- Arsenic acid
-
Arsenic acid 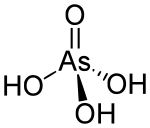
 Arsenic acid, arsoric acidOther namesArsenic acid
Arsenic acid, arsoric acidOther namesArsenic acid
Orthoarsenic acid
Desiccant L-10
ZotoxIdentifiers CAS number 7778-39-4 
ChemSpider 229 
UNII N7CIZ75ZPN 
KEGG C01478 
ChEBI CHEBI:18231 
RTECS number CG0700000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=[As](O)(O)O
Properties Molecular formula H3AsO4 Molar mass 141.94 g/mol Appearance White translucent crystals,
hygroscopic.Density 2.5 g/cm3 Melting point 35.5 °C, 309 K, 96 °F
Boiling point decom ≥ 100 °C
Solubility in water 16.7 g/100 mL Solubility soluble in alcohol Acidity (pKa) 2.19, 6.94, 11.5 Structure Molecular shape Tetrahedral Hazards EU classification Toxic (T)
Dangerous for the environment (N)R-phrases R23/25, R45, R50/53 S-phrases S53, S45, S60, S61 NFPA 704 Flash point Non-flammable Related compounds Other anions Phosphoric acid Other cations Sodium arsenate Related compounds Arsenous acid
Arsenic pentoxide acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
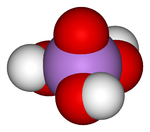
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Arsenic acid is the chemical compound with the formula H3AsO4. More descriptively written as AsO(OH)3, this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but only found in solution where it is largely ionized. Its hemihydrate form (H3AsO4·½H2O) does form stable crystals. Crystalline samples dehydrate with condensation at 100 °C.[1]
Contents
Properties
It is a tetrahedral species of idealized symmetry C3v with As-O bonds lengths ranging from 1.66 to 1.71 Å.[2]
Being a triprotic acid, its acidity is described by three equilibria:
- H3AsO4
 H2AsO−
H2AsO−
4 + H+ (K1 = 10−2.19) - H2AsO−
4 HAsO2−
HAsO2−
4 + H+ (K2 = 10−6.94) - HAsO2−
4 AsO3−
AsO3−
4 + H+ (K3 = 10−11.5)
These Ka values are close to those for phosphoric acid. The highly basic arsenate ion (AsO3−
4) is the product of the third ionization. Unlike phosphoric acid, arsenic acid is oxidizing, illustrated by its ability to convert iodide to iodine.Preparation
Arsenic acid is prepared by treating arsenic trioxide with concentrated nitric acid, or by combination of arsenic pentoxide with water. The latter reaction is very slow. It is also formed when meta- or pyroarsenic acid is treated with cold water.
Other methods
Arsenic acid can be prepared by reacting moist elemental arsenic with ozone.
- 2As + 3H2O + 5O3 → 2H3AsO4 + 5O2
Applications
Commercial applications of arsenic acid are limited by its toxicity. It has found occasional use as a wood preservative, broad-spectrum biocide, a finishing agent for glass and metal, and a reagent in the synthesis of some dyestuffs and organic arsenic compounds. The LD50 in rabbits is 6 mg/kg (0.006 g/kg).[3]
References
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Lee, C.; Harrison, W. T. A. (2007). "Tetraethylammonium dihydrogenarsenate bis(arsenic acid) and 1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane bis(dihydrogenarsenate) arsenic acid: hydrogen-bonded networks containing dihydrogenarsenate anions and neutral arsenic acid molecules". Acta Crystallographica C63 (Pt 7): m308-m311. doi:10.1107/S0108270107023967. PMID 17609552.
- ^ Joachimoglu. Biochem. Z. 70, 144 (1915)
Hydrogen compounds H3AsO3 · H3AsO4 · HAt · HSO3F · HBF4 · HBr · HBrO · HBrO2 · HBrO3 · HBrO4 · HCl · HClO · HClO2 · HClO3 · HClO4 · HCN · HCNO · H2CrO4/H2Cr2O7 · H2CO3 · H2CS3 · HF · HFO · HI · HIO · HNC · HNCO · HNO · HNO3 · H2N2O2 · HNO5S · H3NSO3 · H2O · H2O2 · H2O3 · H3PO2 · H3PO3 · H3PO4 · H4P2O7 · H5P3O10 · H2PtCl6 · H2S · H2Se · H2SeO3 · H2SeO4 · H4SiO4 · H2SiF6 · H2SO3 · H2SO4 · H2SO5 · H2S2O3 · H2S2O6 · H2S2O7 · H2S2O8 · CF3SO3H · H2Te · H2TeO3 · H6TeO6 · H4TiO4 · H2Po · H3VO4 · HCo(CO)4
Categories:- Arsenates
- Hydrogen compounds
- Oxidizing agents
- Oxidizing acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

