- Oral candidiasis
-
Oral candidiasis Classification and external resources
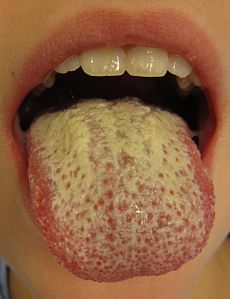
Oral thrushICD-10 B37.0 ICD-9 112.0 DiseasesDB 29743 MedlinePlus 000966 eMedicine derm/68 ped/2245 MeSH D002180 Oral candidiasis (also known as "thrush"[1]:308) is an infection of yeast fungi of the genus Candida on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It is frequently caused by Candida albicans, or less commonly by Candida glabrata or Candida tropicalis. Oral thrush may refer to candidiasis in the mouths of babies, while if occurring in the mouth or throat of adults it may also be termed candidosis or moniliasis.
Contents
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of oral infection by Candida species may not be immediately noticeable but can develop suddenly and may persist for a long time. The infection usually appears as thick white or cream-colored deposits on mucosal membranes such as the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, tonsils, and palate. The infected mucosa may appear inflamed (red and possibly slightly raised) and sometimes have a cottage cheese-like appearance. The lesions can be painful and will become tender and often bleed if rubbed or scraped. Cracking at the corners of the mouth, a cottony-like sensation inside the mouth, and even temporary loss of taste can occur.[2]
In more severe cases, the infection can spread down the esophagus and cause difficulty swallowing - this is referred to as Esophageal candidiasis. Thrush does not usually cause a fever unless the infection has spread beyond the esophagus to other body parts, such as the lungs (systemic candidiasis).[3][4]
In addition to the distinctive lesions, infants can become irritable and may have trouble feeding. The infection can be communicated during breast-feeding to and from the breast and the infant's mouth repeatedly.[2]
Risk factors
- Newborn babies.
- Diabetics with poorly controlled diabetes.
- As a side effect of medication, most commonly having taken antibiotics. Inhaled corticosteroids for treatment of lung conditions (e.g., asthma or COPD) may also result in oral candidiasis: the risk may be reduced by regularly rinsing the mouth with water after taking the medication.
- People with an immune deficiency (e.g. as a result of AIDS/HIV or chemotherapy treatment).
- Women undergoing hormonal changes, like pregnancy or those on birth control pills.
- Denture users.
- Tongue piercing.[5]
Treatment
Oral candidiasis can be treated with topical anti-fungal drugs, such as nystatin, miconazole, Gentian violet or amphotericin B. Topical therapy is given as an oral suspension which is washed around the mouth and then swallowed by the patient.
Patients who are immunocompromised, either with HIV/AIDS or as a result of chemotherapy, may require systemic treatment with oral or intravenous administered anti-fungals.
See also
Notes
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ a b "Oral Thrush: Symptoms". Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. 20 August 2009. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/oral-thrush/DS00408/DSECTION=symptoms. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- ^ Macnair, Trisha (February 2009). "Oral thrush". BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/health/physical_health/conditions/oralthrush2.shtml. Retrieved 8 June 2011.
- ^ "Dental Health and Thrush". WebMD. http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/dental-health-thrush. Retrieved 8 June 2011.
- ^ Zadik Yehuda, Burnstein Saar, Derazne Estella, Sandler Vadim, Ianculovici Clariel, Halperin Tamar (March 2010). "Colonization of Candida: prevalence among tongue-pierced and non-pierced immunocompetent adults". Oral Dis 16 (2): 172–5. doi:10.1111/j.1601-0825.2009.01618.x. PMID 19732353.
References
- Pillinger, John; Andersen, Flemming; & Søderberg, Ulla (6 July 2005). "Oral thrush (fungal infection in the mouth)". NetDoctor. http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/diseases/facts/oralthrush.htm. Retrieved 2007-03-30.
Infectious diseases · Mycoses and Mesomycetozoea (B35–B49, 110–118) Superficial and
cutaneous
(dermatomycosis):
Tinea=skin;
Piedra (exothrix/
endothrix)=hairBy locationTinea barbae/Tinea capitis (Kerion) · Tinea corporis (Ringworm, Dermatophytid) · Tinea cruris · Tinea manuum · Tinea pedis (Athlete's foot) · Tinea unguium/Onychomycosis (White superficial onychomycosis · Distal subungual onychomycosis · Proximal subungual onychomycosis)
Tinea corporis gladiatorum · Tinea faciei · Tinea imbricata · Tinea incognito · FavusBy organismEpidermophyton floccosum · Microsporum canis · Microsporum audouinii · Trichophyton interdigitale/mentagrophytes · Trichophyton tonsurans · Trichophyton schoenleini · Trichophyton rubrumOtherHortaea werneckii (Tinea nigra) · Piedraia hortae (Black piedra)Subcutaneous,
systemic,
and opportunisticDimorphic
(yeast+mold)Coccidioides immitis/Coccidioides posadasii (Coccidioidomycosis, Disseminated coccidioidomycosis, Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. Primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis) · Histoplasma capsulatum (Histoplasmosis, Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis, Primary pulmonary histoplasmosis, Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis) · Histoplasma duboisii (African histoplasmosis) · Lacazia loboi (Lobomycosis) · Paracoccidioides brasiliensis (Paracoccidioidomycosis)OtherBlastomyces dermatitidis (Blastomycosis, North American blastomycosis, South American blastomycosis) · Sporothrix schenckii (Sporotrichosis) · Penicillium marneffei (Penicilliosis)Yeast-likeCandida albicans (Candidiasis, Oral, Esophageal, Vulvovaginal, Chronic mucocutaneous, Antibiotic candidiasis, Candidal intertrigo, Candidal onychomycosis, Candidal paronychia, Candidid, Diaper candidiasis, Congenital cutaneous candidiasis, Perianal candidiasis, Systemic candidiasis, Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) · C. glabrata · C. tropicalis · C. lusitaniae · Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pneumocystosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia)Mold-likeAspergillus (Aspergillosis, Aspergilloma, Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, Primary cutaneous aspergillosis) · Exophiala jeanselmei (Eumycetoma) · Fonsecaea pedrosoi/Fonsecaea compacta/Phialophora verrucosa (Chromoblastomycosis) · Geotrichum candidum (Geotrichosis) · Pseudallescheria boydii (Allescheriasis)Entomophthorales
(Entomophthoramycosis)Basidiobolus ranarum (Basidiobolomycosis) · Conidiobolus coronatus/Conidiobolus incongruus (Conidiobolomycosis)Enterocytozoon bieneusi/Encephalitozoon intestinalisMesomycetozoea Ungrouped Alternariosis · Fungal folliculitis · Fusarium (Fusariosis) · Granuloma gluteale infantum · Hyalohyphomycosis · Otomycosis · PhaeohyphomycosisCategories:- Fungal diseases
- Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions
- Oral pathology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.