- Mycosis fungoides
-
Mycosis fungoides Classification and external resources
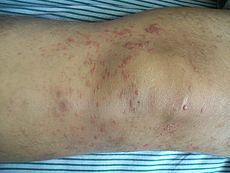
Skin lesions on the knee of a 52 year old male patient with Mycosis fungoidesICD-10 C84.0 ICD-9 202.1 ICD-O: M9700/3 OMIM 254400 DiseasesDB 8595 eMedicine med/1541 MeSH D009182 Mycosis fungoides (also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome[1] or granuloma fungoides), is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time.
Mycosis fungoides was first described in 1806 by French dermatologist Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert.[2] The name mycosis fungoides is somewhat misleading—it loosely means "mushroom-like fungal disease". The disease, however, is not a fungal infection but rather a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It was so named because Alibert described the skin tumors of a severe case as having a mushroom-like appearance.[3]
Contents
History
In 1806, a French physician, Jean Louis Alibert, was the first to describe a patient with mycosis fungoides.[4]
Origins and causes
The cause of mycosis fungoides is unknown, but it is not believed to be hereditary or genetic in the vast majority of cases. One incident has been reported of a possible genetic link.[5] It is not contagious.
It is rare for the disease to appear before age 20, and it appears to be noticeably more common in males than females, especially over the age of 50, where the incidence of the disease (the risk per person in the population) does increase. The average age of onset is between 45 and 55 years of age for patients with patch and plaque disease only, but is over 60 for patients who present with tumours, erythroderma (red skin) or a leukemic form (the Sézary syndrome).
The disease is an unusual expression of CD4 T cells, a part of the immune system. These T cells are skin-associated, meaning that they biochemically and biologically are most related to the skin, in a dynamic manner. Mycosis fungoides is the most common type of 'Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma' (CTCL), but there are many other types of CTCL that have nothing to do with mycosis fungoides and these disorders are treated differently.
Symptoms, diagnosis, and stages
Typical visible symptoms include rashlike patches, tumors, or lesions.[3] Itching (pruritus) is common, perhaps in 20% of patients, and is not universal.
Diagnosis is sometimes difficult because the early phases of the disease often resemble eczema or even psoriasis. As with any serious disease, it is advisable to pursue the opinion of a medical professional if a case is suspected. Diagnosis is generally accomplished through a skin biopsy. Several biopsies are recommended, to be more certain of the diagnosis. The diagnosis is made through a combination of the clinical picture and examination, and is confirmed by biopsy.
To stage the disease, various tests may be ordered, to assess nodes, blood and internal organs, but most patients present with disease apparently confined to the skin, as patches (flat spots) and plaques (slightly raised or 'wrinkled' spots).
Treatments and cures
Mycosis fungoides can be treated in a variety of ways.[6]
If treatment is successful the disease can go into a non-progressing state with clinically clear examination and various tests. This is called remission; it can last indefinitely. Treatments may also cause disease not to progress, while still present, and this is called stable disease; it may last indefinitely but is a more serious situation. Disease may also progress, to involve nodes, blood and internal organs, or transform into a higher-grade lymphoma.
Common treatments include simple sunlight, ultraviolet light, topical steroids, topical and systemic chemotherapies, local superficial radiotherapy, the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat, total skin electron beam radiation, photopheresis and systemic therapies (e.g. interferons, retinoids, rexinoids) or biological therapies. Treatments are often used in combination.
Selection of treatments typically depends on patient preference and access to therapies, as well as recommendations by physicians, the stage of the disease, established resistance to prior therapies, allergies of the patient, clinical evidence of a positive benefit:risk ratio, and so on.
It is incurable, but many patients experience prolonged periods of disease-control. Quality of life is a major objective, in addition to cure, and maximizing periods of remission or stable disease, while minimizing treatments and toxicities, are two central concerns in clinical care.
In 2010, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted orphan drug designation for naloxone lotion, a topical opioid receptor competitive antagonist used as a treatment for pruritus in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.[7][8]
Gallery
See also
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- Pagetoid reticulosis
- Premycotic phase
- Sézary's disease
- Secondary cutaneous CD30+ large cell lymphoma
- Angiocentric lymphoma
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- ^ synd/98 at Who Named It?
- ^ Alibert JLM (1806) (in French). Descriptions des maladies de la peau observées a l’Hôpital Saint-Louis, et exposition des meilleures méthodes suivies pour leur traitement. Paris: Barrois l’ainé. p. 286. http://infohawk.uiowa.edu/F?func=direct&doc_number=000636854&l_base=uiowa.
- ^ a b Cerroni, Lorenzo; Kevin Gatter, Helmut Kerl (2005). An illustrated guide to Skin Lymphomas. Malden, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 13. ISBN 978-1405113762.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. 1867. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ Shelley WB (October 1980). "Familial mycosis fungoides revisited". Arch Dermatol 116 (10): 1177–8. doi:10.1001/archderm.116.10.1177. PMID 7425665. http://archderm.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=7425665.
- ^ Prince HM, Whittaker S, Hoppe RT (2009-11-12). "How I treat mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome". Blood 114 (20): 4337–53. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-07-202895. PMID 19696197.
- ^ Elorac, Inc. announces orphan drug designation for novel topical treatment for pruritus in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) (primary source)
- ^ Wang H, Yosipovitch G (2010 January). "New insights into the pathophysiology and treatment of chronic itch in patients with End-stage renal disease, Chronic liver disease and Lymphoma". Int J Dermatol. 49 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2009.04249.x. PMC 2871329. PMID 20465602. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2871329. (primary source)
Further reading
- Knowles Daniel M (2000). Neoplastic Hematopathology. Lippincott Williams Wilkins. p. 1957. ISBN 0683302469.
- Hwang ST, Janik JE, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH (15 March 2008). "Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome". Lancet 371 (9616): 945–57. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60420-1. PMID 18342689.
- Duvic M, Foss FM (December 2007). "Mycosis fungoides: pathophysiology and emerging therapies". Semin Oncol 34 (6 Suppl 5): S21–8. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2007.11.006. PMID 18086343.
- Olsen E, Vonderheid E, Pimpinelli N, Willemze R, Kim Y, Knobler R, Zackheim H, Duvic M, Estrach T, Lamberg S, Wood G, Dummer R, Ranki A, Burg G, Heald P, Pittelkow M, Bernengo MG, Sterry W, Laroche L, Trautinger F, Whittaker S; ISCL/EORTC (15 September 2007). "Revisions to the staging and classification of mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: a proposal of the International Society for Cutaneous Lymphomas (ISCL) and the cutaneous lymphoma task force of the European Organization of Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)". Blood 110 (6): 1713–22. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-03-055749. PMID 17540844.
External links
- DermAtlas 197
- The Lymphoma Information Network - Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas
- The Doctor's Doctor (detailed information)
- Cutaneous Lymphoma Foundation (formerly MFF)
- ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00106431 "A Single Agent Phase II Study of Romidepsin (Depsipeptide, FK228) in the Treatment of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma"
Hematological malignancy/leukemia histology (ICD-O 9590–9989, C81–C96, 200–208)
Lymphoid/Lymphoproliferative, Lymphomas/Lymphoid leukemias (9590–9739, 9800–9839)By development/
markerCD5+CD22+germinal center/follicular B cell (Follicular, Burkitt's, GCB DLBCL, Primary cutaneous follicular lymphoma)marginal zone/marginal-zone B cell (Splenic marginal zone, MALT, Nodal marginal zone, Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma)see immunoproliferative immunoglobulin disordersBy infectionDiffuse large B-cell lymphoma · Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma · Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma · Primary cutaneous immunocytoma · Plasmacytoma · Plasmacytosis · Primary cutaneous follicular lymphomaBy development/
markerTdT+: ALL (Precursor T acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma)
prolymphocyte (Prolymphocytic)
CD30+ (Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, Lymphomatoid papulosis type A)MF+variantsindolent: Mycosis fungoides · Pagetoid reticulosis · Granulomatous slack skin
aggressive: Sézary's disease · Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphomaNon-MFCD30-: Non-mycosis fungoides CD30− cutaneous large T-cell lymphoma · Pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma · Lymphomatoid papulosis type B
CD30+: CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma · Secondary cutaneous CD30+ large cell lymphoma · Lymphomatoid papulosis type AOther peripheralHepatosplenic · Angioimmunoblastic · Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma · Peripheral T-cell lymphoma-Not-Otherwise-Specified (Lennert lymphoma) · Subcutaneous T-cell lymphomaBy infectionHTLV-1 (Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma)T or NKLymphoid+myeloidCutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia with bandlike and perivascular patterns · Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia with nodular pattern · Jessner lymphocytic infiltrate of the skinCategories:- Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions
- Lymphoma
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.