- Chlortetracycline
-
Chlortetracycline 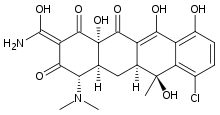
Systematic (IUPAC) name (4S,4aS,5aS,6S,12aS,Z)-2-[amino(hydroxy)methylene]-7-chloro-4-(dimethylamino)-6,10,11,12a-tetrahydroxy-6-methyl-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydrotetracene-1,3,12(2H,4H,12aH)-trione Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes Oral, IV, topical Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 30% Protein binding 50 to 55% Metabolism Hepatic (75%) Half-life 5.6 to 9 hours Excretion Renal and biliary Identifiers CAS number 57-62-5 
ATC code A01AB21 D06AA02 J01AA03 S01AA02 QJ51AA03 ChemSpider 10469370 
UNII WCK1KIQ23Q 
KEGG D07689 
ChEMBL CHEMBL456066 
Chemical data Formula C22H23ClN2O8 Mol. mass 478.88 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Chlortetracycline (trade name Aureomycin, Lederle) is a tetracycline antibiotic, and was the first tetracycline to be identified. It was discovered in 1945 by Dr. Benjamin Duggar working at Lederle Laboratories. Duggar identified the antibiotic as the product of a actinomycete he cultured from a soil sample collected from Sanborn Field at the University of Missouri.[1] The organism was named Streptomyces aureofaciens and the isolated drug, Aureomycin, because of their golden color.
In veterinary medicine, chlortetracycline is commonly used to treat conjunctivitis in cats.[2]
References
- ^ Jukes, Thomas H. Some historical notes on chlortetracycline. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 7(5):702-707 (1985).
- ^ Merck Veterinary Manual. http://merckvetmanual.com/mvm/index.jsp?cfile=htm/bc/30200.htm.
Stomatological preparations (A01) Caries prophylactic agents Anti-infectives and antiseptics Amphotericin B • Benzoxonium chloride • Chlorhexidine • Chlortetracycline • Clotrimazole • Domiphen bromide • Doxycycline • Eugenol • Hexetidine • Hydrogen peroxide • Mepartricin • Metronidazole • Miconazole • Minocycline • Natamycin • Neomycin • Oxyquinoline • Polynoxylin • Sodium perborate • Tetracycline • Tibezonium iodideCorticosteroids (Glucocorticoids) Other Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use (D06) Antibiotics Tetracycline and derivativesOthersChemotherapeutics Aciclovir • Penciclovir • Idoxuridine • Edoxudine
Imiquimod/Resiquimod • Podophyllotoxin
Docosanol • Tromantadine • Inosine • Lysozyme • IbacitabineOtherAntibacterials: protein synthesis inhibitors (J01A, J01B, J01F, J01G, QJ01XQ) 30S -mycin (Streptomyces)Neomycin# (Framycetin, Paromomycin, Ribostamycin)
Kanamycin# (Amikacin, Arbekacin, Bekanamycin, Dibekacin, Tobramycin)
Paromomycin-micin (Micromonospora)TetracyclinesDoxycycline# •Chlortetracycline • Clomocycline • Demeclocycline • Lymecycline • Meclocycline • Metacycline • Minocycline • Oxytetracycline • Penimepicycline • Rolitetracycline • Tetracycline50S Linezolid • Torezolid • Eperezolid • Posizolid • RadezolidPleuromutilinsRetapamulin • Tiamulin • ValnemulinErythromycin# • Azithromycin# • Spiramycin • Midecamycin • Oleandomycin • Roxithromycin • Josamycin • Troleandomycin • Clarithromycin • Miocamycin • Rokitamycin • Dirithromycin • Flurithromycin • Ketolide (Telithromycin, Cethromycin, Solithromycin)EF-G Steroid antibacterials
This systemic antibacterial-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This dermatologic drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
