- Masson's trichrome stain
-
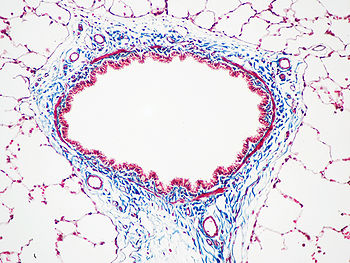 Masson's trichrome stain of rat airway. Connective tissue is stained blue, nuclei are stained dark red/purple, and cytoplasm is stained red/pink.
Masson's trichrome stain of rat airway. Connective tissue is stained blue, nuclei are stained dark red/purple, and cytoplasm is stained red/pink.
Masson's trichrome is a three-colour staining protocol used in histology. The recipes evolved from Claude L. Pierre Masson's original formulation to different specific applications, but all are suited for distinguishing cells from surrounding connective tissue.
Most recipes produce red keratin and muscle fibers, blue or green collagen and bone, light red or pink cytoplasm, and dark brown to black cell nuclei.
The trichrome is applied by immersion of the fixated sample into Weigert's iron hematoxylin, and then three different solutions, labeled A, B, and C:
- Weigert's hematoxylin is a sequence of three solutions: ferric chloride in diluted hydrochloric acid, hematoxylin in 95% ethanol, and potassium ferricyanide solution alkalized by sodium borate. It is used to stain the nuclei.
- Solution A, also called plasma stain, contains acid fuchsin, Xylidine Ponceau, glacial acetic acid, and distilled water. Other red acid dyes can be used, e.g. the Biebrich scarlet in Lillie's trichrome.
- Solution B contains phosphomolybdic acid in distilled water.
- Solution C, also called fibre stain, contains Light Green SF yellowish, or alternatively Fast Green FCF. It is used to stain collagen. If blue is preferred to green, methyl blue, water blue or aniline blue can be substituted.
Variants
A common variant is Lillie's trichrome. It is often erroneously called Masson's trichrome. It differs in the dyes used, their concentrations, and the immersion times.
Another common variant is the Masson trichrome & Verhoeff stain, which combines the Masson trichrome stain and Verhoeff stain.[1] It is sometimes just referred to as a Masson trichrome . A reference is needed for the previous statement, since the Masson's trichrome method on its own does not stain elastin fiber black. This combination is useful for the examination of blood vessels; the Verhoeff stain highlights elastin (black) and allows one to easily differentiate small arteries (which typically have two elastic laminae) and veins (which have one elastic lamina).
References
- ^ Masson Trichrome & Verhoeff Stain. vetmed.vt.edu. URL: http://education.vetmed.vt.edu/Curriculum/VM8054/Labs/Lab2/Examples/exvrmass.htm. Accessed on: August 20, 2009.
External links
Stains Iron/Hemosiderin Lipids Carbohydrates Amyloid Bacteria Gram staining (Methyl violet/Gentian violet, Safranin) · Ziehl–Neelsen stain/acid-fast (Carbol fuchsin/Fuchsine, Methylene blue) · Auramine-rhodamine stain (Auramine O, Rhodamine B)Connective tissue trichrome stain: Masson's trichrome stain/Lillie's trichrome (Light Green SF yellowish, Biebrich scarlet, Phosphomolybdic acid, Fast Green FCF)
Van Gieson's stainOther H&E stain (Haematoxylin, Eosin Y) · Silver stain (Grocott's methenamine silver stain, Warthin–Starry stain) · Methyl blue · Wright's stain · Giemsa stain · Gömöri trichrome stain · Neutral red · Janus Green BTissue stainability Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
