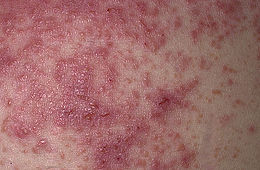
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
-
Dermatitis herpetiformis Classification and external resources 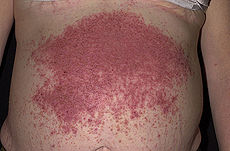
Dermatitis herpetiformis characteristic rashICD-10 L12.2, L13 ICD-9 694.0 DiseasesDB 3597 MedlinePlus 001480 eMedicine derm/95 MeSH D003874 Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH), or Duhring's disease,[1][2] is a chronic blistering skin condition,[3] characterised by blisters filled with a watery fluid.[4] Despite its name, DH is not related to or caused by herpes virus: the name means that it is a skin inflammation having an appearance similar to herpes.
DH was first described by Dr. Louis Duhring in 1884.[5] A connection between DH and gluten intolerance (celiac disease) was recognised in 1967,[5][6] although the exact causal mechanism is not known.
The age of onset is usually about 15-40, but DH can also affect children and the elderly. Men and women are equally affected. Estimates of DH prevalence vary from 1 in 400 to 1 in 10000.[7][8][9][10]
Contents
Symptoms
Dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by intensely itchy, chronic papulovesicular eruptions, usually distributed symmetrically on extensor surfaces (buttocks, back of neck, scalp, elbows, knees, back).[1]:616[8][11] The blisters vary in size from very small up to 1 cm across.
The condition is extremely itchy, and the desire to scratch can be overwhelming.[12] This sometimes causes the sufferer to scratch the blisters off before they are examined by a doctor.[8] Intense itching or burning sensations are sometimes felt before the blisters appear in a particular area.[4][13]
Untreated, the severity of DH can vary significantly over time, it is presumed, in response to the amount of gluten ingested.[13]
Dermatitis herpetiformis symptoms typically first appear in the early years of adulthood between 20 and 30 years of age.[14]
Although the first signs and symptoms of dermatitis herpetiformis are intense itching and burning, the first visible signs are the small papules or vesicles that usually look like red bumps or blisters. Sometimes they appear on the face and along the hairline, and, on occasion, on the shoulders, the lower end of the spinal column, and within the mouth. The rash rarely occurs on other mucous membranes, excepting the mouth or lips. The symptoms range in severity from mild to serious, but they are likely to disappear if gluten ingestion is avoided and appropriate treatment is administered. However, the consumption of aliments that contain gluten as well as oral contraceptives may exacerbate the symptoms.[15]
Dermatitis herpetiformis symptoms are chronic, and they tend to come and go, mostly in short periods of time. Sometimes, these symptoms may be accompanied by symptoms of coeliac disease, commonly including abdominal pain and fatigue.
The rash caused by dermatitis herpetiformis forms and disappears in three stages. In the first stage, the patient may notice a slight discoloration of the skin at the site where the lesions appear. In the next stage, the skin lesions transform into obvious vesicles and papules that are likely to occur in groups. Healing of the lesions is the last stage of the development of the symptoms, usually characterized by a change in the skin color. This can result in areas of the skin turning darker or lighter than the color of the skin on the rest of the body. Because of the intense itching, patients usually scratch, which leads to the formation of crusts.
Usually, itching and burning are the first symptoms to be experienced in dermatitis herpetiformis, and they may occur up to 12 hours before the rash becomes visible.[citation needed] After the blisters develop, itching and burning may persist to up to 10 days, when they finally begin to crust.[citation needed]
Inflammation and pus formation within the blisters is not specific.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
Dermatitis herpetiformis is often misdiagnosed, being confused with drug eruptions, contact dermatitis, dishydrotic eczema (dyshidrosis), and even scabies. [16]
Diagnosis is confirmed by a simple blood test for IgA antibodies,[17] and by a skin biopsy in which the pattern of IgA deposits in the dermal papillae, revealed by direct immunofluorescence, distinguishes it from linear IgA bullous dermatosis[8] and other forms of dermatitis. These tests should be done before the patient starts on a gluten-free diet, otherwise they might produce false negatives. If the patient has already started a gluten-free diet (there is a strong relationship with DH and coeliac sprue), it might be necessary for them to come off it for some weeks before the tests can be done reliably.
Treatment
Dermatitis herpetiformis responds well to medication and changes in diet.
Dapsone is an effective treatment for most patients. DH responds to dapsone so quickly (itching is significantly reduced within 2–3 days[12][18]) that this response may almost be considered diagnostic. However, dapsone treatment has no effect on any intestinal damage (see coeliac disease) that might be present.[10]
Therefore, a strict gluten-free diet must also be followed,[17] and this will usually be a lifelong requirement. This will reduce any associated intestinal damage[12][17] and the risk of other complications. After some time on a gluten-free diet, the dosage of dapsone can usually be reduced or even stopped,[12] although this can take up to 1 to 3 years.
Dapsone is an antibacterial, and its role in the treatment of DH, which is not caused by bacteria, is poorly understood. It can cause adverse effects on the blood, so regular blood monitoring is required.[4]
Dapsone is the drug of choice, but, for patients unable to tolerate dapsone for any reason, the following can be tried, although they are less effective:
Pathology
In terms of pathology, the first signs of the condition may be observed within the dermis. The changes that can take place at this level may include edema, vascular dilatation, and cellular infiltration. It is common for lymphocytes and eosinophils to be seen. The bullae found in the skin affected by dermatitis herpetiformis are subepidermal and have rounded lateral borders.
When looked at under the microscope, the skin affected by dermatitis herpetiformis presents a collection of cells known as neutrophils. They have an increased prevalence in the areas where the dermis and is the closest to the epidermis.
Direct IMF studies of uninvolved skin show IgA in the dermal papillae and patchy granular IgA along the basement membrane. The jejunal mucosa may show partial villous atrophy, but the changes tend to be milder than in coeliac disease.[19]
Immunological studies revealed findings that are similar to those of coeliac disease in terms of autoantigens. The main autoantigen of dermatitis herpetiformis is epidermal transglutaminase (eTG), a cytosolic enzyme involved in cell envelope formation during keratinocyte differentiation.[15]
Various research studies have pointed out different potential factors that may play a larger or smaller role in the development of dermatitis herpetiformis. The fact that eTG has been found in precipitates of skin-bound IgA from skin affected by this condition has been used to conclude that dermatitis herpetiformis may be caused by a deposition of both IgA and eTG within the dermis. It is estimated that these deposits may resorb after 10 years of following a gluten-free diet. Moreover, it is suggested that this condition is closely linked to genetics. This theory is based on the arguments that individuals with a family history of gluten sensitivity that still consume foods containing gluten are more likely to develop the condition as a result of the formation of antibodies to gluten. These antibodies cross-react with eTG, and IgA/eTG complexes deposit within the papillary dermis to cause the lesions of dermatitis herpetiformis. These IgA deposits can disappear after long-term (up to 10 years) avoidance of dietary gluten.[15] Genetics are thought to play an important role in the development of the condition, as well as environmental factors.[citation needed] Monozygotic twins, for example, have an increased risk of developing dermatitis herpetiformis.[citation needed] It has been shown that androgen levels may affect the immune system in terms of suppression, leading to a decreased immunity. Some specialists argue that low levels of androgens may trigger this condition.[citation needed]
Complications
DH is an autoimmune disease, and patients with DH are more likely than others to have thyroid problems[8][17] and intestinal lymphoma.[8][9][11]
Dermatitis herpetiformis does not usually cause complications on its own, without being associated with another condition. Complications from this condition, however, arise from the autoimmune character of the disease, as an over-reacting immune system is a sign that something does not work well and might cause problems to other parts of the body that do not necessarily involve the digestive system.[20]
Gluten intolerance and the body's reaction to it make the disease more worrying in what concerns the possible complications. This means that complications that may arise from dermatitis herpetiformis are the same as those resulting from coeliac disease, which include osteoporosis, certain kinds of gut cancer, and an increased risk of other autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease.[21]
The risks of developing complications from dermatitis herpetiformis decrease significantly if the patients follow a gluten-free diet. The disease has been associated with auto-immune thyroid disease, insulin-dependent diabetes, lupus erythematosus, Sjögren's syndrome, sarcoidosis, and vitiligo or alopecia areata.[22]
Notable cases
It has been suggested that French revolutionary Jean-Paul Marat suffered from DH,[23] leading him to spend much of his time in, and even work from, a bathtub filled with an herbal mixture that he used to calm the sores.
See also
References
- ^ a b Freedberg, et al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-138076-0.
- ^ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ Singal A, Bhattacharya SN, Baruah MC (2002). "Dermatitis herpetiformis and rheumatoid arthritis". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 68 (4): 229–30. PMID 17656946. http://www.ijdvl.com/article.asp?issn=0378-6323;year=2002;volume=68;issue=4;spage=229;epage=230;aulast=Singal.
- ^ a b c d e "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". American Osteopathic College of Dermatology. http://www.aocd.org/skin/dermatologic_diseases/dermatitis_herpeti.html.
- ^ a b "What Is Dermatitis Herpetiformis?". http://www.dermatitisherpetiformis.org.uk/whatisdh.html.
- ^ Marietta EV, Camilleri MJ, Castro LA, Krause PK, Pittelkow MR, Murray JA (February 2008). "Transglutaminase autoantibodies in dermatitis herpetiformis and coeliac sprue". J. Invest. Dermatol. 128 (2): 332–5. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5701041. PMID 17762854.
- ^ Miller JL, Collins K, Sams HH, Boyd A (2007-05-18). "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". emedicine from WebMD. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1062640-overview.
- ^ a b c d e f Van L, Browning JC, Krishnan RS, Kenner-Bell BM, Hsu S (2008). "Dermatitis herpetiformis: Potential for confusion with linear IgA bullous dermatosis on direct immunofluorescence". Dermatology Online Journal 14 (1): 21. PMID 18319038. http://dermatology.cdlib.org/141/correspondence/dh/van.html.
- ^ a b "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". Patient UK. http://www.patient.co.uk/doctor/Dermatitis-Herpetiformis.htm.
- ^ a b "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse. http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/celiac/.
- ^ a b Turchin I, Barankin B (2005). "Dermatitis herpetiformis and gluten-free diet". Dermatology Online Journal 11 (1): 6. PMID 15748547. http://dermatology.cdlib.org/111/reviews/herpetiformis/barankin.html.
- ^ a b c d "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". The HealthScout Network. http://www.healthscout.com/ency/1/646/main.html.
- ^ a b "Detecting Celiac Disease in Your Patients". American Family Physician (American Academy of Family Physicians). http://www.aafp.org/afp/980301ap/pruessn.html.
- ^ "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". http://gluten-intolerance-symptoms.com/dermatitis-herpetiformis/. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ a b c "Dermatitis Herpetiformis". http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1062640-overview. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ "What’s The Diagnosis #9". Emergency Physicians Monthly. http://www.epmonthly.com/whitecoat/2010/04/whats-the-diagnosis-9/. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ a b c d e "Dermatitis herpetiformis". DermNet NZ. http://dermnetnz.org/immune/dermatitis-herpetiformis.html.
- ^ "Dapsone". Dermatology Online Journal. http://dermatology.cdlib.org/DOJvol8num1/reviews/dapsone/wolf.html.
- ^ "How to get rid of Dermatitis herpetiformis". http://www.beauty-cosmetic-guide.com/dermatitis-herpetiformis.htm. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ "Herpetiformis Dermatitis Effects And Complications". http://www.herpetiformisdermatitis.com/effects-complications.html. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ "Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH)". http://www.coeliac.org.uk/coeliac-disease/what-is-coeliac-disease/dermatitis-herpetiformis-dh. Retrieved 2010-06-23.
- ^ Reunala, T; Collin, P. "Diseases associated with dermatitis herpetiformis". The British journal of dermatology 136 (3): 315–8. PMID 9115907.
- ^ Jelinek JE (1979). "Jean-Paul Marat: The differential diagnosis of his skin disease". American Journal of Dermatopathology 1 (3): 251–2. PMID 396805.
External links
- Pictures: Elbow Arms
- Pictures: DermNet NZ
- Pictures: The Gastrolab Image Library
- Pictures: mediscan
- DermNet immune/dermatitis-herpetiformis
- A collection of articles from Celiac.com
- Journal of Investigative Dermatology
- Medline Plus
Vesiculobullous disease (L10–L14, 694) Acantholysis
(epidermis)Pemphigus vulgaris: Pemphigus vegetans (Pemphigus vegetans of Hallopeau, Pemphigus vegetans of Neumann)Pemphigus foliaceus: Pemphigus erythematosus · Endemic pemphigusParaneoplastic pemphigusIgA pemphigus (Subcorneal pustular dermatosis, Intraepidermal neutrophilic IgA dermatosis)OtherPemphigoid
(dermis)IgG: Bullous pemphigoid · Cicatricial pemphigoid (Localized cicatricial pemphigoid) · Gestational pemphigoid · Pemphigoid nodularis · Epidermolysis bullosa acquisitaIgA: Linear IgA bullous dermatosis (Childhood linear IgA disease, Adult linear IgA disease)Other bullous Dermatitis herpetiformisIn diseases
classified elsewhereGluten sensitivity Conditions general: Wheat allergy · Oat sensitivity
nervous system: GS idiopathic neuropathies
digestive system: Coeliac disease · GSE associated conditions
integumentary system: Dermatitis herpetiformisAntibodies HLA-DQ Other Categories:- Chronic blistering cutaneous conditions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.