- Olaparib
-
Olaparib 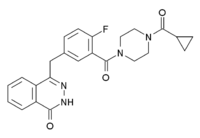
Systematic (IUPAC) name 4-[(3-[(4-cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazin-4-yl]carbonyl) -4-fluorophenyl]methyl(2H)phthalazin-1-one Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Investigational Routes Oral Identifiers CAS number 763113-22-0 ATC code None PubChem CID 23725625 ChemSpider 23343272 
UNII WOH1JD9AR8 
Chemical data Formula C24H23FN4O3 Mol. mass 435.08 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Olaparib (AZD-2281) is a chemotherapeutic agent developed by KuDOS Pharmaceuticals and later by Astra Zeneca. It is an inhibitor of PARP, an enzyme involved in DNA repair.[1] It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which includes many ovarian, breast and prostate cancers. Early (Phase I) trials have been promising, and it is now in Phase II trials, but is not clinically approved.
Contents
Mechanism of action
Olaparib acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme Poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) and is one of the first PARP inhibitors. Patients with BRCA1/2 mutations may be genetically predisposed to developing some forms of cancer, and are often resistant to other forms of cancer treatment, but this also sometimes gives their cancers a unique vulnerability, as the cancer cells have increased reliance on PARP to repair their DNA and enable them to continue dividing. This means that drugs which selectively inhibit PARP may be of significant benefit in patients whose cancers are susceptible to this treatment.[2][3][4][5][6][7]
Trial results
Phase I clinical trials, in patients with BRCA-mutated tumors including ovarian cancer, were encouraging.[8] In one of these studies, it was given to 19 patients with inherited forms of advanced breast, ovarian and prostate cancers caused by mutations of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. In 12 of the patients, none of whom had responded to other therapies, tumours shrank or stabilised.[9] One of the first patients to be given the treatment (who had castration-resistant prostate cancer) was as of July 2009[update] still in remission after two years.
Phase II clinical trials are ongoing in breast, ovarian and colorectal cancer.[10][11] A phase II trial that included 63 cases of ovarian cancer concluded that olaparib is promising for women with ovarian cancer. [7 responses in 17 patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and 11 responses in the 46 who did not have these mutations.][12]
Side effects
Olaparib is generally well tolerated, the side effects consist mainly of fatigue, somnolence, nausea, loss of appetite and thrombocytopenia.
References
- ^ "Olaparib, a PARP Inhibitor". Health and Life. http://healthlifeandstuff.com/2010/03/olaparib-a-parp-inhibitor/.
- ^ New cancer drug 'shows promise' BBC News 24 June 2009
- ^ Olaparib for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
- ^ Vasiliou S, Castaner R, Bolos J. Olaparib. Drugs of the Future. 2009; 34(2): 101.
- ^ Menear KA, Adcock C, Boulter R, Cockcroft XL, Copsey L, Cranston A, Dillon KJ, Drzewiecki J, Garman S, Gomez S, Javaid H, Kerrigan F, Knights C, Lau A, Loh VM, Matthews IT, Moore S, O'Connor MJ, Smith GC, Martin NM (October 2008). "4-[3-(4-cyclopropanecarbonylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one: a novel bioavailable inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51 (20): 6581–91. doi:10.1021/jm8001263. PMID 18800822.
- ^ Rottenberg S, Jaspers JE, Kersbergen A, van der Burg E, Nygren AO, Zander SA, Derksen PW, de Bruin M, Zevenhoven J, Lau A, Boulter R, Cranston A, O'Connor MJ, Martin NM, Borst P, Jonkers J (November 2008). "High sensitivity of BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors to the PARP inhibitor AZD2281 alone and in combination with platinum drugs". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105 (44): 17079–84. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806092105. PMC 2579381. PMID 18971340. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2579381.
- ^ Hay T, Matthews JR, Pietzka L, Lau A, Cranston A, Nygren AO, Douglas-Jones A, Smith GC, Martin NM, O'Connor M, Clarke AR (May 2009). "Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor treatment regresses autochthonous Brca2/p53-mutant mammary tumors in vivo and delays tumor relapse in combination with carboplatin". Cancer Research 69 (9): 3850–5. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2388. PMID 19383921.
- ^ http://www.ncri.org.uk/ncriconference/archive/2007/abstracts/pdf/LB57.pdf "A Phase I trial of AZD2281 (KU-0059436), a PARP inhibitor with single agent anticancer activity in patients with BRCA deficient tumours, particularly ovarian cancer"
- ^ Fong PC, Boss DS, Yap TA, et al. (July 2009). "Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers". N. Engl. J. Med. 361 (2): 123–34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0900212. PMID 19553641. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=19553641&promo=ONFLNS19.
- ^ http://www.cancercompass.com/cancer-news/1,15869,00.htm "Phase II Trials Investigating Oral PARP Inhibitor, Olaparib, In BRCA-Deficient Advanced Breast And Ovarian Cancer" June 2009
- ^ http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00912743 Efficacy and Safety of Olaparib in Pretreated Patients With Measurable Colorectal Cancer, Stratified by Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Status
- ^ "Olaparib Looks Promising in Treatment of Non-BRCA Ovarian Cancer". 26 Aug 2011. http://www.cancernetwork.com/ovarian-cancer/content/article/10165/1937112.
Categories:- PARP inhibitors
- Phthalazines
- Lactams
- Organofluorides
- Amides
- Piperazines
- Experimental cancer drugs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
