- Tobramycin
-
Tobramycin 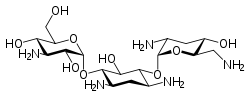
Systematic (IUPAC) name (2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4-amino-2-{[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-{[(2R,3R,5S,6R)-3-amino-6-(aminomethyl)-5-hydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy}-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,5-diol Clinical data Trade names Tobrex AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682660 Pregnancy cat. D (Injection, Inhalation); B (Ophthalmic) (US) Legal status ? Routes IV, IM, inhalation, ophthalmic Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding < 30% Identifiers CAS number 32986-56-4 
ATC code J01GB01 S01AA12 PubChem CID 36294 DrugBank APRD00582 ChemSpider 33377 
UNII VZ8RRZ51VK 
KEGG D00063 
ChEBI CHEBI:28864 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1747 
Chemical data Formula C18H37N5O9 Mol. mass 467.515 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat various types of bacterial infections, particularly Gram-negative infections.
Contents
Mechanism of action
Tobramycin works by binding to a site on the bacterial 30S and 50S ribosome, preventing formation of the 70S complex. As a result, mRNA cannot be translated into protein and cell death ensues. Tobramycin is preferred over gentamicin for Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia due to better lung penetration and bactericidal activity.
Administration
Like all aminoglycosides, tobramycin does not pass the gastro-intestinal tract, so for systemic use it can only be given intravenously, intramuscularly, eyedrops (commonly with Dextramethsone), or it can be administered and inhaled via nebuliser. The formulation for injection is branded Nebcin. Patients with cystic fibrosis will often take an inhalational (nebulised) form (Tobi) for suppression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Tobramycin is also combined with dexamethasone as an ophthalmic solution (TobraDex).
Bausch & Lomb Pharmaceuticals produces a sterile tobramycin solution (eye-drops) with a tobramycin concentration of 0.3%, which is available by prescription only in the United States and Canada. (In some countries, such as Italy, it is available over the counter.) It is mixed with 0.01% benzalkonium chloride as a preservative. These concentrations result in 3 mg per ml and 0.1 mg per ml, respectively.
A proprietary formulation of micronized, nebulized tobramycin has been tested as a treatment for bacterial sinusitis.[1]
Side effects
Like other aminoglycosides, tobramycin can cause deafness or a loss of equilibrioception (vertigo) in genetically susceptible individuals. These individuals have a normally harmless mutation in their DNA, that allows the tobramycin to affect their cells. The cells of the ear are particularly sensitive to this.
Tobramycin can also be highly toxic to the kidneys, particularly if multiple doses accumulate over a course of treatment.
For these reasons, when tobramycin is given parenterally, it is usually dosed by body weight. Various formulae exist for calculating tobramycin dosage. Also serum levels of tobramycin are monitored during treatment.
References
- ^ "Nebulized Tobramycin in treating bacterial Sinusitis" (Press release). July 22, 2008. http://www.mmdnewswire.com/nebulized-tobramycin-in-treating-bacterial-sinusitis-3630.html. Retrieved 2009-12-06.
Antibacterials: protein synthesis inhibitors (J01A, J01B, J01F, J01G, QJ01XQ) 30S -mycin (Streptomyces)Neomycin# (Framycetin, Paromomycin, Ribostamycin)
Kanamycin# (Amikacin, Arbekacin, Bekanamycin, Dibekacin, Tobramycin)
Paromomycin-micin (Micromonospora)Tetracyclines50S Linezolid • Torezolid • Eperezolid • Posizolid • RadezolidPleuromutilinsRetapamulin • Tiamulin • ValnemulinErythromycin# • Azithromycin# • Spiramycin • Midecamycin • Oleandomycin • Roxithromycin • Josamycin • Troleandomycin • Clarithromycin • Miocamycin • Rokitamycin • Dirithromycin • Flurithromycin • Ketolide (Telithromycin, Cethromycin, Solithromycin)EF-G Steroid antibacterialsCategories:- Aminoglycoside antibiotics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
