- Cefoxitin
-
Cefoxitin 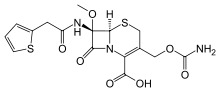
Systematic (IUPAC) name (6S,7R)-4-(carbamoyloxymethyl)-7-methoxy-
8-oxo-7-[(2-thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-
1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acidClinical data Trade names Mefoxin AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682737 Pregnancy cat. B Legal status ? Routes IV Pharmacokinetic data Metabolism minimal Half-life 41-59 min Excretion 85% urine Identifiers CAS number 35607-66-0 
ATC code J01DC01 PubChem CID 441199 DrugBank DB01331 ChemSpider 389981 
UNII 6OEV9DX57Y 
KEGG D02345 
ChEBI CHEBI:209807 
ChEMBL CHEMBL996 
Chemical data Formula C16H17N3O7S2 Mol. mass 427.454 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Cefoxitin is a cephamycin antibiotic developed by Merck & Co., Inc., often grouped with the second−generation cephalosporins. It is sold under the brand name Mefoxin.
Microbiology
Cefoxitin acts by interfering with cell wall synthesis. Its activity spectrum includes a broad range of gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria including anaerobes. It is inactive in vitro to most strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and enterococci and many strains of Enterobacter cloacae. Staphylococci resistant to methicillin/oxacillin should be considered resistant to cefoxitin. [1]
Cefoxitin is considered a strong beta-lactamase inducer, as are certain other antibiotics (such as imipenem).[2]
References
- ^ Mefoxin Official FDA information at Drugs.com
- ^ Phillips I, Shannon K (1993). "Importance of beta-lactamase induction". Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 12 Suppl 1: S19–26. PMID 8477758.
This systemic antibacterial-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
