- Morphea
-
For the drug, see Morphine.
Morphea Classification and external resources ICD-10 L94.0 ICD-9 701.0 DiseasesDB 8351 eMedicine derm/272 MeSH D012594 Morphea is a medical term for localized scleroderma.[1] The disease involves isolated patches of hardened skin - there generally is no internal organ involvement.[2]
Contents
Background, nomenclature, classification & codification
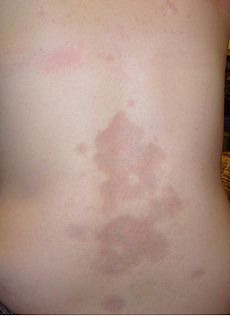
Morphea, also known as localized scleroderma, is a thickening and hardening of the skin and subcutaneous tissues from excessive collagen deposition. Morphea includes specific conditions ranging from very small plaques only involving the skin to widespread disease causing functional and cosmetic deformities. Morphea discriminates from systemic sclerosis by its supposed lack of internal organ involvement. The most widely used classification divides morphea into five general subtypes: plaque morphea, generalized morphea, linear scleroderma, bullous morphea, and deep morphea.[3] This classification scheme does not include the mixed form of morphea in which different morphologies of skin lesions are present in the same individual. Up to 15% of morphea patients may fall into this previously unrecognized category.[4]
Epidemiology
Morphea is an uncommon condition that is thought to affect .02 to .04 in 100,000 people.[5] Adequate studies on the incidence and prevalence have not been performed. Morphea also may be under-reported as physicians may be unaware of this disorder and smaller morphea plaques may be less often referred to a dermatologist or rheumatologist. As in many other connective tissue or autoimmune disorders, morphea mainly involves women with a F:M ratio of 3:1.[6]
Etiology
Physicians and scientists do not know what causes morphea. Case reports and observational studies suggest there is a higher frequency of family history of autoimmune diseases in patients with morphea.[4] Tests for autoantibodies associated with morphea have shown results in higher frequencies of anti-histone and anti-topoisomerase IIa antibodies.[7] Case reports of morphea co-existing with other systemic autoimmune diseases such as primary biliary cirrhosis, vitiligo, and systemic lupus erythematosus lend support to morphea as an autoimmune disease.[8][9][10]
Treatment
Throughout the years, many different treatments have been tried for morphea including topical, intra-lesional, and systemic corticosteroids. Antimalarials such as hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine have been used. Other immunomodulators such as methotrexate, topical tacrolimus, and penicillamine have been tried. Ultraviolet A (UVA) light, with or without psoralens have also been tried. UVA-1, a more specific wavelength of UVA light, is able to penetrate the deeper portions of the skin and thus, thought to soften the plaques in morphea by acting in two fashions:
- 1) by causing a systemic immunosuppression from UV light.
- 2) by inducing enzymes that naturally degrade the collagen matrix in the skin as part of natural sun-aging of the skin.
As with all of these treatments for morphea, the difficulty in assessing outcomes in an objective way has limited the interpretation of most studies involving these treatment modalities.
See also
References
- ^ "morphea" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Morpea CNN.com, (May 05, 2006).
- ^ Peterson LS, Nelson AM, Su WP (1995). "Classification of morphea (localized scleroderma)". Mayo Clin. Proc. 70 (11): 1068–76. doi:10.4065/70.11.1068. PMID 7475336.
- ^ a b Zulian F, Athreya BH, Laxer R, et al. (2006). "Juvenile localized scleroderma: clinical and epidemiological features in 750 children. An international study". Rheumatology (Oxford) 45 (5): 614–20. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei251. PMID 16368732.
- ^ Peterson LS, Nelson AM, Su WP, Mason T, O'Fallon WM, Gabriel SE (1997). "The epidemiology of morphea (localized scleroderma) in Olmsted County 1960-1993". J. Rheumatol. 24 (1): 73–80. PMID 9002014.
- ^ Laxer RM, Zulian F (2006). "Localized scleroderma". Curr Opin Rheumatol 18 (6): 606–13. doi:10.1097/01.bor.0000245727.40630.c3. PMID 17053506.
- ^ Hayakawa I, Hasegawa M, Takehara K, Sato S (2004). "Anti-DNA topoisomerase IIalpha autoantibodies in localized scleroderma". Arthritis Rheum. 50 (1): 227–32. doi:10.1002/art.11432. PMID 14730620.
- ^ Majeed M, Al-Mayouf SM, Al-Sabban E, Bahabri S (2000). "Coexistent linear scleroderma and juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus". Pediatr Dermatol 17 (6): 456–9. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1470.2000.01820.x. PMID 11123778. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0736-8046&date=2000&volume=17&issue=6&spage=456.
- ^ Bonifati C, Impara G, Morrone A, Pietrangeli A, Carducci M (2006). "Simultaneous occurrence of linear scleroderma and homolateral segmental vitiligo". J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 20 (1): 63–5. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01336.x. PMID 16405610.
- ^ González-López MA, Drake M, González-Vela MC, Armesto S, Llaca HF, Val-Bernal JF (2006). "Generalized morphea and primary biliary cirrhosis coexisting in a male patient". J. Dermatol. 33 (10): 709–13. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2006.00165.x. PMID 17040502.
External links
- UT-Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas Morphea Registry
- Scleroderma Foundation
- Scleroderma Society of Ontario
- International Scleroderma Network
- The Scleroderma Research Foundation
- UK Scleroderma Society
Cutaneous keratosis, ulcer, atrophy, and necrobiosis (L82–L94, 700–701.5) Epidermal thickening keratoderma: Keratoderma climactericum • Paraneoplastic keratoderma (Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex ) • Aquagenic keratoderma · Drug-induced keratoderma · Paraneoplastic keratoderma • psoriasis (Keratoderma blennorrhagica)
keratosis: Seborrheic keratosis (Clonal seborrheic keratosis · Common seborrheic keratosis · Irritated seborrheic keratosis · Seborrheic keratosis with squamous atypia · Reticulated seborrheic keratosis · Dermatosis papulosa nigra) • Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases
other hyperkeratosis: Acanthosis nigricans (Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis) · Callus • Ichthyosis acquisita · Arsenical keratosis · Chronic scar keratosis · Hyperkeratosis lenticularis perstans · Hydrocarbon keratosis · Hyperkeratosis of the nipple and areola · Inverted follicular keratosis · Lichenoid keratosis · Multiple minute digitate hyperkeratosis · PUVA keratosis · Reactional keratosis · Stucco keratosis · Thermal keratosis · Viral keratosis · Warty dyskeratoma · Waxy keratosis of childhood
other hypertrophy: Keloid · Hypertrophic scar • Cutis verticis gyrata ·Necrobiosis/granuloma Granuloma annulare (Perforating, Generalized, Subcutaneous, Granuloma annulare in HIV disease, Localized granuloma annulare, Patch-type granuloma annulare) · Necrobiosis lipoidica · Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma · Granuloma multiforme · Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma · Palisaded neutrophilic and granulomatous dermatitis · Rheumatoid nodulosis · Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis/Interstitial granulomatous drug reactionForeign body granulomaBeryllium granuloma • Mercury granuloma • Silica granuloma • Silicone granuloma • Zirconium granuloma • Soot tattoo • Tattoo • Carbon stainOther/ungroupedeosinophilic dermatosis (Granuloma faciale)Dermis/
localized CTDCutaneous lupus
erythematosusScleroderma/
MorpheaLocalized scleroderma (Localized morphea, Morphea–lichen sclerosus et atrophicus overlap, Generalized morphea, Atrophoderma of Pasini and Pierini, Pansclerotic morphea, Morphea profunda, Linear scleroderma)Atrophic/
atrophodermaLichen sclerosus · Anetoderma (Schweninger–Buzzi anetoderma, Jadassohn–Pellizzari anetoderma) · Atrophoderma of Pasini and Pierini · Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans · Semicircular lipoatrophy · Follicular atrophoderma · Linear atrophoderma of MoulinKyrle disease · Reactive perforating collagenosis · Elastosis perforans serpiginosa · Perforating folliculitis · Acquired perforating dermatosisOtherCategories:- Autoimmune diseases
- Rheumatology
- Connective tissue diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.