- Periodic acid-Schiff stain
-
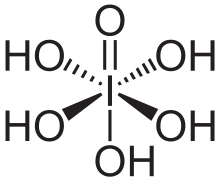
Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) is a staining method used to detect glycogen and other polysaccharides in tissues. The reaction of periodic acid oxidizes the diol functional groups in glucose and other sugars, creating aldehydes that react with the Schiff reagent to give a purple-magenta color. A suitable basic stain is often used as a counterstain.
Contents
Uses
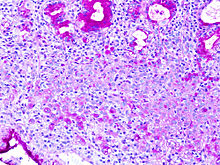
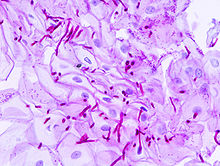
PAS staining is mainly used for staining structures containing a high proportion of carbohydrate macromolecules (glycogen, glycoprotein, proteoglycans), typically found in e.g. connective tissues, mucus, the glycocalyx, and basal laminae.
PAS staining can be used to assist in the diagnosis of several medical conditions:
- Glycogen storage disease (versus other storage disorders)
- Paget's disease[1]
- Alveolar soft part sarcoma [2]
- staining macrophages in Whipple's disease[3]
- It can be used to diagnose α1-antitrypsin deficiency if periportal liver hepatocytes stain positive.
- aggregates of PAS positive lymphocytes are present in epidermis in Mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome, called Pautrier microabscesses.
- erythroleukemia, a leukemia of immature red blood cells. These cells stain a bright fuchsia.[4]
- Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- Fungal infection, the cell walls of fungi stain magenta. This only works on living fungi; in contrast, Grocott's methenamine silver stain(GMS) will stain both living and dead fungal organisms.
Presence of glycogen can be confirmed on a section of tissue by using diastase to digest the glycogen from a section, then comparing a diastase digested PAS section with a normal PAS section. The diastase negative slide will show a magenta staining where glycogen is present within a section of tissue. The slide that has been treated with diastase will lack any positive PAS staining in those locations on the slide
PAS staining is also used for staining cellulose. One example would be looking for implanted medical devices composed of nonoxidized cellulose.
If the PAS stain will be performed on tissue, the recommended fixative is 10% neutral-buffered formalin or Bouin solution. For blood smears, the recommended fixative is methanol. Glutaraldehyde is not recommended because free aldehyde groups may be available to react with the Schiff reagent, which may result in false positive staining.[5]
See also
- PAS diastase
- Methyl violet
- Prussian blue
- Egyptian Blue
- Methyl blue
- Methylene blue
- New methylene blue
- Han Purple
- Potassium ferrocyanide
- Potassium ferricyanide
- Gentian violet
- Eosin
- Fluorescein
- Carboxyfluorescein
- Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)
- Fluorescein amidite (FAM)
- Erythrosine
- Rose Bengal
- DyLight Fluor, a product line of fluorescent dyes
- Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis, a biochemistry laboratory test
- Laser dyes
References
- ^ Thomas J. Lawton (27 April 2009). Breast. Cambridge University Press. pp. 55–. ISBN 9780521881593. http://books.google.com/books?id=z17R70VGhnsC&pg=PA55. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ (Ladanyi et al 2002
- ^ C. Hauser (29 August 2005). Mayo Clinic Gastroenterology and Hepatology Board Review. CRC Press. pp. 108–. ISBN 9780203502747. http://books.google.com/books?id=nStxzRQlNaAC&pg=PA108. Retrieved 16 November 2010.
- ^ http://www.answers.com/topic/leukemia-stains-1
- ^ Carson, Freida L.; Hladik, Christa (2009). Histotechnology: A Self-Instructional Text (3 ed.). Hong Kong: American Society for Clinical Pathology Press. pp. 137–139. ISBN 9780891895817.
External links
Stains Iron/Hemosiderin Lipids Carbohydrates Periodic acid-Schiff stainAmyloid Bacteria Gram staining (Methyl violet/Gentian violet, Safranin) · Ziehl–Neelsen stain/acid-fast (Carbol fuchsin/Fuchsine, Methylene blue) · Auramine-rhodamine stain (Auramine O, Rhodamine B)Connective tissue Other H&E stain (Haematoxylin, Eosin Y) · Silver stain (Grocott's methenamine silver stain, Warthin–Starry stain) · Methyl blue · Wright's stain · Giemsa stain · Gömöri trichrome stain · Neutral red · Janus Green BTissue stainability 
This science article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.