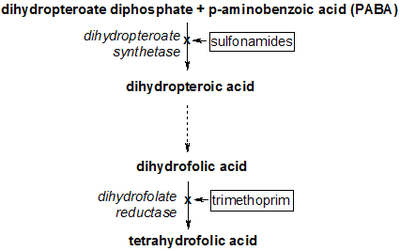
- Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor
-
A dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor is a molecule that inhibits the function of dihydrofolate reductase, and is a type of antifolate.
Since folate is needed by rapidly dividing cells to make thymine, this effect may be used to therapeutic advantage. For example, methotrexate is used as cancer chemotherapy because it can prevent neoplastic cells from dividing.[1][2] Bacteria also need DHFR to grow and multiply and hence inhibitors selective for bacterial vs. host DHFR have found application as antibacterial agents.[3]
A variety of drugs act as inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase:
- the antibiotic trimethoprim and its derivatives brodimoprim, tetroxoprim, and iclaprim.
- the antimalarial drugs pyrimethamine and proguanil.
- the experimental new antimalarial drug JPC-2056, which may also be more effective and better tolerated than current treatments against toxoplasmosis.[4]
- the chemotherapeutic agents methotrexate and pemetrexed. Methotrexate acts on this enzyme binding to it some 1000 times more tightly than folate itself.
References
- ^ Huennekens FM (1994). "The methotrexate story: a paradigm for development of cancer chemotherapeutic agents". Adv. Enzyme Regul. 34: 397–419. doi:10.1016/0065-2571(94)90025-6. PMID 7942284.
- ^ McGuire JJ (2003). "Anticancer antifolates: current status and future directions". Curr. Pharm. Des. 9 (31): 2593–613. doi:10.2174/1381612033453712. PMID 14529544.
- ^ Hawser S, Lociuro S, Islam K (March 2006). "Dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors as antibacterial agents". Biochem. Pharmacol. 71 (7): 941–8. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2005.10.052. PMID 16359642.
- ^ Mui EJ, Schiehser GA, Milhous WK, et al. (2008). Matlashewski, Greg. ed. "Novel Triazine JPC-2067-B Inhibits Toxoplasma gondii In Vitro and In Vivo". PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2 (3): e190. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000190. PMC 2254147. PMID 18320016. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2254147.
Pharmacology: enzyme inhibition Class Substrate 1.1 Aldose reductase · HMG-CoA reductase
1.5 Dihydrofolate reductase
1.13 Lipoxygenase
1.17 Xanthine oxidase · Ribonucleotide reductase2.1 COMT · Thymidylate synthase
2.4 PARP
2.5 Dihydropteroate synthetase · Farnesyltransferase
2.6 GABA transaminase
2.7 Nucleotidyltransferase (Integrase, Reverse transcriptase) · Protein kinase (Tyrosine-kinase (Janus kinase))3.1 Phosphodiesterase · Acetylcholinesterase · Ribonuclease
3.2 Polygalacturonase · Neuraminidase · Alpha-glucosidase
3.4 Protease: Exopeptidase (Dipeptidyl peptidase-4, ACE) · Endopeptidase (Trypsin, Renin, Matrix metalloproteinase)
3.5 Histone deacetylase · Beta-lactamase4.1 Dopa decarboxylase
4.2 Carbonic anhydraseAntibacterials: nucleic acid inhibitors (J01E, J01M) Antifolates
(inhibits
purine metabolism,
thereby inhibiting
DNA and RNA synthesis)DHFR inhibitorOther/ungroupedCombinationsTopoisomerase
inhibitors/
quinolones/
(inhibits
DNA replication)1st g.2nd g.Ciprofloxacin# • Enoxacin‡ • Fleroxacin‡ • Lomefloxacin • Nadifloxacin • Ofloxacin • Norfloxacin • Pefloxacin • Rufloxacin3rd g.4th g.Besifloxacin • Clinafloxacin† • Garenoxacin • Gemifloxacin • Moxifloxacin • Gatifloxacin‡ • Sitafloxacin • Trovafloxacin‡/Alatrofloxacin‡ • PrulifloxacinVet.Related (DG)Anaerobic DNA
inhibitorsNitrofuran derivativesRNA synthesis #WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – Chromalveolate antiparasitics (P01) Alveo-
lateIndividual
agentsOtherDHFR inhibitors
(antifols)Sulfadoxine • sulfamethoxypyrazineCoformulationFansidar# (sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine)OtherCombi-
nationsartemether-lumefantrine#
artesunate-amodiaquine (ASAQ)
artesunate-mefloquine (ASMQ)
dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine
artesunate-pyronaridineOther combinations
(not co-formulated)artesunate/SP • artesunate/mefloquine •
quinine/tetracycline • quinine/doxycycline • quinine/clindamycinHetero-
kont#WHO-EM. ‡Withdrawn from market. Clinical trials: †Phase III. §Never to phase III 
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This antineoplastic or immunomodulatory drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.