- Diol
-
A diol or glycol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups (—OH groups) [1]
A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom. Examples include methanediol H2C(OH)2 and 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoropropane-2,2-diol (F3C)2C(OH)2, the hydrated form of hexafluoroacetone.
A vicinal diol is a diol with two hydroxyl groups in vicinal positions, that is, attached to adjacent atoms. Examples include 1,2-ethanediol or ethylene glycol HO—(CH2)2—OH, a common ingredient of antifreeze products; and propane-1,2-diol or alpha propylene glycol, HO—CH2—CH(OH)—CH3 used in the food and medicine industry as well as a relatively non-poisonous antifreeze product.
Examples of diols in which the hydroxyl functional groups are more widely separated include 1,4-butanediol HO—(CH2)4—OH and bisphenol A, and propylene-1,3-diol or beta propylene glycol, HO-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH.
Contents
Classification
Diols can be:
- Linear or branched;
- Aliphatic or aromatic (bisphenol A).
Examples of aliphatic diols:
Linearity of the diol Hydroxyls on adjacent carbons (vicinal diols) Hydroxyls on non-adjacent carbons Linear Ethylene glycol 1,3-Propanediol, 1,4-Butanediol, 1,5-Pentanediol, 1,8-octanediol, Branched 1,2-Propanediol, 1,2-Butanediol, 2,3-Butanediol 1,3-Butanediol, 1,2-pentanediol, Etohexadiol, p-Menthane-3,8-diol, 2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol Synthesis
Because diols are a common functional group arrangement, numerous methods of preparation have been developed.
- Vicinal diols can be produced from the oxidation of alkenes, usually with dilute acidic potassium permanganate, also known as potassium manganate(VII). Using alkaline potassium manganate(VII) produces a colour change from clear deep purple to clear green; acidic potassium manganate(VII) turns clear colourless.
- Osmium tetroxide can similarly be used to oxidize alkenes to vicinal diols.
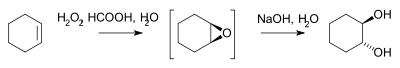
- Hydrogen peroxide reacts with an alkene to the epoxide and then by saponification to the diol for example in the synthesis of trans-cyclohexanediol batch[2] or by microreactor [3]:
- A chemical reaction called Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation can be used to produce chiral diols from alkenes using an osmate reagent and a chiral catalyst.
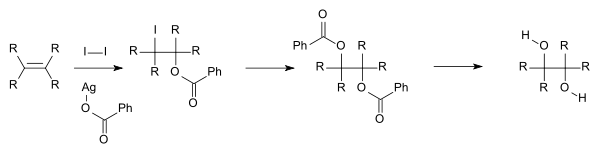
- Another method is the Woodward cis-hydroxylation (cis diol) and the related Prévost reaction (anti diol), depicted below, which both use iodine and the silver salt of a carboxylic acid.
- In the Prins reaction 1,3-diols can be formed in a reaction between an alkene and formaldehyde.
- Geminal diols can be formed by the hydration of ketones.
Reactions
General diols
Diols react as alcohols, by esterification and ether formation.
Diols such as ethylene glycol are used as co-monomers in polymerization reactions forming polymers including some polyesters and polyurethanes. A different monomer with two identical functional groups, such as a dioyl dichloride or dioic acid is required to continue the process of polymerization through repeated esterification processes.
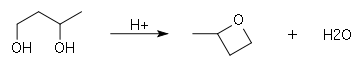
A diol can be converted to cyclic ether by using an acid catalyst, this is diol cyclization. Firstly, it involves protonation of the hydroxyl group. Then, followed by intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, the second hydroxyl group attacks the electron deficient carbon. Provided that there are enough carbon atoms that the angle strain is not too much, a cyclic ether can be formed.

Vicinal diols
In glycol cleavage, the C-C bond in a vicinal diol is cleaved with formation of ketone or aldehyde functional groups. See Diol oxidation.
Geminal diols
In general, organic geminal diols readily dehydrate to form a carbonyl group. For example, carbonic acid ((HO)2C=O) is unstable and has a tendency to convert to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Nevertheless, in rare situations the chemical equilibrium is in favor of the geminal diol. For example, when formaldehyde (H2C=O) is dissolved in water the geminal diol (H2C(OH)2), methanediol, is favored. Other examples are the cyclic geminal diols decahydroxycyclopentane (C5(OH)10) and dodecahydroxycyclohexane (C6(OH)12), which are stable, whereas the corresponding oxocarbons (C5O5 and C6O6) do not seem to be.
See also
- Alcohols, chemical compounds with one hydroxyl group
- Triols, chemical compounds with three hydroxyl group
- Polyols, chemical compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups
- Ethylene glycol
References
- ^ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 0-471-85472-7
- ^ trans-cyclohexanediol Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 3, p.217 (1955); Vol. 28, p.35 (1948) http://www.orgsynth.org/orgsyn/pdfs/CV3P0217.pdf.
- ^ Advantages of Synthesizing trans-1,2-Cyclohexanediol in a Continuous Flow Microreactor over a Standard Glass Apparatus Andreas Hartung, Mark A. Keane, and Arno Kraft J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 10235-10238 doi:10.1021/jo701758p
Categories:- Functional groups
- Diols
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.