- Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta
-
Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta Classification and external resources 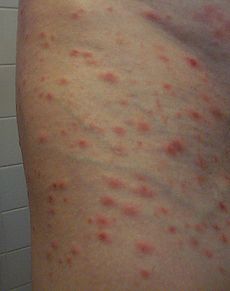
ICD-10 L41.0 ICD-9 696.2 eMedicine derm/334 Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta (also known as "Acute guttate parapsoriasis," "Acute parapsoriasis," "Acute pityriasis lichenoides," "Mucha-Habermann disease," "Parapsoriasis acuta," "Parapsoriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta," and "Parapsoriasis varioliformis"[1]:456[2]:736) is a disease of the immune system. It is the more severe version of Pityriasis lichenoides chronica. The disease is characterized by rashes and small lesions on the skin. The disease is most common in females and usually occurs in young adulthood, although it has been seen in every age group and every race. It is possible for the disease to go into remission for short periods of time or forever.
Contents
Diagnosis
It is commonly misdiagnosed as chickenpox or rosacea. Pleva is also often misidentified as a form of Staph. The most accurate way to diagnose is by biopsy. This disease has not been known to be life threatening. However, there may be mutations of the disease that can cause ulcers on the exterior.
Causes
There is no known cause of this disease;[3] however, many links from viruses, vaccines, and other illnesses have been made. There is some evidence associating it with Parvovirus B19.[4]
The easiest way to understand this disease is to think of it like this: Everyone has T cells that fight disease; in a person with PLEVA, the T cells get mixed up and decide to form in the skin, causing the lesions. It is unknown why this happens.
The trigger which causes the dysfunctional immune system response, PLEVA, is unknown; bacterial, viral, and environmental causes are suspected, but not conclusively demonstrated. There is another theory that the cause of PLEVA may be linked to lymphs and/or lymph nodes.
Treatment
It is not contagious and currently there is no cure for the disease, although the lesions can be treated with ultraviolet therapy as well as topical steroids and antibiotics.
Treatment often involves multiple therapies that address the immune system and bacterial, viral, or dermatological causes.
See also
References
- ^ Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071380760.
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ "PLEVA, or Mucha-Habermann disease - MayoClinic.com". Archived from the original on 2007-07-15. http://web.archive.org/web/20070715202757/http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/pleva/AN00709. Retrieved 2007-11-18.
- ^ Tomasini D, Tomasini CF, Cerri A et al. (2004). "Pityriasis lichenoides: a cytotoxic T-cell-mediated skin disorder. Evidence of human parvovirus B19 DNA in nine cases". J. Cutan. Pathol. 31 (8): 531–8. doi:10.1111/j.0303-6987.2004.00186.x. PMID 15268707.
External links
Papulosquamous disorders (L40–L45, 696–697) Psoriasis PustularGeneralized pustular psoriasis (Impetigo herpetiformis) · Acropustulosis/Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris (Pustular bacterid) · Annular pustular psoriasis · Localized pustular psoriasisOtherParapsoriasis Pityriasis lichenoides (Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta, Pityriasis lichenoides chronica) · Lymphomatoid papulosis · Small plaque parapsoriasis (Digitate dermatosis, Xanthoerythrodermia perstans) · Large plaque parapsoriasis (Retiform parapsoriasis)Other pityriasis Other lichenoid configuration: Annular lichen planus · Linear lichen planus
morphology of lesion: Hypertrophic lichen planus · Atrophic lichen planus · Bullous lichen planus · Ulcerative lichen planus · Lichen planus actinicus · Lichen planus pigmentosus
site of involvement: Mucosal lichen planus · Lichen planus of the nails · Peno-gingival syndrome · Vulvovaginal gingival syndromeoverlap: Lichen planus–lichen sclerosus overlap syndrome · Lichen planus–lupus erythematosus overlap syndrome
special forms: Hepatitis-associated lichen planus · Lichen planus pemphigoidesOtherungrouped lichenoid eruptions: Erythema dyschromicum perstans · Idiopathic eruptive macular pigmentation · Keratosis lichenoides chronica · Kraurosis vulvae · Lichen sclerosus · Lichenoid dermatitis · Lichenoid reaction of graft-versus-host diseaseCategories:- Immune system disorders
- Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
