- Lomefloxacin
-
Lomefloxacin 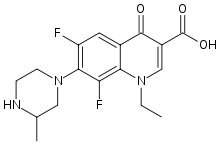
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-1-ethyl-6,8-difluoro- 7-(3-methylpiperazin-1-yl)- 4-oxo-quinoline-3- carboxylic acid Clinical data Trade names Maxaquin AHFS/Drugs.com Consumer Drug Information MedlinePlus a600002 Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding 10% Half-life 8 hours Identifiers CAS number 98079-51-7 
ATC code J01MA07 S01AX17 PubChem CID 3948 DrugBank APRD01076 ChemSpider 3811 
UNII 9VC7S3ZXXB 
KEGG D02318 
ChEBI CHEBI:116278 
ChEMBL CHEMBL561 
Chemical data Formula C17H19F2N3O3 Mol. mass 351.348 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Lomefloxacin hydrochloride (sold under the following brand names in English speaking countries Maxaquin, Okacyn, Uniquin), is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections including bronchitis and urinary tract infections. It is also used to prevent urinary tract infections prior to surgery. Lomefloxacin is associated with phototoxicity and central nervous system adverse effects.[1]
October 2008 the FDA added the following Black Box Warning to the product insert for Maxaquin:
WARNING: Fluoroquinolones, including Maxaquin, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants (See WARNINGS). To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Maxaquin and other antibacterial drugs, Maxaquin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria'.[2]
Lomefloxacin is unique in that it forms a magnesium chelate with itself. The chelate is formed between the 2-carbonyl group of two separate lomefloxacin molecules.
See also
- Fluoroquinolone toxicity
- Fluoroquinolone
References
- ^ Rubinstein, E. (2001). "History of quinolones and their side effects.". Chemotherapy 47 (Suppl 3): 3–8; discussion 44–8. doi:10.1159/000057838. PMID 11549783.
- ^ October 2008 revision of the package insert for maxaquin
Antibacterials: nucleic acid inhibitors (J01E, J01M) Antifolates
(inhibits
purine metabolism,
thereby inhibiting
DNA and RNA synthesis)Sulfonamides
(DHPS inhibitor)Other/ungroupedCombinationsTopoisomerase
inhibitors/
quinolones/
(inhibits
DNA replication)1st g.2nd g.Ciprofloxacin# • Enoxacin‡ • Fleroxacin‡ • Lomefloxacin • Nadifloxacin • Ofloxacin • Norfloxacin • Pefloxacin • Rufloxacin3rd g.4th g.Besifloxacin • Clinafloxacin† • Garenoxacin • Gemifloxacin • Moxifloxacin • Gatifloxacin‡ • Sitafloxacin • Trovafloxacin‡/Alatrofloxacin‡ • PrulifloxacinVet.Related (DG)Anaerobic DNA
inhibitorsNitrofuran derivativesRNA synthesis 
This systemic antibacterial-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
