- Tigecycline
-
Tigecycline 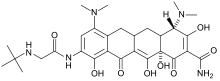
Systematic (IUPAC) name N-[(5aR,6aS,7S,9Z,10aS)-9-[amino(hydroxy)methylidene]-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,10a,12-trihydroxy-8,10,11-trioxo-5,5a,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a,11-decahydrotetracen-2-yl]-2-(tert-butylamino)acetamide Clinical data Trade names Tygacil AHFS/Drugs.com monograph Pregnancy cat. D(AU) D(US) Legal status Prescription Only (S4) (AU) ℞-only (US) Routes IV only Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability NA Protein binding 71-89% Metabolism not metabolised Half-life 42.4 hours Excretion 59% biliary, 33% renal Identifiers CAS number 220620-09-7 
ATC code J01AA12 PubChem CID 5282044 DrugBank APRD01307 ChemSpider 10482314 
UNII 70JE2N95KR 
KEGG D01079 
ChEBI CHEBI:149836 
ChEMBL CHEMBL376140 
Synonyms N-[(5aR,6aS,7S,9Z,10aS)-9-(amino-hydroxy-methylidene)-4,7-bis(dimethylamino)-1,10a,12-trihydroxy-8,10,11-trioxo-5a,6,6a,7-tetrahydro-5H-tetracen-2-yl]-2-(tert-butylamino)acetamide Chemical data Formula C29H39N5O8 Mol. mass 585.65 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Tigecycline (INN) (
 /ˌtaɪɡəˈsaɪkliːn/) is a glycylcycline antibiotic[1][2] developed by Francis Tally[3] and marketed by Wyeth under the brand name Tygacil. It was given a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) fast-track approval and was approved on June 17, 2005. It was developed in response to the growing prevalence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii. The New Delhi metallo-β-Lactamase multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae has also shown susceptibility to tigecycline.[4]
/ˌtaɪɡəˈsaɪkliːn/) is a glycylcycline antibiotic[1][2] developed by Francis Tally[3] and marketed by Wyeth under the brand name Tygacil. It was given a U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) fast-track approval and was approved on June 17, 2005. It was developed in response to the growing prevalence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii. The New Delhi metallo-β-Lactamase multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae has also shown susceptibility to tigecycline.[4]Contents
Structure
This antibiotic is the first clinically-available drug in a new class of antibiotics called the glycylcyclines. It is structurally similar to the tetracyclines in that it contains a central four-ring carbocyclic skeleton and is actually a derivative of minocycline. Tigecycline has a substitution at the D-9 position which is believed to confer broad spectrum activity.
Mechanism of action
Tigecycline is bacteriostatic and is a protein synthesis inhibitor by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit of bacteria and thereby blocking entry of Aminoacyl-tRNA into the A site of the ribosome during prokaryotic translation.[5]
Indications
Tigecycline is given intravenously and has activity against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial pathogens, many of which are resistant to existing antibiotics. Tigecycline successfully completed phase III trials in which it was at least equal to intravenous vancomycin and aztreonam to treat complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSI), and to intravenous imipenem and cilastatin to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI).[6] Tigecycline is active against many Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria and anaerobes – including activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae (with MIC values reported at 2mcg/mL) and multi-drug resistant strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. It has no activity against Pseudomonas spp. or Proteus spp. The drug is licenced for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections as well as intra-abdominal infections.
Dosing
Tigecycline is given by slow intravenous infusion (30 to 60 minutes). A single dose of 100 mg is given first, followed by 50 mg every twelve hours after that. Patients with impaired liver function need to be given a lower dose. No adjustment is needed for patients with impaired kidney function. It is not licensed for use in children. There is no oral form available.
Side effects
Tigecycline has similar side effects to the tetracyclines. The most common side effects of tigecycline are diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. Nausea and vomiting is mild or moderate and usually occurs during the first two days of therapy. Other side effects include pain at the injection site, swelling and irritation; increased or decreased heart rate and infections. Also avoid use in children and pregnancy, due to its effects on teeth and bone. As with other antibiotics, overgrowth of organisms that are not susceptible to tigecycline can occur.
Tigecycline showed an increased mortality in patients treated for hospital-acquired pneumonia, especially ventilator-associated pneumonia, but also in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections, complicated intra-abdominal infections and diabetic foot infection.[7]
Other uses
It may have potential for use in acute myeloid leukaemia.[8]
Synonyms
- GAR-936[9]
- Tygacil
References
- ^ Rose W, Rybak M (2006). "Tigecycline: first of a new class of antimicrobial agents.". Pharmacotherapy 26 (8): 1099–110. doi:10.1592/phco.26.8.1099. PMID 16863487.
- ^ Kasbekar N (2006). "Tigecycline: a new glycylcycline antimicrobial agent.". Am J Health Syst Pharm 63 (13): 1235–43. doi:10.2146/ajhp050487. PMID 16790575.
- ^ Projan, Steven J (Jan. 2010). "Francis Tally and the discovery and development of tigecycline: a personal reminiscence". Clin. Infect. Dis. (United States) 50 Suppl 1: S24–5. doi:10.1086/647941. PMID 20067389.
- ^ Kumarasamy et. al.; Toleman, Mark A; Walsh, Timothy R; Bagaria, Jay; Butt, Fafhana; Balakrishnan, Ravikumar; Chaudhary, Uma; Doumith, Michel et al. (2010). "Emergence of a new antibiotic resistance mechanism in India, Pakistan, and the UK: a molecular, biological, and epidemiological study". The Lancet Infectious Diseases 10 (9): 597–602. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70143-2. PMC 2933358. PMID 20705517. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2933358.
- ^ Tigecycline: A Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial: Pharmacology and Mechanism of Action Christine M. Slover, PharmD, Infectious Diseases Fellow, Keith A. Rodvold, PharmD and Larry H. Danziger, PharmD, Professor, Department of Pharmacy Practice, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL
- ^ Scheinfeld N (2005). "Tigecycline: a review of a new glycylcycline antibiotic.". The Journal of dermatological treatment 16 (4): 207–12. doi:10.1080/09546630510011810. PMID 16249141.
- ^ http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm224370.htm
- ^ Skrtić M, Sriskanthadevan S, Jhas B, Gebbia M, Wang X, Wang Z, Hurren R, Jitkova Y, Gronda M, Maclean N, Lai CK, Eberhard Y, Bartoszko J, Spagnuolo P, Rutledge AC, Datti A, Ketela T, Moffat J, Robinson BH, Cameron JH, Wrana J, Eaves CJ, Minden MD, Wang JC, Dick JE, Humphries K, Nislow C, Giaever G, Schimmer AD (2011) Inhibition of mitochondrial translation as a therapeutic strategy for human acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 20(5):674-688
- ^ Betriu C, Rodríguez-Avial I, Sánchez BA, Gómez M, Picazo JJ (2002). "Comparative in vitro activities of tigecycline (GAR-936) and other antimicrobial agents against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia". J Antimicrob Chemother 50 (5): 758–59. doi:10.1093/jac/dkf196. PMID 12407139.
External links
Antibacterials: protein synthesis inhibitors (J01A, J01B, J01F, J01G, QJ01XQ) 30S -mycin (Streptomyces)Neomycin# (Framycetin, Paromomycin, Ribostamycin)
Kanamycin# (Amikacin, Arbekacin, Bekanamycin, Dibekacin, Tobramycin)
Paromomycin-micin (Micromonospora)TetracyclinesTigecycline50S Linezolid • Torezolid • Eperezolid • Posizolid • RadezolidPleuromutilinsRetapamulin • Tiamulin • ValnemulinErythromycin# • Azithromycin# • Spiramycin • Midecamycin • Oleandomycin • Roxithromycin • Josamycin • Troleandomycin • Clarithromycin • Miocamycin • Rokitamycin • Dirithromycin • Flurithromycin • Ketolide (Telithromycin, Cethromycin, Solithromycin)EF-G Steroid antibacterials#WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III Categories:- Glycylcycline antibiotics
- Amides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
