- Thiamphenicol
-
Thiamphenicol 
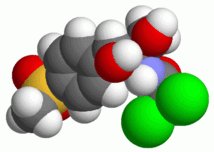
Systematic (IUPAC) name 2,2-dichloro-N-{(1R,2R)-2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)-2-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]ethyl}acetamide Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status none Routes IV, IM, oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability ? Metabolism hepatic Half-life 5.0 hours Excretion renal Identifiers CAS number 15318-45-3 
ATC code J01BA02 QJ51BA02 PubChem CID 27200 DrugBank DB08621 ChemSpider 25315 
UNII FLQ7571NPM 
KEGG D01407 
ChEBI CHEBI:32215 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1236282 
Chemical data Formula C12H15Cl2NO5S Mol. mass 356.223 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Thiamphenicol (also known as thiophenicol and dextrosulphenidol) is an antibiotic. It is the methyl-sulfonyl analogue of chloramphenicol and has a similar spectrum of activity, but is 2.5 to 5 times as potent. Like chloramphenicol, it is insoluble in water, but highly soluble in lipids. It is used in many countries as a veterinary antibiotic, but is available in China and Italy for use in humans. Its main advantage over chloramphenicol is that it has never been associated with aplastic anaemia.
Thiamphenicol is also widely used in Brazil, particularly for the treatment of sexually transmitted infections and pelvic inflammatory disease.[1]
References
External links
- Overview at World Health Organization - Food and Agriculture Organization
- Raymond J, Boutros N, Bergeret M (2004). "Role of thiamphenicol in the treatment of community-acquired lung infections". Med Trop (Mars) 64 (1): 33–8. PMID 15224555.
- Marchese A, Debbia E, Tonoli E, Gualco L, Schito A (2002). "In vitro activity of thiamphenicol against multiresistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus in Italy.". J Chemother 14 (6): 554–61. PMID 12583545.
Antibacterials: protein synthesis inhibitors (J01A, J01B, J01F, J01G, QJ01XQ) 30S -mycin (Streptomyces)Neomycin# (Framycetin, Paromomycin, Ribostamycin)
Kanamycin# (Amikacin, Arbekacin, Bekanamycin, Dibekacin, Tobramycin)
Paromomycin-micin (Micromonospora)Tetracyclines50S Linezolid • Torezolid • Eperezolid • Posizolid • RadezolidPleuromutilinsRetapamulin • Tiamulin • ValnemulinErythromycin# • Azithromycin# • Spiramycin • Midecamycin • Oleandomycin • Roxithromycin • Josamycin • Troleandomycin • Clarithromycin • Miocamycin • Rokitamycin • Dirithromycin • Flurithromycin • Ketolide (Telithromycin, Cethromycin, Solithromycin)EF-G Steroid antibacterials
This systemic antibacterial-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
