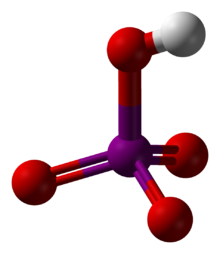
- Periodic acid
-
Orthoperiodic acid 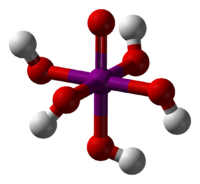 Other namesParaperiodic acid
Other namesParaperiodic acidIdentifiers CAS number 10450-60-9 
PubChem 65185 ChemSpider 58684 
ChEBI CHEBI:29149 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1161637 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - OI(=O)(=O)=O
Properties Molecular formula H5IO6 Molar mass 227.941 g/mol Appearance Colorless crystals Melting point 122 °C, 395 K, 252 °F
Hazards MSDS External MSDS EU classification Oxidizer (O), Toxic (T), Corrosive (C) R-phrases R23 R24 R25 R34 R41 NFPA 704  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Periodic acid,[1] or iodic(VII) acid[2] is an oxoacid of iodine having chemical formula HIO4 or H5IO6.
In dilute aqueous solution, periodic acid exists as discrete hydronium (H3O+) and metaperiodate (IO4−) ions. When more concentrated, orthoperiodic acid, H5IO6, is formed; this dissociates into hydronium and orthoperiodate (IO65−) ions. In practice, the metaperiodate and orthoperiodate ions co-exist in a pH-dependent chemical equilibrium:
Orthoperiodic acid can be obtained as a crystalline solid that can be dehydrated to metaperiodic acid, HIO4. Further heating gives diiodine pentoxide (I2O5) and oxygen rather than the expected anhydride diiodine heptoxide; this anhydride does not occur in nature but can be formed synthetically.
There being two forms of periodic acid, it follows that two types of periodate salts are formed. For example, sodium metaperiodate, NaIO4, can be synthesised from HIO4 whilst sodium orthoperiodate, Na5IO6 can be synthesised from H5IO6. Metaperiodates have solubilities and chemical properties similar to perchlorates (similar but larger ion size) though they are less oxidizing than perchlorates.
Periodic acid is used in organic chemistry for structural analysis. Periodic acid will cleave vicinal diols into two aldehyde or ketone fragments. This can be useful in determining the structure of carbohydrates. It is also used in organic synthesis as an oxidising agent of moderate strength
Notes and references
- ^ The name is not derived from "period", but from "iodine": per-iodic acid (compare iodic acid, perchloric acid), and it is thus pronounced per-iodic /ˌpɜr.aɪˈɒdɨk/ purr-eye-od-ik, and not as /ˌpɪərɪˈɒdɨk/ peer-ee-od-ik.
- ^ Alan Isaacs, John Daintith, Elizabeth Martin, ed (1984). Concise Science Dictionary. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 356. ISBN 0192115936.
Hydrogen compounds H3AsO3 · H3AsO4 · HAt · HSO3F · HBF4 · HBr · HBrO · HBrO2 · HBrO3 · HBrO4 · HCl · HClO · HClO2 · HClO3 · HClO4 · HCN · HCNO · H2CrO4/H2Cr2O7 · H2CO3 · H2CS3 · HF · HFO · HI · HIO · HNC · HNCO · HNO · HNO3 · H2N2O2 · HNO5S · H3NSO3 · H2O · H2O2 · H2O3 · H3PO2 · H3PO3 · H3PO4 · H4P2O7 · H5P3O10 · H2PtCl6 · H2S · H2Se · H2SeO3 · H2SeO4 · H4SiO4 · H2SiF6 · H2SO3 · H2SO4 · H2SO5 · H2S2O3 · H2S2O6 · H2S2O7 · H2S2O8 · CF3SO3H · H2Te · H2TeO3 · H6TeO6 · H4TiO4 · H2Po · H3VO4 · HCo(CO)4
Categories:- Hydrogen compounds
- Periodates
- Oxidizing agents
- Oxidizing acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.