- Imipenem
-
Imipenem 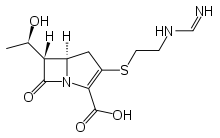
Systematic (IUPAC) name (5R,6S)-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-3-({2-[(iminomethyl)amino]ethyl}thio)-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names MedlinePlus a686013 Pregnancy cat. C(US) Legal status ? Routes IM, IV Pharmacokinetic data Metabolism Renal Half-life 60 minutes Identifiers CAS number 74431-23-5 
ATC code J01DH51 PubChem CID 5282372 DrugBank DB01598 ChemSpider 4445535 
UNII 71OTZ9ZE0A 
KEGG D00206 
ChEBI CHEBI:51799 
ChEMBL CHEMBL43708 
Chemical data Formula C12H17N3O4S Mol. mass 299.347 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Imipenem is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic developed in 1980.[1] It has an extremely broad spectrum of activity.[citation needed]
Imipenem belongs to the subgroup of carbapenems. It is derived from a compound called thienamycin, which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces cattleya. Imipenem has a broad spectrum of activity against aerobic and anaerobic, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is particularly important for its activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the Enterococcus species. It is not active against MRSA, however. Imipenem and other drugs in the carbapenem class are typically restricted in use, to avoid widespread bacterial resistance.[citation needed]
Contents
Method of action
Imipenem acts as an antimicrobial through inhibiting cell wall synthesis of various Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It remains very stable in the presence of beta-lactamase (both penicillinase and cephalosporinase) produced by some bacteria, and is a strong inhibitor of beta-lactamases from some Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to most beta-lactam antibiotics.[citation needed]
Coadministration with cilastatin
Imipenem is rapidly degraded by the renal enzyme dehydropeptidase 1 when administered alone, and is always coadministered with cilastatin to prevent this inactivation (imipenem/cilastatin).[citation needed]
Adverse effects
Common adverse drug reactions are nausea and vomiting. People who are allergic to penicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics should take caution if taking imipenem, as cross-reactivity rates are low. At high doses, imipenem is actually seizuregenic.[citation needed]
References
- ^ Kesado, Tadataka; Hashizume, Terutaka; Asahi, Yoshinari (1980). "Antibacterial activities of a new stabilized thienamycin, N-formimidoyl thienamycin, in comparison with other antibiotics". Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 17 (6): 912–7. PMC 283902. PMID 6931548. http://aac.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=6931548.
Further reading
- Clissold, SP; Todd, PA; Campoli-Richards, DM (1987). "Imipenem/cilastatin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy". Drugs 33 (3): 183–241. PMID 3552595. http://adisonline.com/drugs/Abstract/1987/33030/Imipenem_Cilastatin__A_Review_of_its_Antibacterial.1.aspx.
- Buckley, MM; Brogden, RN; Barradell, LB; Goa, KL (1992). "Imipenem/cilastatin. A reappraisal of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy". Drugs 44 (3): 408–44. PMID 1382937. http://adisonline.com/drugs/Abstract/1992/44030/Imipenem_Cilastatin__A_Reappraisal_of_its.8.aspx.
Categories:- Carbapenem antibiotics
- Enantiopure drugs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
