- Onychomycosis
-
Onychomycosis Classification and external resources 
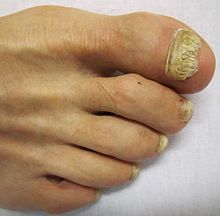
A toenail affected by onychomycosisICD-10 B35.1 ICD-9 110.1 DiseasesDB 13125 MedlinePlus 001330 eMedicine derm/300 MeSH D014009 Onychomycosis (also known as "dermatophytic onychomycosis,"[1] "ringworm of the nail,"[1] and "tinea unguium"[1]) means fungal infection of the nail.[2] It is the most common disease of the nails and constitutes about a half of all nail abnormalities.[3]
This condition may affect toenails or fingernails, but toenail infections are particularly common. The prevalence of onychomycosis is about 6-8% in the adult population.[4]
Contents
Classification
There are four classic types of onychomycosis:[5]
- Distal subungual onychomycosis is the most common form of tinea unguium, and is usually caused by Trichophyton rubrum, which invades the nail bed and the underside of the nail plate.
- White superficial onychomycosis (WSO) is caused by fungal invasion of the superficial layers of the nail plate to form "white islands" on the plate. It accounts for only 10 percent of onychomycosis cases. In some cases, WSO is a misdiagnosis of "keratin granulations" which are not a fungus, but a reaction to nail polish that can cause the nails to have a chalky white appearance. A laboratory test should be performed to confirm.[6]
- Proximal subungual onychomycosis is fungal penetration of the newly formed nail plate through the proximal nail fold. It is the least common form of tinea unguium in healthy people, but is found more commonly when the patient is immunocompromised.
- Candidal onychomycosis is Candida species invasion of the fingernails, usually occurring in persons who frequently immerse their hands in water. This normally requires the prior damage of the nail by infection or trauma.
Signs and symptoms
The nail plate can have a thickened, yellow, or cloudy appearance. The nails can become rough and crumbly, or can separate from the nail bed. There is usually no pain or other bodily symptoms, unless the disease is severe.[7]
Dermatophytids are fungus-free skin lesions that sometimes form as a result of a fungus infection in another part of the body. This could take the form of a rash or itch in an area of the body that is not infected with the fungus. Dermatophytids can be thought of as an allergic reaction to the fungus. People with onychomycosis may experience significant psychosocial problems due to the appearance of the nail. This is particularly increased when fingernails are affected.[8]
Causes
The causative pathogens of onychomycosis include dermatophytes, Candida, and nondermatophytic molds. Dermatophytes are the fungi most commonly responsible for onychomycosis in the temperate western countries; while Candida and nondermatophytic molds are more frequently involved in the tropics and subtropics with a hot and humid climate.[9]
Dermatophytes
Trichophyton rubrum is the most common dermatophyte involved in onychomycosis. Other dermatophytes that may be involved are T. interdigitale, Epidermophyton floccosum, T. violaceum, Microsporum gypseum, T. tonsurans, T. soudanense (considered by some to be an African variant of T. rubrum rather than a full-fledged separate species) and the cattle ringworm fungus T. verrucosum. A common outdated name that may still be reported by medical laboratories is Trichophyton mentagrophytes for T. interdigitale. The name T. mentagrophytes is now restricted to the agent of favus skin infection of the mouse; though this fungus may be transmitted from mice and their danders to humans, it generally infects skin and not nails.
Other
Other causative pathogens include Candida and nondermatophytic molds, in particular members of the mold generation Scytalidium (name recently changed to Neoscytalidium), Scopulariopsis, and Aspergillus. Candida spp. mainly cause fingernail onychomycosis in people whose hands are often submerged in water. Scytalidium mainly affects people in the tropics, though it persists if they later move to areas of temperate climate.
Other molds more commonly affect people older than 60 years, and their presence in the nail reflects a slight weakening in the nail's ability to defend itself against fungal invasion.
Risk factors
Risk factors for onychomycosis include family history, increasing age, poor health, prior trauma, warm climate, participation in fitness activities, immunosuppression (e.g., HIV, drug induced), communal bathing, and occlusive footwear.
Diagnosis
To avoid misdiagnosis as nail psoriasis, lichen planus, contact dermatitis, trauma, nail bed tumor or yellow nail syndrome, laboratory confirmation may be necessary. The three main approaches are potassium hydroxide smear, culture and histology. This involves microscopic examination and culture of nail scrapings or clippings. Recent results indicate the most sensitive diagnostic approaches are direct smear combined with histological examination,[10] and nail plate biopsy using periodic acid-Schiff stain.[11] To reliably identify nondermatophyte molds, several samples may be necessary.[12]
Treatment
Treatment of onychomycosis is challenging because the infection is embedded within the nail and is difficult to reach. As a result, full removal of symptoms is very slow and may take a year or more.
Pharmacological
Most treatments are either systemic antifungal medications, such as terbinafine and itraconazole, or topical, such as nail paints containing ciclopirox or amorolfine. There is also evidence for combining systemic and topical treatments.[13]
For superficial white onychomycosis, systemic rather than topical antifungal therapy is advised.[14]
In July 2007, a meta-study reported on clinical trials for topical treatments of fungal nail infections. The study included six randomised, controlled trials dating up to March 2005.[15] The main findings are:
- There is some evidence ciclopiroxolamine and butenafine are both effective, but both need to be applied daily for prolonged periods (at least 1 year).
- There is evidence topical ciclopiroxolamine has poor cure rates, and that amorolfine might be substantially more effective.
- Further research into the effectiveness of antifungal agents for nail infections is required.
A 2002 study compared the efficacy and safety of terbinafine in comparison to placebo, itraconazole and griseofulvin in treating fungal infections of the nails.[16] The main findings were for reduced fungus, terbinafine was found to be significantly better than itraconazole and griseofulvin, and terbinafine was better tolerated than itraconazole.
- A small study in 2004 showed ciclopirox nail paint was more effective when combined with topical urea cream.[17]
- A study of 504 patients in 2007 found aggressive debridement of the nail, combined with oral terbinafine, significantly reduced symptom frequency over terbinafine alone.[18]
- A 2007 randomised clinical trial with 249 patients showed a combination of amorolfine nail lacquer and oral terbinafine enhanced clinical efficacy and is more cost-effective than terbinafine alone.[19]
Lasers
A Noveon-type laser, already in use by physicians for some types of cataract surgery, is used by some podiatrists, although the only scientific study on its efficacy, while showing positive results, included far too few test subjects for the laser to be proven generally effective.[20]
In 2011, several lasers were seeking approval and two been cleared by the Food and Drug Administration.[21]
Light Age, Inc. has approval to market a Nd:YAG laser for onychomycosis treatment.[22]
Alternative medicine
As with many diseases, there are also some scientifically unverified folk or alternative medicine remedies.
- Australian tea tree oil[23][24] has been tested, but there is insufficient information to make recommendations for its use for onychomycosis.[25]
- Grapefruit seed extract as a natural antimicrobial is not demonstrated. Its effectiveness is scientifically unverified. Multiple studies indicate the universal antimicrobial activity is due to contamination with synthetic preservatives that were unlikely to be made from the seeds of the grapefruit.[26][27][28][29][30]
- Snakeroot leaf extract has, in studies, shown ability to treat superficial onychomycosis, although the results show it is less effective, and equal to conventional drugs ciclopirox and ketaconazole, respectively.[31][32]
Epidemiology
A 2003 survey of diseases of the foot in 16 European countries found onychomycosis to be the most frequent fungal foot infection and estimates its prevalence at 27%.[33][34] Prevalence was observed to increase with age. In Canada, the prevalence was estimated to be 6.48%.[35] Onychomycosis affects approximately one-third of diabetics[36] and is 56% more frequent in people suffering from psoriasis.[37]
Research
Most drug development activities are focused on the discovery of new antifungals and novel delivery methods to promote access of existing antifungal drugs into the infected nail plate. Active clinical trials investigating onychomycosis:[38]
Phase III
- A topical treatment, AN2690, is being developed by Anacor Pharmaceuticals.[39] It is active against Trichophyton species.[40]
- A medicinal nail lacquer, MycoVa from Apricus Biosciences,[41] contains terbinafine as the active ingredient and a permeation enhancer DDAIP which facilitates the delivery of the drug into the nail bed where the fungus resides.[42][43]
- A comparison of delivery methods for itraconzole[44]
- Safety and tolerability of topical terbinafine[45]
- Laser-based treatments[46]
- Topical IDP-108[47]
- Bifonazole cream application after nail ablation with urea paste[48]
Phase II
- Posaconazole, taken orally.[49]
- A topical treatment, NB-002, is being developed by NanoBio Corporation.[44] It has completed Phase II trials.[50]
References
- ^ a b c Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1135. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ "onychomycosis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Szepietowski JC, Salomon J (2007). "Do fungi play a role in psoriatic nails?". Mycoses 50 (6): 437–42. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2007.01405.x. PMID 17944702.
- ^ "Impact 07 - Dermatology" (PDF). Bay Bio. 2007. http://www.baybio.org/pdf/IMPACT07_Derm.pdf. Retrieved 2007-06-13.
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ "AAPA". Cmecorner.com. http://www.cmecorner.com/macmcm/aapa/aapa2004_05.htm. Retrieved 2010-08-05.
- ^ Onychomycosis at eMedicine
- ^ Szepietowski JC, Reich A (September 2008). "Stigmatisation in onychomycosis patients: a population-based study". Mycoses 52: 343. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2008.01618.x. PMID 18793262.
- ^ Chi CC, Wang SH, Chou MC (2005). "The causative pathogens of onychomycosis in southern Taiwan". Mycoses 48 (6): 413–20. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2005.01152.x. PMID 16262878.
- ^ Karimzadegan-Nia M; Mir-Amin-Mohammadi A; Bouzari N, Firooz A (2007). "Comparison of direct smear, culture and histology for the diagnosis of onychomycosis". Australas. J. Dermatol. 48 (1): 18–21. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2007.00320.x. PMID 17222296.
- ^ Weinberg JM; Koestenblatt EK; Tutrone WD; Tishler HR; Najarian L (2003). "Comparison of diagnostic methods in the evaluation of onychomycosis". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 49 (2): 193–7. doi:10.1067/S0190-9622(03)01480-4. PMID 12894064.
- ^ PubMed
- ^ Rodgers P, Bassler M (2001). "Treating onychomycosis". Am Fam Physician 63 (4): 663–72, 677–8. doi:10.1038/jid.1954.5. PMID 11237081. http://www.aafp.org/afp/20010215/663.html.
- ^ Baran R, Faergemann J, Hay RJ (2007). "Superficial white onychomycosis--a syndrome with different fungal causes and paths of infection". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 57 (5): 879–82. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2007.05.026. PMID 17610995.
- ^ Crawford F, Hollis S (2007). "Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD001434. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001434.pub2. PMID 17636672.
- ^ Haugh M, Helou S, Boissel JP, Cribier BJ (2002). "Terbinafine in fungal infections of the nails: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials". Br. J. Dermatol. 147 (1): 118–21. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04825.x. PMID 12100193.
- ^ Mitchel L. Zoler (April 1, 2004). "Boosts drug entry into nails: urea, ciclopirox combo tested for onychomycosis.(Focus on Skin Disorders)". Internal Medical News. p. 69.
- ^ Potter LP, Mathias SD, Raut M, Kianifard F, Landsman A, Tavakkol A (2007). "The impact of aggressive debridement used as an adjunct therapy with terbinafine on perceptions of patients undergoing treatment for toenail onychomycosis". The Journal of dermatological treatment 18 (1): 46–52. doi:10.1080/09546630600965004. PMID 17373090.
- ^ Baran R, Sigurgeirsson B, Berker DD, et al. (2007). "A multicentre, randomized, controlled study of the efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness of a combination therapy with amorolfine nail lacquer and oral terbinafine compared with oral terbinafine alone for the treatment of onychomycosis with matrix involvement". British Journal of Dermatology 157 (1): 149. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.07974.x. PMID 17553051.
- ^ Landsman, Adam S.; et al. (2010). "Treatment of mild, moderate, and severe onychomycosis using 870- and 930-nm light exposure". Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association 100 (3): 166–177. http://www.japmaonline.org/cgi/content/abstract/100/3/166.
- ^ Cathy Becker, Jonann Brady (April 9, 2009). "Promising New Treatment for Fungus-Free Feet". ABC news. http://abcnews.go.com/Health/OnCall/story?id=7113863&page=1. Retrieved 2009-11-06.
- ^ http://www.medica.de/cipp/md_medica/custom/pub/content,oid,34955/lang,2/ticket,g_u_e_s_t/~/Light_Age_Inc._receives_FDA_approval_for_the_treatment_of_onychomycosis.html
- ^ Buck DS, Nidorf DM, Addino JG (1994). "Comparison of two topical preparations for the treatment of onychomycosis: Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and clotrimazole". J Fam Pract 38 (6): 601–5. PMID 8195735.
- ^ Nenoff P, Haustein UF, Brandt W (1996). "Antifungal activity of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil) against pathogenic fungi in vitro". Skin Pharmacol. 9 (6): 388–94. doi:10.1159/000211450. PMID 9055360.
- ^ "Tea tree oil (Melaleuca alternifolia)". Drugs & Supplements. Mayo Clinic. May 1, 2006. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/tea-tree-oil/NS_patient-teatreeoil#31C383D1-E7FF-0DBD-1B59A74BE7EB5F8D. Retrieved 2008-01-29.
- ^ von Woedtke T, Schlüter B, Pflegel P, Lindequist U, Jülich WD (1999). "Aspects of the antimicrobial efficacy of grapefruit seed extract and its relation to preservative substances contained". Pharmazie 54 (6): 452–6. PMID 10399191.
- ^ Sakamoto S, Sato K, Maitani T, Yamada T (1996). [Analysis "of components in natural food additive "grapefruit seed extract" by HPLC and LC/MS"] (in Japanese). Eisei Shikenjo hōkoku. Bulletin of National Institute of Hygienic Sciences (114): 38–42. PMID 9037863. Analysis.
- ^ Takeoka G, Dao L, Wong RY, Lundin R, Mahoney N (2001). "Identification of benzethonium chloride in commercial grapefruit seed extracts". J. Agric. Food Chem. 49 (7): 3316–20. doi:10.1021/jf010222w. PMID 11453769.
- ^ Takeoka GR, Dao LT, Wong RY, Harden LA (2005). "Identification of benzalkonium chloride in commercial grapefruit seed extracts". J. Agric. Food Chem. 53 (19): 7630–6. doi:10.1021/jf0514064. PMID 16159196.
- ^ Ganzera M, Aberham A, Stuppner H (2006). "Development and validation of an HPLC/UV/MS method for simultaneous determination of 18 preservatives in grapefruit seed extract". J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (11): 3768–72. doi:10.1021/jf060543d. PMID 16719494.
- ^ Romero-Cerecero, O.; Román-Ramos, R.; Zamilpa, A.; Jiménez-Ferrer, J. E.; Rojas-Bribiesca, G.; Tortoriello, J. (2009). "Clinical trial to compare the effectiveness of two concentrations of the Ageratina pichinchensis extract in the topical treatment of onychomycosis". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 126 (1): 74–78. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.007. PMID 19683043.
- ^ Romero-Cerecero, O.; Zamilpa, A.; Jiménez-Ferrer, J.; Rojas-Bribiesca, G.; Román-Ramos, R.; Tortoriello, J. (2008). "Double-Blind Clinical Trial for Evaluating the Effectiveness and Tolerability ofAgeratina pichinchensisExtract on Patients with Mild to Moderate Onychomycosis. A Comparative Study with Ciclopirox". Planta Medica 74 (12): 1430–1435. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1081338. PMID 18671197.
- ^ Burzykowski, T.; Molenberghs, G.; Abeck, D.; Haneke, E.; Hay, R.; Katsambas, A.; Roseeuw, D.; Van De Kerkhof, P. et al. (2003). "High prevalence of foot diseases in Europe: Results of the Achilles Project". Mycoses 46 (11–12): 496–505. doi:10.1046/j.0933-7407.2003.00933.x. PMID 14641624.
- ^ Verma S, Heffernan MP (2008). Superficial fungal infection: Dermatophytosis, onychomycosis, tinea nigra, piedra. In K Wolff et al., eds., Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine, 7th ed., vol 2, pp. 1807–1821. New York: McGraw Hill.
- ^ Vender, R.; Lynde, C.; Poulin, Y. (2006). "Prevalence and epidemiology of onychomycosis". Journal of cutaneous medicine and surgery 10 Suppl 2: S28–S33. PMID 17204229.
- ^ Gupta, A.; Konnikov, N.; MacDonald, P.; Rich, P.; Rodger, N.; Edmonds, M.; McManus, R.; Summerbell, R. (1998). "Prevalence and epidemiology of toenail onychomycosis in diabetic subjects: A multicentre survey". The British journal of dermatology 139 (4): 665–671. PMID 9892911.
- ^ Gupta, A.; Lynde, C.; Jain, H.; Sibbald, R.; Elewski, B.; Daniel Cr, 3.; Watteel, G.; Summerbell, R. (1997). "A higher prevalence of onychomycosis in psoriatics compared with non-psoriatics: A multicentre study". The British journal of dermatology 136 (5): 786–789. PMID 9205520.
- ^ clinicaltrials.gov
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01270971 >
- ^ Barak O, Loo DS (2007). "AN-2690, a novel antifungal for the topical treatment of onychomycosis". Curr Opin Investig Drugs 8 (8): 662–8. PMID 17668368.
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00459537
- ^ "Apricus Biosciences Announces Expanded European Patent Coverage For MycoVa(TM) For Nail Fungus". The Street. http://www.thestreet.com/story/11027033/1/apricus-biosciences-announces-expanded-european-patent-coverage-for-mycovatm-for-nail-fungus.html. Retrieved 2011-03-14.
- ^ NEXMED Medicines of the Future
- ^ a b ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00356915
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00443820 and ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00443898
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00935649 and ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00776464
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01008033
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00781820
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00491764
- ^ NanoBio - Onychomycosis
Infectious diseases · Mycoses and Mesomycetozoea (B35–B49, 110–118) Superficial and
cutaneous
(dermatomycosis):
Tinea=skin;
Piedra (exothrix/
endothrix)=hairBy locationTinea barbae/Tinea capitis (Kerion) · Tinea corporis (Ringworm, Dermatophytid) · Tinea cruris · Tinea manuum · Tinea pedis (Athlete's foot) · Tinea unguium/Onychomycosis (White superficial onychomycosis · Distal subungual onychomycosis · Proximal subungual onychomycosis)
Tinea corporis gladiatorum · Tinea faciei · Tinea imbricata · Tinea incognito · FavusBy organismEpidermophyton floccosum · Microsporum canis · Microsporum audouinii · Trichophyton interdigitale/mentagrophytes · Trichophyton tonsurans · Trichophyton schoenleini · Trichophyton rubrumOtherHortaea werneckii (Tinea nigra) · Piedraia hortae (Black piedra)Subcutaneous,
systemic,
and opportunisticDimorphic
(yeast+mold)Coccidioides immitis/Coccidioides posadasii (Coccidioidomycosis, Disseminated coccidioidomycosis, Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. Primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis) · Histoplasma capsulatum (Histoplasmosis, Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis, Primary pulmonary histoplasmosis, Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis) · Histoplasma duboisii (African histoplasmosis) · Lacazia loboi (Lobomycosis) · Paracoccidioides brasiliensis (Paracoccidioidomycosis)OtherBlastomyces dermatitidis (Blastomycosis, North American blastomycosis, South American blastomycosis) · Sporothrix schenckii (Sporotrichosis) · Penicillium marneffei (Penicilliosis)Yeast-likeCandida albicans (Candidiasis, Oral, Esophageal, Vulvovaginal, Chronic mucocutaneous, Antibiotic candidiasis, Candidal intertrigo, Candidal onychomycosis, Candidal paronychia, Candidid, Diaper candidiasis, Congenital cutaneous candidiasis, Perianal candidiasis, Systemic candidiasis, Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) · C. glabrata · C. tropicalis · C. lusitaniae · Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pneumocystosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia)Mold-likeAspergillus (Aspergillosis, Aspergilloma, Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, Primary cutaneous aspergillosis) · Exophiala jeanselmei (Eumycetoma) · Fonsecaea pedrosoi/Fonsecaea compacta/Phialophora verrucosa (Chromoblastomycosis) · Geotrichum candidum (Geotrichosis) · Pseudallescheria boydii (Allescheriasis)Entomophthorales
(Entomophthoramycosis)Basidiobolus ranarum (Basidiobolomycosis) · Conidiobolus coronatus/Conidiobolus incongruus (Conidiobolomycosis)Enterocytozoon bieneusi/Encephalitozoon intestinalisMesomycetozoea Ungrouped Alternariosis · Fungal folliculitis · Fusarium (Fusariosis) · Granuloma gluteale infantum · Hyalohyphomycosis · Otomycosis · PhaeohyphomycosisDisorders of skin appendages (L60–L75, 703–706) Nail behavior: Onychotillomania · Onychophagiaother: Ingrown nail · Anonychiaungrouped: Paronychia (Acute paronychia, Chronic paronychia ) · Chevron nail · Congenital onychodysplasia of the index fingers · Green nails · Half and half nails · Hangnail · Hapalonychia · Hook nail · Lichen planus of the nails · Longitudinal erythronychia · Malalignment of the nail plate · Median nail dystrophy · Mees' lines · Melanonychia · Muehrcke's lines · Nail–patella syndrome · Onychoatrophy · Onychocryptosis · Onycholysis · Onychomadesis · Onychomatricoma · Onychomycosis · Onychophosis · Onychoptosis defluvium · Onychorrhexis · Onychoschizia · Platonychia · Pincer nails · Plummer's nail · Psoriatic nails · Pterygium inversum unguis · Pterygium unguis · Purpura of the nail bed · Racquet nail · Red lunulae · Shell nail syndrome · Splinter hemorrhage · Spotted lunulae · Staining of the nail plate · Stippled nails · Subungual hematoma · Terry's nails · Twenty-nail dystrophyHair noncicatricial alopecia: Alopecia/Alopecia areata (Alopecia totalis, Alopecia universalis, Ophiasis)
Androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness) · Hypotrichosis · Telogen effluvium · Traction alopecia · Lichen planopilaris · Trichorrhexis nodosa · Alopecia neoplastica · Anagen effluvium · Alopecia mucinosacicatricial alopecia: Pseudopelade of Brocq · Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia · Pressure alopecia · Traumatic alopecia · Tumor alopecia · Hot comb alopecia · Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens · Graham-Little syndrome · Folliculitis decalvansHirsutism · Acquired generalized hypertrichosis · Generalized congenital hypertrichosis · Localized acquired hypertrichosis · Localized congenital hypertrichosis · Patterned acquired hypertrichosis · Prepubertal hypertrichosis · X-linked hypertrichosisAcneAcne vulgaris · Acne conglobata · Acne miliaris necrotica · Tropical acne · Infantile acne/Neonatal acne · Excoriated acne · Acne fulminans · Acne medicamentosa (e.g., steroid acne) · Halogen acne (Iododerma, Bromoderma, Chloracne) · Oil acne · Tar acne · Acne cosmetica · Occupational acne · Acne aestivalis · Acne keloidalis nuchae · Acne mechanica · Acne with facial edema · Pomade acne · Acne necrotica · Blackhead · Lupus miliaris disseminatus facieiPerioral dermatitis (Granulomatous perioral dermatitis) · Phymatous rosacea (Rhinophyma, Blepharophyma, Gnathophyma, Metophyma, Otophyma) · Papulopustular rosacea · Lupoid rosacea · Erythrotelangiectatic rosacea · Glandular rosacea · Gram-negative rosacea · Steroid rosacea · Ocular rosacea · Persistent edema of rosacea · Rosacea conglobata · variants (Periorificial dermatitis, Pyoderma faciale)UngroupedGranulomatous facial dermatitis · Idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma · Periorbital dermatitis · SAPHO syndromeFollicular cystsFolliculitis (Folliculitis nares perforans, Tufted folliculitis) · Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Hidradenitis (Hidradenitis suppurativa, Recurrent palmoplantar hidradenitis, Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis)UngroupedAcrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex · Acroosteolysis · Bubble hair deformity · Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis · Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp · Erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli · Hair casts · Hair follicle nevus · Intermittent hair–follicle dystrophy · Keratosis pilaris atropicans · Kinking hair · Koenen's tumor · Lichen planopilaris · Lichen spinulosus · Loose anagen syndrome · Menkes kinky hair syndrome · Monilethrix · Parakeratosis pustulosa · Pili (Pili annulati · Pili bifurcati · Pili multigemini · Pili pseudoannulati · Pili torti) · Pityriasis amiantacea · Plica neuropathica · Poliosis · Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome · Setleis syndrome · Traumatic anserine folliculosis · Trichomegaly · Trichomycosis axillaris · Trichorrhexis (Trichorrhexis invaginata · Trichorrhexis nodosa) · Trichostasis spinulosa · Uncombable hair syndrome · Wooly hair · Wooly hair nevusSweat glands Miliaria (Colloid milium • Miliaria crystalline • Miliaria profunda • Miliaria pustulosa • Miliaria rubra • Occlusion miliaria • Postmiliarial hypohidrosis), Granulosis rubra nasi, Ross’ syndrome, Anhidrosis, Hyperhidrosis (Generalized, Gustatory, Palmoplantar)Body odor, Chromhidrosis, Fox–Fordyce diseaseCategories:- Conditions of the skin appendages
- Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.