- Meticillin
-
Meticillin 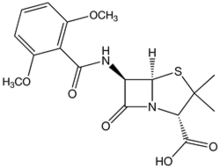
Systematic (IUPAC) name (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2,6-dimethoxybenzoyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes IV Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Not orally absorbed Metabolism hepatic, 20–40% Half-life 25–60 minutes Excretion renal Identifiers CAS number 61-32-5 
ATC code J01CF03 QJ51CF03 PubChem CID 6087 DrugBank DB01603 ChemSpider 5862 
UNII Q91FH1328A 
ChEMBL CHEMBL575 
Chemical data Formula C17H20N2O6S Mol. mass 380.42 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Meticillin (INN, BAN) or methicillin (USAN) is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It should not be confused with the antibiotic metacycline.
Contents
History
Methicillin was developed by Beecham in 1959.[1] It was previously used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria, in particular, beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus that would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins, but it is no longer clinically used.
Its role in therapy has been largely replaced by flucloxacillin and dicloxacillin, however the term methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) continues to be used to describe Staphylococcus aureus strains resistant to all penicillins.
Methicillin is no longer manufactured because the more stable and similar penicillins such as oxacillin (used for clinical antimicrobial susceptibility testing), flucloxacillin, and dicloxacillin are used medically.
Mode of action
Main article: Beta-lactam antibioticLike other beta-lactam antibiotics, methicillin acts by inhibiting the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. It inhibits cross-linkage between the linear peptidoglycan polymer chains that make up a major component of the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. It does this by binding to and competitively inhibiting the transpeptidase enzyme used by bacteria to cross-link the peptide (D-alanyl-alanine) used in peptidoglycan synthesis. Methicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics are structural analogs of D-alanyl-alanine, and the transpeptidase enzymes that bind to them are sometimes called penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). [2]
Medicinal chemistry
Methicillin is insensitive to beta-lactamase (also known as penicillinase) enzymes secreted by many penicillin-resistant bacteria. The presence of the ortho-dimethoxyphenyl group directly attached to the side-chain carbonyl group of the penicillin nucleus facilitates the β-lactamase resistance, since those enzymes are relatively intolerant of side-chain steric hindrance. Thus, it is able to bind to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) and inhibit peptidoglycan crosslinking, but it is not bound by or inactivated by β-lactamases.
Clinical use
Methicillin is no longer used to treat patients. Compared to other beta-lactamase-resistant penicillins, it is less active, can be administered only parenterally, and has a higher frequency of interstitial nephritis, an otherwise-rare side-effect of penicillins. But it serves a purpose in the laboratory to determine the antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus to other beta-lactamase-resistant penicillins.
References
- ^ Graham Dutfield (30 July 2009). Intellectual property rights and the life science industries: past, present and future. World Scientific. pp. 140–. ISBN 9789812832276. http://books.google.com/books?id=hnleY38aUxYC&pg=PA140. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- ^ Gladwin M., Trattler B. Clinical Microbiology made ridiculously simple. 3rd edition. Miami: MedMaster, Inc.; 2004.
Categories:- Beta-lactam antibiotics
- Benzamides
- Phenol ethers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
