- Blastomycosis
-
"Blasto" redirects here. For the video game, see Blasto (video game).
- The term "South American blastomycosis" is sometimes used to describe infection with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis,[1] though the term Paracoccidioidomycosis is more frequently used to describe this condition.
Blastomycosis Classification and external resources
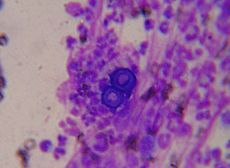
Blastomyces dermatitidis, the causative agent of blastomycosis.ICD-10 B40 ICD-9 116.0 DiseasesDB 1439 MedlinePlus 000102 eMedicine med/231 ped/254 MeSH D001759 Blastomycosis (also known as "North American blastomycosis," "Blastomycetic dermatitis," and "Gilchrist's disease"[2]:319) is a fungal infection caused by the organism Blastomyces dermatitidis. Endemic to portions of North America, blastomycosis causes clinical symptoms similar to histoplasmosis.[3]
Contents
Signs and symptoms
Blastomycosis can present in one of the following ways:
- a flu-like illness with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and a nonproductive cough which resolves within days.
- an acute illness resembling bacterial pneumonia, with symptoms of high fever, chills, a productive cough, and pleuritic chest pain.
- a chronic illness that mimics tuberculosis or lung cancer, with symptoms of low-grade fever, a productive cough, night sweats, and weight loss.
- a fast, progressive, and severe disease that manifests as ARDS, with fever, shortness of breath, tachypnea, hypoxemia, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates.
- skin lesions, usually asymptomatic, appear as ulcerated lesions with small pustules at the margins
- bone lytic lesions can cause bone or joint pain.
- prostatitis may be asymptomatic or may cause pain on urinating.
- laryngeal involvement causes hoarseness.
Cause
Infection occurs by inhalation of the fungus from its natural soil habitat. Once inhaled in the lungs, they multiply and may disseminate through the blood and lymphatics to other organs, including the skin, bone, genitourinary tract, and brain. The incubation period is 30 to 100 days, although infection can be asymptomatic.
Diagnosis
Once suspected, the diagnosis of blastomycosis can usually be confirmed by demonstration of the characteristic broad based budding organisms[4] in sputum or tissues by KOH prep, cytology, or histology. Tissue biopsy of skin or other organs may be required in order to diagnose extra-pulmonary disease. Commercially available urine antigen testing appears to be quite sensitive in suggesting the diagnosis in cases where the organism is not readily detected. While culture of the organism remains the definitive diagnostic standard, its slow growing nature can lead to delays in treatment of up to several weeks.
However, sometimes blood and sputum cultures may not detect blastomycosis; lung biopsy is another option, and results will be shown promptly.
Treatment
Itraconazole given orally is the treatment of choice for most forms of the disease. Ketoconazole may also be used. Cure rates are high, and the treatment over a period of months is usually well tolerated. Amphotericin B is considerably more toxic, and is usually reserved for immunocompromised patients who are critically ill and those with central nervous system disease. Fluconazole has also been tested on patients in Canada.
Prognosis
Mortality rate in treated cases
- 0-2% in treated cases among immunocompetent patients
- 29% in immunocompromised patients
- 40% in the subgroup of patients with AIDS
- 68% in patients presenting as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Epidemiology
In the United States, blastomycosis is endemic in the Mississippi river and Ohio river basins and around the Great Lakes. The annual incidence is less than 1 case per 100,000 people in Mississippi, Louisiana, Kentucky, and Arkansas. The cases are greater in northern states such as Wisconsin, where from 1986 to 1995 there were 1.4 cases per 100,000 people.[5] It also frequently affects hunting dogs in northern Wisconsin and the upper Mississippi and Wisconsin Rivers.[6]
In Canada, most cases of blastomycosis occur in Northwestern Ontario, particularly around the Kenora area. The moist, acidic soil in the surrounding woodland harbors the fungus.
Blastomycosis is distributed internationally; cases are sometimes reported from Africa.[7]
History
Blastomycosis was first described by Thomas Casper Gilchrist[8] in 1894 and sometimes goes by the eponym Gilchrist's disease.[9] It is also sometimes referred to as Chicago Disease.
See also
- South American blastomycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Paracoccidioidomycosis
References
- ^ "South American Blastomycosis: Overview - eMedicine Dermatology". http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1092860-overview. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Ryan KJ; Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 676–8. ISBN 0838585299.
- ^ Veligandla SR, Hinrichs SH, Rupp ME, Lien EA, Neff JR, Iwen PC (October 2002). "Delayed diagnosis of osseous blastomycosis in two patients following environmental exposure in nonendemic areas". Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 118 (4): 536–41. doi:10.1309/JEJ0-3N98-C3G8-21DE. PMID 12375640. http://ajcp.metapress.com/openurl.asp?genre=article&issn=0002-9173&volume=118&issue=4&spage=536.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (1996). "Blastomycosis--Wisconsin, 1986-1995". MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 45 (28): 601–3. PMID 8676851.
- ^ Pet Center Blasto in Dogs
- ^ Alvarez G, Burns B, Desjardins M, Salahudeen S, AlRashidi F, Cameron D (2006). "Blastomycosis in a young African man presenting with a pleural effusion". Can Respir J 13 (8): 441–4. PMC 2683332. PMID 17149463. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2683332.
- ^ "Thomas Caspar Gilchrist (www.whonamedit.com)". http://www.whonamedit.com/doctor.cfm/2763.html. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ^ "Gilchrist's disease (www.whonamedit.com)". http://www.whonamedit.com/synd.cfm/3327.html. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
External links
Infectious diseases · Mycoses and Mesomycetozoea (B35–B49, 110–118) Superficial and
cutaneous
(dermatomycosis):
Tinea=skin;
Piedra (exothrix/
endothrix)=hairBy locationTinea barbae/Tinea capitis (Kerion) · Tinea corporis (Ringworm, Dermatophytid) · Tinea cruris · Tinea manuum · Tinea pedis (Athlete's foot) · Tinea unguium/Onychomycosis (White superficial onychomycosis · Distal subungual onychomycosis · Proximal subungual onychomycosis)
Tinea corporis gladiatorum · Tinea faciei · Tinea imbricata · Tinea incognito · FavusBy organismEpidermophyton floccosum · Microsporum canis · Microsporum audouinii · Trichophyton interdigitale/mentagrophytes · Trichophyton tonsurans · Trichophyton schoenleini · Trichophyton rubrumOtherHortaea werneckii (Tinea nigra) · Piedraia hortae (Black piedra)Subcutaneous,
systemic,
and opportunisticDimorphic
(yeast+mold)Coccidioides immitis/Coccidioides posadasii (Coccidioidomycosis, Disseminated coccidioidomycosis, Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. Primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis) · Histoplasma capsulatum (Histoplasmosis, Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis, Primary pulmonary histoplasmosis, Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis) · Histoplasma duboisii (African histoplasmosis) · Lacazia loboi (Lobomycosis) · Paracoccidioides brasiliensis (Paracoccidioidomycosis)OtherBlastomyces dermatitidis (Blastomycosis, North American blastomycosis, South American blastomycosis) · Sporothrix schenckii (Sporotrichosis) · Penicillium marneffei (Penicilliosis)Yeast-likeCandida albicans (Candidiasis, Oral, Esophageal, Vulvovaginal, Chronic mucocutaneous, Antibiotic candidiasis, Candidal intertrigo, Candidal onychomycosis, Candidal paronychia, Candidid, Diaper candidiasis, Congenital cutaneous candidiasis, Perianal candidiasis, Systemic candidiasis, Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) · C. glabrata · C. tropicalis · C. lusitaniae · Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pneumocystosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia)Mold-likeAspergillus (Aspergillosis, Aspergilloma, Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, Primary cutaneous aspergillosis) · Exophiala jeanselmei (Eumycetoma) · Fonsecaea pedrosoi/Fonsecaea compacta/Phialophora verrucosa (Chromoblastomycosis) · Geotrichum candidum (Geotrichosis) · Pseudallescheria boydii (Allescheriasis)Entomophthorales
(Entomophthoramycosis)Basidiobolus ranarum (Basidiobolomycosis) · Conidiobolus coronatus/Conidiobolus incongruus (Conidiobolomycosis)Enterocytozoon bieneusi/Encephalitozoon intestinalisMesomycetozoea Ungrouped Alternariosis · Fungal folliculitis · Fusarium (Fusariosis) · Granuloma gluteale infantum · Hyalohyphomycosis · Otomycosis · PhaeohyphomycosisCategories:- Fungal diseases
- Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.