- Mitotic inhibitor
-
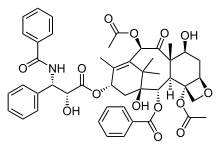 The structure of paclitaxel, a widely used mitotic inhibitor.
The structure of paclitaxel, a widely used mitotic inhibitor.
A mitotic inhibitor is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division. These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the cell apart when it divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment, because cancer cells are able to grow and eventually spread through the body (metastasize) through continuous mitotic division and so are more sensitive to inhibition of mitosis than normal cells. Mitotic inhibitors are also used in cytogenetics (the study of chromosomes), where they stop cell division at a stage where chromosomes can be easily examined.[1]
Mitotic inhibitors are derived from natural substances such as plant alkaloids, and prevent cells from undergoing mitosis by disrupting microtubule polymerization, thus preventing cancerous growth. Microtubules are long, ropelike proteins that extend through the cell and move cellular components around. Microtubules are long polymers made of smaller units (monomers) of the protein tubulin. Microtubules are created during normal cell functions by assembling (polymerizing) tubulin components, and are disassembled when they are no longer needed. One of the important functions of microtubules is to move and separate chromosomes and other components of the cell for cell division (mitosis). Mitotic inhibitors interfere with the assembly and disassembly of tubulin into microtubule polymers. This interrupts cell division, usually during the mitosis (M) phase of the cell cycle when two sets of fully formed chromosomes are supposed to separate into daughter cells.[2][3]
Examples of mitotic inhibitors frequently used in the treatment of cancer include paclitaxel, docetaxel, vinblastine, vincristine, and vinorelbine.[1] Colchicine is a mitotic inhibitor used in the treatment of gout.[4]
Contents
Use of mitotic inhibitors in cytogenetics
Main article: CytogeneticsCytogenetics, the study of chromosomal material by analysis of G-Banded chromosomes, uses mitotic inhibitors extensively. In order to prepare a slide for cytogenetic study, a mitotic inhibitor is added to the cells being studied. This stops the cells during mitosis, while the chromosomes are still visible. Once the cells are centrifuged and placed in a hypotonic solution, they swell, spreading the chromosomes. After preparation, the chromosomes of the cells can be viewed under a microscope to have the banding patterns of the chromosomes examined. This experiment is crucial to many forms of cancer research.
Specific agents
Taxanes
Main article: TaxanesTaxanes are complex terpenes produced by the plants of the genus Taxus (yews). Originally derived from the Pacific yew tree, they are now synthesized artificially. Their principal mechanism is the disruption of the cell's microtubule function by stabilizing microtubule formation. Microtubules are essential to mitotic reproduction, so through the inactivation of the microtubule function of a cell, taxanes inhibit the cell's division.
- Paclitaxel—used to treat lung cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, and advanced forms of Kaposi's sarcoma.[5]
- Docetaxel—used to treat breast, ovarian, and non-small cell lung cancer.[6][7]
Vinca alkaloids
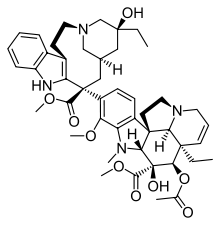 Skeletal formula of vinblastine
Skeletal formula of vinblastine Main article: Vinca alkaloids
Main article: Vinca alkaloidsVinca alkaloids are amines produced by the hallucinogenic plant Catharanthus roseus (Madagascar Periwinkle). Vinca alkaloids inhibit microtubule depolymerization, thereby inhibiting mitosis.
- Vinblastine—used to treat leukaemia, Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer and testicular cancer. It is also a component in a large number of chemotherapy regimens.[8]
- Vincristine—used to treat lymphoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia.[8]
- Vindesine—used to treat leukaemia, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer.[8]
- Vinorelbine—used to treat breast cancer and non-small-cell lung cancer.[8]
Colchicine
Main article: ColchicineColchicine is an alkaloid derived from the autumn crocus (Colchicum autumnale). It inhibits mitosis by inhibiting microtubule polymerization. While colchicine is not used to treat cancer in humans, it is commonly used to treat acute attacks of gout.[4]
References
- ^ a b "What Are the Different Types of Chemotherapy Drugs?". American Cancer Society. http://www.cancer.org/docroot/ETO/content/ETO_1_4X_What_Are_The_Different_Types_Of_Chemotherapy_Drugs.asp. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ "Definition of mitotic inhibitor". National Cancer Institute. http://www.cancer.gov/Templates/db_alpha.aspx?CdrID=46705. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ "Treatment Options: Mitotic Inhibitors". Drug Digest. Archived from the original on 2007-02-16. http://web.archive.org/web/20070216002600/http://www.drugdigest.org/DD/HC/HCDrugClass/0,4055,47-8,00.html. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ a b Cyberbotanica. University of Texas. "Pharmacology of Colchicine." Last updated November 5, 1997. Last accessed July 14, 2007.
- ^ Saville M, Lietzau J, Pluda J, Feuerstein I, Odom J, Wilson W, Humphrey R, Feigal E, Steinberg S, Broder S (July 1 1995). "Treatment of HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma with paclitaxel.". Lancet 346 (8966): 26–8. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(95)92654-2. PMID 7603142.
- ^ Lyseng-Williamson KA, Fenton C. Docetaxel: a review of its use in metastatic breast cancer. Drugs 2005;65(17):2513-31.
- ^ Clarke SJ, Rivory LP. Clinical pharmacokinetics of docetaxel. Clin Pharmacokinet 1999;36(2):99-114
- ^ a b c d "Vincristine (Oncovin)". http://www.cancerbackup.org.uk/Treatments/Chemotherapy/Individualdrugs/Vincristine. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
See also
Antigout preparations (M04) Uricosurics primary: Probenecid • Sulfinpyrazone • Benzbromarone • Isobromindione
secondary: Amlodipine • Atorvastatin • Fenofibrate • Guaifenesin • LosartanXanthine oxidase inhibitors purine analogues: Allopurinol# • Oxypurinol • Tisopurine
other: Febuxostat • Inositols (Phytic acid, Myo-inositol)Mitotic inhibitors Other M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Mitosis
- Medical research
- Mitotic inhibitors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
