- Tinea versicolor
-
Tinea versicolor Classification and external resources 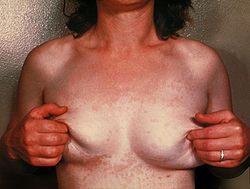
ICD-10 B36.0 ICD-9 111.0 DiseasesDB 10071 MedlinePlus 001465 eMedicine derm/423 MeSH D014010 Tinea versicolor (also known as Dermatomycosis furfuracea,[1] Pityriasis versicolor,[1] and Tinea flava)[1] is a condition characterized by a rash on the trunk and proximal extremities.[1] Recent research has shown that the majority of Tinea versicolor is caused by the Malassezia globosa fungus, although Malassezia furfur is responsible for a small number of cases.[2][3] These yeasts are normally found on the human skin and only become troublesome under certain circumstances, such as a warm and humid environment, although the exact conditions that cause initiation of the disease process are poorly understood.[2][4]
The condition pityriasis versicolor was first identified in 1846.[5]
Contents
Symptoms
The symptoms of this condition include:
- Generally oval or irregularly-shaped spots of 1⁄4 to 1 inch (0.6 to 2.5 cm) in diameter, often merging together to form a larger patch
- Occasional fine scaling of the skin producing a very superficial ash-like scale
- Pale, dark tan, or pink in color, with a reddish undertone that can darken when the patient is overheated, such as in a hot shower or during/after exercise
- Sharp border
- Sometimes severe "pin-prick" itching in the affected areas; usually when the person's body temperature is elevated by exercise or a hot/warm environment, but the person hasn't started sweating yet. Once sweating begins the "pin-prick" itching subsides.[citation needed]
These spots commonly affect the back, underarm, upper arm, chest, lower legs, and neck. Occasionally it can also be present on the face. The yeasts can often be seen under the microscope within the lesions and typically have a so called "spaghetti and meat ball appearance"[6] as the round yeasts produce filaments.
In people with dark skin tones, pigmentary changes such as hypopigmentation (loss of color) are common, while in those with lighter skin color, hyperpigmentation (increase in skin color) are more common. These discolorations have led to the term "sun fungus".[7]
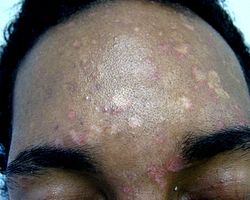 Pityriasis versicolor commonly causes hypopigmentation in people with dark skin tones
Pityriasis versicolor commonly causes hypopigmentation in people with dark skin tones
Prevalence
Tinea versicolor is a common condition. It is estimated that 2 to 8% of the population of the United States has it. This skin disease commonly affects adolescents and young adults, especially in warm and humid climates. It is thought that the yeast feeds on skin oils (lipids) as well as dead skin cells. Infections are more common in people who have seborrheic dermatitis, dandruff, and hyperhidrosis.[4]
Treatment
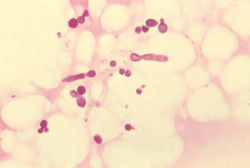 Malassezia furfur in skin scale from a patient with tinea versicolor
Malassezia furfur in skin scale from a patient with tinea versicolor
Treatments for tinea versicolor include:
- Topical antifungal medications containing 2.5% selenium sulfide (Selsun Extra Strength shampoo) are often recommended. Selsun Blue works for some people, but not all, because it only contains 1% selenium sulfide. Products containing more than 1% selenium sulfide are considered prescription strength. Other products that contain 1% selenium sulfide include [ZunSpot] medicated cream.[8] Ketoconazole (Nizoral ointment and shampoo) is another treatment. It is normally applied to dry skin and washed off after 10 minutes, repeated daily for 2 weeks. Ciclopirox (Ciclopirox olamine) is an alternative treatment to ketoconazole as it suppresses growth of the yeast Malassezia furfur. Initial results show similar efficacy to ketoconazole with a relative increase in subjective symptom relief due to its inherent anti-inflammatory properties.[9] Other topical antifungal agents such as clotrimazole, miconazole or terbinafine are less widely recommended[citation needed]. Additionally, hydrogen peroxide has been known to lessen symptoms, and on certain occasions, remove the problem, although permanent scarring occurs with this treatment.[citation needed] Clotrimazole (1%) is also used combined with selenium sulfide (2.5%) (Candid-TV).
- Oral antifungal prescription-only medications include 400 mg of ketoconazole or fluconazole in a single dose, or ketoconazole 200 mg daily for 7 days, or itraconazole[10][11] 400 mg daily for 3–7 days. The single-dose regimens, or pulse therapy regimes, can be made more effective by having the patient exercise 1–2 hours after the dose, to induce sweating. The sweat is allowed to evaporate, and showering is delayed for a day, leaving a film of the medication on the skin.[12]
- Some success with Senna alata has been reported.[13]
- Recurrence is common and may be reduced by intermittent application of topical anti-fungal agents like tea tree oil or selenium sulfide.
Pevaryl Foaming Solution (for fungal skin infections an tinea - Apply Pevaryl Foaming Solution to freshly showered skin and scalp. Rub in well for 3-5 minutes. Dry hair but DO NOT rinse the solution off your body. Shower off next morning if desired. Repeat the process for the next 2 evenings. Repeat the course 1 month and 3 months after the initial treatment to prevent relapse
References
- ^ a b c d Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. pp. Chapter 76. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ a b Morishita N; Sei Y. Microreview of Pityriasis versicolor and Malassezia species. Mycopathologia. 2006 Dec;162(6):373-6
- ^ Prohic A; Ozegovic L. Malassezia species isolated from lesional and non-lesional skin in patients with pityriasis versicolor. Mycoses. 2007 Jan;50(1):58-63.
- ^ a b Weedon, D. 2002. Skin pathology. 2nd Ed. Churchil Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-07069-5
- ^ Inamadar AC, Palit A (2003). "The genus Malassezia and human disease". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 69 (4): 265–70. PMID 17642908. http://www.ijdvl.com/article.asp?issn=0378-6323;year=2003;volume=69;issue=4;spage=265;epage=270;aulast=Inamadar.
- ^ "Adolescent Health Curriculum - Medical Problems - Dermatology - Papulosquamous Lesions (B4)". http://www.usc.edu/student-affairs/Health_Center/adolhealth/content/b4derm4.html. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ^ "Tioconazole (Topical Route) - MayoClinic.com". http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/drug-information/DR601345. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ^ MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia: Tinea versicolor
- ^ Ratnavel RC, Squire RA, Boorman GC (2007). "Clinical efficacies of shampoos containing ciclopirox olamine (1.5%) and ketoconazole (2.0%) in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis". J Dermatolog Treat 18 (2): 88–96. doi:10.1080/16537150601092944. PMID 17520465.
- ^ Faergemann J, Gupta AK, Al Mofadi A, Abanami A, Shareaah AA, Marynissen G (January 2002). "Efficacy of itraconazole in the prophylactic treatment of pityriasis (tinea) versicolor". Arch Dermatol 138 (1): 69–73. doi:10.1001/archderm.138.1.69. PMID 11790169. http://archderm.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=11790169.
- ^ Mohanty J, Sethi J, Sharma MK (2001). "Efficacy of itraconazole in the treatment of tinea versicolor". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 67 (5): 240–1. PMID 17664760. http://www.ijdvl.com/article.asp?issn=0378-6323;year=2001;volume=67;issue=5;spage=240;epage=241;aulast=Mohanty.
- ^ Ketoconazole
- ^ Damodaran S, Venkataraman S (March 1994). "A study on the therapeutic efficacy of Cassia alata, Linn. leaf extract against Pityriasis versicolor". J Ethnopharmacol 42 (1): 19–23. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(94)90018-3. PMID 8046939. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0378-8741(94)90018-3.
External links
- Health in Plain English - Tinea versicolor
- Tinea versicolor is harmless but can recur
- Tinea versicolor Images from the US Medical Videos Journal
Infectious diseases · Mycoses and Mesomycetozoea (B35–B49, 110–118) Superficial and
cutaneous
(dermatomycosis):
Tinea=skin;
Piedra (exothrix/
endothrix)=hairBy locationTinea barbae/Tinea capitis (Kerion) · Tinea corporis (Ringworm, Dermatophytid) · Tinea cruris · Tinea manuum · Tinea pedis (Athlete's foot) · Tinea unguium/Onychomycosis (White superficial onychomycosis · Distal subungual onychomycosis · Proximal subungual onychomycosis)
Tinea corporis gladiatorum · Tinea faciei · Tinea imbricata · Tinea incognito · FavusBy organismEpidermophyton floccosum · Microsporum canis · Microsporum audouinii · Trichophyton interdigitale/mentagrophytes · Trichophyton tonsurans · Trichophyton schoenleini · Trichophyton rubrumOtherHortaea werneckii (Tinea nigra) · Piedraia hortae (Black piedra)Subcutaneous,
systemic,
and opportunisticDimorphic
(yeast+mold)Coccidioides immitis/Coccidioides posadasii (Coccidioidomycosis, Disseminated coccidioidomycosis, Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. Primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis) · Histoplasma capsulatum (Histoplasmosis, Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis, Primary pulmonary histoplasmosis, Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis) · Histoplasma duboisii (African histoplasmosis) · Lacazia loboi (Lobomycosis) · Paracoccidioides brasiliensis (Paracoccidioidomycosis)OtherBlastomyces dermatitidis (Blastomycosis, North American blastomycosis, South American blastomycosis) · Sporothrix schenckii (Sporotrichosis) · Penicillium marneffei (Penicilliosis)Yeast-likeCandida albicans (Candidiasis, Oral, Esophageal, Vulvovaginal, Chronic mucocutaneous, Antibiotic candidiasis, Candidal intertrigo, Candidal onychomycosis, Candidal paronychia, Candidid, Diaper candidiasis, Congenital cutaneous candidiasis, Perianal candidiasis, Systemic candidiasis, Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) · C. glabrata · C. tropicalis · C. lusitaniae · Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pneumocystosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia)Mold-likeAspergillus (Aspergillosis, Aspergilloma, Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, Primary cutaneous aspergillosis) · Exophiala jeanselmei (Eumycetoma) · Fonsecaea pedrosoi/Fonsecaea compacta/Phialophora verrucosa (Chromoblastomycosis) · Geotrichum candidum (Geotrichosis) · Pseudallescheria boydii (Allescheriasis)Entomophthorales
(Entomophthoramycosis)Basidiobolus ranarum (Basidiobolomycosis) · Conidiobolus coronatus/Conidiobolus incongruus (Conidiobolomycosis)Enterocytozoon bieneusi/Encephalitozoon intestinalisMesomycetozoea Ungrouped Alternariosis · Fungal folliculitis · Fusarium (Fusariosis) · Granuloma gluteale infantum · Hyalohyphomycosis · Otomycosis · PhaeohyphomycosisCategories:- Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions
- Fungal diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
