- Azole
-
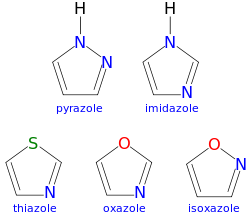
An azole is a class of five-membered nitrogen heterocyclic ring compounds containing at least one other non-carbon atom of either nitrogen, sulfur, or oxygen.[1] The parent compounds are aromatic and have two double bonds; there are successively reduced analogs (azolines and azolidines) with fewer. One, and only one, lone pair of electrons from each heteroatom in the ring is part of the aromatic bonding in an azole. Names of azoles maintain the prefix upon reduction (e.g., pyrazoline, pyrazolidine). The numbering of ring atoms in azoles starts with the heteroatom that is not part of a double bond, and then proceeds towards the other heteroatom.
(Six-membered aromatic heterocyclic systems with two nitrogens include pyrimidine and purine, important biochemicals.)
Contents
Compound classes
The azoles include:
- 1 nitrogen (but it only includes one nitrogen and no other heteroatom)
- 2 or more nitrogen atoms
- 1 nitrogen atom and 1 sulfur atom
A "dioxole" is a similar compound with two oxygen atoms in a five membered ring. Dioxolane is a derivative of dioxole.
Uses
Many azoles are used as antifungal drugs, inhibiting the fungal enzyme 14α-demethylase which produces ergosterol (an important component of the fungal plasma membrane).
Antifungals
- Clotrimazole
- Posaconazole
- Ravuconazole
- Econazole
- Ketoconazole
- Voriconazole
Triazole-based
Treatment for hyperthyrodism/thyrotoxicosis
Precautions
Some people are allergic to azole(s).[citation needed]
Some azole drugs have adverse side-effects.[2]
Some azole drugs may disrupt estrogen production in pregnancy, affecting pregnancy outcome.[3]
References
This article incorporates material from the Citizendium article "Azole", which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License but not under the GFDL.
- ^ Eicher, T.; Hauptmann, S. (June 2003). The Chemistry of Heterocycles: Structure, Reactions, Synthesis, and Applications (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 3527307206.
- ^ Stein GE, Christensen S, Mummaw N (June 1991). "Comparative study of fluconazole and clotrimazole in the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis". DICP 25 (6): 582–5. PMID 1877264. http://www.theannals.com/cgi/content/abstract/25/6/582. Retrieved 2009-11-11.
- ^ Kragie L, Turner SD, Patten CJ, Crespi CL, Stresser DM (August 2002). "Assessing pregnancy risks of azole antifungals using a high throughput aromatase inhibition assay". Endocr. Res. 28 (3): 129–40. doi:10.1081/ERC-120015045. PMID 12489563.
External links
Categories:- Azoles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.