Michael H. Ross, Wojciech Pawlina, (2006). Histology: A Text and Atlas. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-5056-3.
The Nissl method and Golgi's method are useful in identifying neurons.
Alternative techniques
Alternative techniques include cryosection. The tissue is frozen using a cryostat, and cut. Tissue staining methods are similar to those of wax sections. Plastic embedding is commonly used in the preparation of material for electron microscopy. Tissues are embedded in epoxy resin. Very thin sections (less than 0.1 micrometer) are cut using diamond or glass knives. The sections are stained with electron dense stains (uranium and lead) so that they can possibly be seen with the electron microscope.
History
In the 19th century, histology was an academic discipline in its own right. The 1906 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to histologists Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal. They had dueling interpretations of the neural structure of the brain based in differing interpretations of the same images. Cajal won the prize for his correct theory and Golgi for the staining technique he invented to make it possible.
Histological classification of animal tissues
There are four basic types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All tissue types are subtypes of these four basic tissue types (for example, blood cells are classified as connective tissue, since they generally originate inside bone marrow).
- Epithelium: the lining of glands, bowel, skin, and some organs like the liver, lung, and kidney
- Endothelium: the lining of blood and lymphatic vessels
- Mesothelium: the lining of pleural and pericardial spaces
- Mesenchyme: the cells filling the spaces between the organs, including fat, muscle, bone, cartilage, and tendon cells
- Blood cells: the red and white blood cells, including those found in lymph nodes and spleen
- Neurons: any of the conducting cells of the nervous system
- Germ cells: reproductive cells (spermatozoa in men, oocytes in women)
- Placenta: an organ characteristic of true mammals during pregnancy, joining mother and offspring, providing endocrine secretion and selective exchange of soluble, but not particulate, blood-borne substances through an apposition of uterine and trophoblastic vascularised parts
- Stem cells: cells with the ability to develop into different cell types
Note that tissues from plants, fungi, and microorganisms can also be examined histologically. Their structure is very different from animal tissues.
Related sciences
- Cell biology is the study of living cells, their DNA and RNA and the proteins they express.
- Anatomy is the study of organs visible by the naked eye.
- Morphology studies entire organisms.
Artifacts
Artifacts are structures or features in tissue that interfere with normal histological examination. These are not always present in normal tissue and can come from outside sources. Artifacts interfere with histology by changing the tissues appearance and hiding structures. These can be divided into two categories:
Pre-histology
These are features and structures that have being introduced prior to the collection of the tissues. A common example of these include: ink from tattoos and freckles (melanin) in skin samples.
Post-histology
Artifacts can result from tissue processing. Processing commonly leads to changes like shrinkage, washing out of particular cellular components, color changes in different tissues types and alterations of the structures in the tissue. Because these are caused in a laboratory the majority of post histology artifacts can be avoided or removed after being discovered. A common example is mercury pigment left behind after using Zenker's fixative to fix a section.
See also
- Pathology
- Anatomical pathology
- Cooperative Human Tissue Network (CHTN)
- Histopathology
- Biological staining
- Digital Pathology
- Important publications in histology
- Geoffrey Bourne
- Laser capture microdissection
- Automated tissue image analysis
Notes
- ^ Weiss AT, Delcour NM, Meyer A, Klopfleisch R. (2010). "Efficient and Cost-Effective Extraction of Genomic DNA From Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded Tissues". Veterinary Pathology 227 (4): 834–8. doi:10.1177/0300985810380399. PMID 20817894.
References
- Merck Source (2002). Dorland's Medical Dictionary. Retrieved 2005-01-26.
- Stedman's Medical Dictionaries (2005). Stedman's Online Medical Dictionary. Retrieved 2005-01-26.
- 4,000يonline histology images (2007). (http://histology-online.com)
External links
- Histology Protocols
- Histology atlas and more
- Histoweb
- SIU SOM Histology
- Visual Histology Atlas
- Histology Glossary
- Histology Group of Victoria Incorporated
- Histology Photomicrographs
- Virtual Slidebox
- Blue Histology
Histology: Epithelial proteins (TH H1.00.01.1) Lateral/cell-cell Cell adhesion molecules: Adherens junction (Cadherin) · Desmosome (Desmoglein)
Ion channels: Gap junction/Connexon (Connexin)
Cytoskeleton: Desmosome (Desmoplakin, Plakoglobin, Tonofibril)
other membrane proteins: Tight junction (Claudin, Occludin, MARVELD2)Basal/cell-matrix Apical B strc: edmb (perx), skel (ctrs), epit, cili, mito, nucl (chro) Histology: connective tissue (TH H2.00.03) Composition ResidentCollagen fibers
Reticular fibers: COL3A1
Elastic fibers: Elastin · Fibrillin (FBN1, FBN2, FBN3) · EMILIN1
ElauninClassification LooseRelated see also Template:Soft tissue tumors and sarcomas
Histology: muscle tissue (TH H2.00.05, H3.3) Smooth
muscleStriated
muscleMembrane/
extracellularIntracellularDystrophin · Dystrobrevin (A, B) · Syntrophin (A, B1, B2, G1, G2) · Syncoilin · Dysbindin · Synemin/desmuslin
related: NOS1 · Caveolin 3GeneralNeuromuscular junction · Motor unit · Muscle spindle · Excitation-contraction coupling · Sliding filament mechanismBothFiberCellsOtherOther/
ungroupedHistology: nervous tissue (TA A14, GA 9.849, TH H2.00.06, H3.11) CNS GeneralGrey matter · White matter (Projection fibers · Association fiber · Commissural fiber · Lemniscus · Funiculus · Fasciculus · Decussation · Commissure) · meningesOtherPNS GeneralPosterior (Root, Ganglion, Ramus) · Anterior (Root, Ramus) · rami communicantes (Gray, White) · Autonomic ganglion (Preganglionic nerve fibers · Postganglionic nerve fibers)Myelination: Schwann cell (Neurolemma, Myelin incisure, Myelin sheath gap, Internodal segment)
Satellite glial cellNeurons/
nerve fibersPartsPerikaryon (Axon hillock)
Axon (Axon terminals, Axoplasm, Axolemma, Neurofibril/neurofilament)
Dendrite (Nissl body, Dendritic spine, Apical dendrite/Basal dendrite)TypesGSA · GVA · SSA · SVA
fibers (Ia, Ib or Golgi, II or Aβ, III or Aδ or fast pain, IV or C or slow pain)GSE · GVE · SVE
Upper motor neuron · Lower motor neuron (α motorneuron, γ motorneuron, β motorneuron)Termination Synapse
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.