- Oxacillin
-
Oxacillin 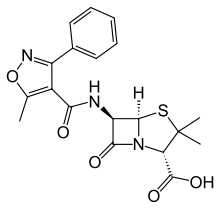
Systematic (IUPAC) name (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-6-[(5-methyl-3-phenyl-
1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl)amino]-7-oxo-4-thia-1-
azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acidClinical data Trade names Bactocill AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a685020 Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Identifiers CAS number 66-79-5 
ATC code J01CF04 QJ51CF04 PubChem CID 6098 DrugBank DB00713 ChemSpider 5873 
UNII UH95VD7V76 
KEGG D08307 
ChEBI CHEBI:49566 
ChEMBL CHEMBL891 
Chemical data Formula C19H19N3O5S Mol. mass 401.436 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem Physical data Density 1.49 g/cm³ Boiling point 686.8 °C (1268 °F)  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Oxacillin sodium (trade name Bactocill) is a narrow spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.
It was developed by Beecham.[1]
Uses
Oxacillin is a penicillinase-resistant β-lactam. It is similar to methicillin, and has replaced methicillin in clinical use. Another related compound is nafcillin. Since it is resistant to penicillinase enzymes, such as that produced by Staphylococcus aureus, it is widely used clinically in the US to treat penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. However, resistant strains called oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA/ORSA) are highly prevalent in the U.S. and the U.K.
References
- ^ David Greenwood (2008). Antimicrobial drugs: chronicle of a twentieth century medical triumph. Oxford University Press US. pp. 124–. ISBN 9780199534845. http://books.google.com/books?id=i4_FZHmzjzwC&pg=PA124. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
This systemic antibacterial-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
