- Nadifloxacin
-
Nadifloxacin 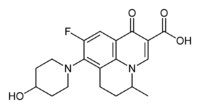
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-9-Fluoro-8-(4-hydroxy-piperidin-1-yl)-5-methyl-1-oxo-6,7-dihydro-1H,5H-pyrido[3,2,1-ij]quinoline-2-carboxylic acid Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes topical (epicutaneous) Identifiers CAS number 124858-35-1 ATC code None PubChem CID 4410 UNII 6CL9Y5YZEQ 
Chemical data Formula C19H21FN2O4 Mol. mass 360.379 g/mol  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Nadifloxacin (INN, brand names Acuatim, Nadiflox, Nadoxin, Nadixa, activon) is a topical fluoroquinolone antibiotic for the treatment of acne vulgaris.[1] It is also used to treat bacterial skin infections.
Contents
Pharmacology
Antibacterial spectrum
In vitro studies of nadifloxacin showed potent and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against aerobic Gram-positive, Gram-negative and anaerobic bacteria, including Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nadifloxacin showed potent antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which was similar to potency against methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA). The drug was also active against new quinolone-resistant MRSA. Nadifloxacin does not show cross-resistance with other new quinolones.
In patients with skin lesions, topical application of nadifloxacin can result in plasma concentrations of 1 to 3 ng/ml. Consequently, it has been argued that it should not be used to treat relatively harmless diseases like acne vulgaris, risking the development of quinolone resistances.[2]
Mechanism of action
Nadifloxacin inhibits the enzyme DNA gyrase that is involved in bacterial DNA synthesis and replication, thus inhibiting the bacterial multiplication.
Pharmacokinetics
Following a single topical application of 10 g nadifloxacin 1% cream to normal human back skin, the highest plasma concentration was determined to be 107 ng/mL with an elimination half-life of 19.4 hours. Approximately 0.09% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine over 48 hours post- dosing. The plasma concentration reached a steady state on Day 5 of repeated administration study when nadifloxacin 1% cream was applied at 5 gm twice daily to normal healthy individuals for a period of 7 days. The plasma concentration reached a peak of 4.1 ng/ml at 8 hours post-final dosing with an elimination half-life of 23.2 hours. The urinary excretion rate reached 0.16% on Day 7.
See also
- Adverse effects of fluoroquinolones
References
- ^ Murata K, Tokura Y (March 2007). "[Anti-microbial therapies for acne vulgaris: anti-inflammatory actions of anti-microbial drugs and their effectiveness]" (in Japanese). J. UOEH 29 (1): 63–71. PMID 17380730.
- ^ Steinhilber; Schubert-Zsilavecz, Roth (2004). Medizinische Chemie: Targets und Arzneistoffe. WVG Stuttgart.
Antibiotics and chemotherapeutics for dermatological use (D06) Antibiotics Tetracycline and derivativesOthersAminoglycosides: Neomycin • Gentamicin • Amikacin
Quinolone: Nadifloxacin
other: Fusidic acid • Bacitracin • Tyrothricin • MupirocinChemotherapeutics Aciclovir • Penciclovir • Idoxuridine • Edoxudine
Imiquimod/Resiquimod • Podophyllotoxin
Docosanol • Tromantadine • Inosine • Lysozyme • IbacitabineOtherAntibacterials: nucleic acid inhibitors (J01E, J01M) Antifolates
(inhibits
purine metabolism,
thereby inhibiting
DNA and RNA synthesis)Sulfonamides
(DHPS inhibitor)Other/ungroupedCombinationsTopoisomerase
inhibitors/
quinolones/
(inhibits
DNA replication)1st g.2nd g.Ciprofloxacin# • Enoxacin‡ • Fleroxacin‡ • Lomefloxacin • Nadifloxacin • Ofloxacin • Norfloxacin • Pefloxacin • Rufloxacin3rd g.4th g.Besifloxacin • Clinafloxacin† • Garenoxacin • Gemifloxacin • Moxifloxacin • Gatifloxacin‡ • Sitafloxacin • Trovafloxacin‡/Alatrofloxacin‡ • PrulifloxacinVet.Related (DG)Anaerobic DNA
inhibitorsNitrofuran derivativesRNA synthesis #WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III Categories:- Fluoroquinolone antibiotics
- Piperidines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
