- Cyclic compound
-
In chemistry, a cyclic compound is a compound in which a series of atoms is connected to form a loop or ring.[1] While the vast majority of cyclic compounds are organic, a few inorganic substances form cyclic compounds as well, including sulfur, silanes, phosphanes, phosphoric acid, and triboric acid. Cyclic compounds may or may not be aromatic. Benzene is a well known example. The term "polycyclic" is used when more than one ring is formed in a single molecule for instance in naphthalene, and the term macrocycle is used for a ring containing more than a dozen atoms.
-
Cycloheptane, a non-aromatic cyclic compound.
-
Benzene, a cyclic compound.
-
Naphthalene, a polycyclic compound.
-
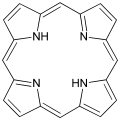
Porphyrin, a macrocyclic compound.
-

Pentazole, an inorganic cyclic compound.
Alicyclic compound are named according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature by attaching the prefix cyclo- to the name of the corresponding open chain hydrocarbon possessing the same number of carbon atoms. The common names resemble the IUPAC names. For example: Cyclo pantane, cyclo butane etc....
Contents
Ring-closing & opening reactions
Related concepts in organic chemistry are so-called ring-closing reactions in which a cyclic compound is formed and ring-opening reactions in which rings are opened.
Examples of ring-closing reactions:
- Ring-closing metathesis
- Nazarov cyclization reaction
- Ruzicka large ring synthesis
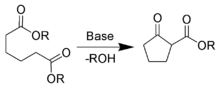
- Dieckmann condensation
- Wenker synthesis
- Radical cyclization
Example of ring-opening reactions:
- A general type of polymerization reaction: Ring-opening polymerization
- Ring opening metathesis polymerisation
See also
- open-chain compound
- Ring expansion and ring contraction
- Macrocycle
- Effective molarity
External links
References
- ^ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (3rd ed.), New York: Wiley, ISBN 0-471-85472-7
Categories:- Molecular geometry
- Chemical bond properties
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.