- Clotrimazole
-
Clotrimazole 

Systematic (IUPAC) name 1-[(2-chlorophenyl)(diphenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazole Clinical data Trade names Lotriminaf, Mycelex AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682753 Pregnancy cat. A(AU) C (oral) & B (topical) (US) Legal status P (UK) Routes topical Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Poorly and erratically absorbed orally Protein binding 90% Metabolism hepatic Half-life 2 hours Identifiers CAS number 23593-75-1 
ATC code A01AB18 D01AC01 G01AF02 QJ02AB90 PubChem CID 2812 DrugBank APRD00244 ChemSpider 2710 
UNII G07GZ97H65 
KEGG D00282 
ChEBI CHEBI:3764 
ChEMBL CHEMBL104 
Chemical data Formula C22H17ClN2 Mol. mass 344.837 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Clotrimazole (brand name Canesten or Lotrimin) is an antifungal medication commonly used in the treatment of fungal infections (of both humans and other animals) such as vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and ringworm. It is also used to treat athlete's foot and jock itch.
Contents
Medical uses
It is commonly available as an over-the-counter substance in various dosage forms, such as a cream, and also (especially in the case of ear infection) as a combination medicine. It is also available as a troche (prescription only). For ear infection, it is often applied in liquid form, as ear drops. Fungal infections can be slow to clear up, so the usual course for an anti-fungal agent is, in general, longer than the typical 3–7 days of an antibiotic. Clotrimazole is also commonly found in conjunction with Betamethasone, known as Lotriderm, to add steroid properties.[1]
Method of action
Clotrimazole alters the permeability of the fungal cell wall and inhibits the activity of enzymes within the cell. This leads eventually to the cell's death. It does not appreciably spread through the user's body but remains at the point of application. [2]
Drug interactions
Potential for drug interactions with clotrimazole oral exists, as it is a potent, specific inhibitor of cytochrome P450 oxidase and may alter the metabolism of other drugs.
Side-effects
Side effects include skin rash, hives, blistering, burning, itching, peeling, redness, stinging, swelling, or other sign of skin irritation.[3]
Production
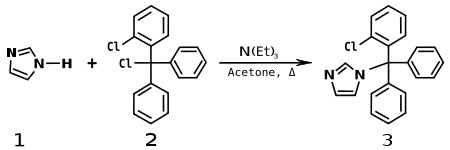
This compound (3) is produced by alkylating imidazole (1) with o-chlorotrityl chloride (2) in acetone, with triethylamine as the base.[4]
Environmental impact
Some research suggests that, in combination with other commonly used chemicals, clotrimazole has negative effects on the ocean environment, in particular microalgae.[5]
References
- ^ http://www.rxmed.com/b.main/b2.pharmaceutical/b2.1.monographs/CPS-%20Monographs/CPS-%20%28General%20Monographs-%20L%29/LOTRIDERM.html
- ^ "Clotrimazole". Fungal Guide .ca. Vancouver , B.C. Canada. http://www.fungalguide.ca/treatments/clotrimazole.html. Retrieved 15 February 2011.
- ^ Canesten Topical consumer information from Drugs.com
- ^ OSPAR Commission: Hazardous Substances Series: OSPAR background document on clotrimazole. OSPAR Publication 2005/199, 2005, ISBN 1-904426-38-7 (pdf, engl.)
- ^ Drug used to treat skin conditions is a marine pollutant
External links
Stomatological preparations (A01) Caries prophylactic agents Anti-infectives and antiseptics Amphotericin B • Benzoxonium chloride • Chlorhexidine • Chlortetracycline • Clotrimazole • Domiphen bromide • Doxycycline • Eugenol • Hexetidine • Hydrogen peroxide • Mepartricin • Metronidazole • Miconazole • Minocycline • Natamycin • Neomycin • Oxyquinoline • Polynoxylin • Sodium perborate • Tetracycline • Tibezonium iodideCorticosteroids (Glucocorticoids) Other Antifungals (D01 and J02) Wall/
membraneErgosterol
inhibitorstopical: Bifonazole, Clomidazole, Clotrimazole#, Croconazole, Econazole, Fenticonazole, Ketoconazole, Isoconazole, Miconazole#, Neticonazole, Oxiconazole, Sertaconazole, Sulconazole, Tioconazoletopical: (Fluconazole#, Fosfluconazole)
systemic: (Fluconazole, Hexaconazole, Itraconazole, Posaconazole, Voriconazole)topical: Thiabendazoleβ-glucan synthase
inhibitorsIntracellular Pyrimidine analogues/
Thymidylate synthase inhibitorsOthers Bromochlorosalicylanilide • Methylrosaniline • Tribromometacresol • Undecylenic acid • Polynoxylin • Chlorophetanol • Chlorphenesin • Ticlatone • Sulbentine • Ethyl hydroxybenzoate • Haloprogin • Salicylic acid • Selenium sulfide# • Ciclopirox • Amorolfine • Dimazole • Tolnaftate • Tolciclate • Sodium thiosulfate# • Whitfield's ointment# • Potassium iodide#
Tea tree oil • citronella oil • lemon grass • orange oil • patchouli • lemon myrtle
PCP: Pentamidine • Dapsone • AtovaquoneGynecological anti-infectives and antiseptics (G01) Antibiotics Arsenic compounds Quinoline derivatives Organic acids Sulfonamides SulfatolamideImidazole derivatives Metronidazole • Clotrimazole • Miconazole • Econazole • Ornidazole • Isoconazole • Tioconazole • Ketoconazole • Fenticonazole • Azanidazole • Propenidazole • Butoconazole • Omoconazole • Oxiconazole • FlutrimazoleTriazole derivatives Other Clodantoin • Inosine • Policresulen • Nifuratel • Furazolidone • Methylrosaniline • Povidone-iodine • Ciclopirox • Protiofate • Lactobacillus fermentum • Copper usnate
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.