- Non-competitive inhibition
-
Non-competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme, by binding not to the active site on the enzyme, but to a different site.[1] More specifically, it is a special instance of mixed inhibition where the inhibitor has an equal affinity for both free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex.
Contents
Mechanism
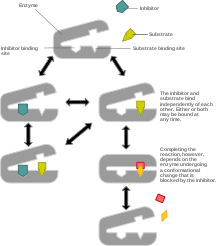
Non-competitive inhibition models a system where the inhibitor and the substrate may both be bound to the enzyme at any given time. When both the substrate and the inhibitor are bound, the enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex cannot form product and can only be converted back to the enzyme-substrate complex or the enzyme-inhibitor complex. Non-competitive inhibition is distinguished from general mixed inhibition in that the inhibitor has an equal affinity for the enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex.
The most common mechanism of non-competitive inhibition involves reversible binding of the inhibitor to an allosteric site, but it is possible for the inhibitor to operate via other means including direct binding to the active site. It differs from competitive inhibition in that the binding of the inhibitor does not prevent binding of substrate, and vice versa, it simply prevents product formation for a limited time.
This type of inhibition reduces the maximum rate of a chemical reaction without changing the apparent binding affinity of the catalyst for the substrate (Kmapp – see Michaelis-Menten kinetics).
Equation
In the presence of a non-competitive inhibitor, the apparent enzyme affinity is equivalent to the actual affinity. In terms of Michaelis-Menten kinetics, Kmapp = Km. This can be seen as a consequence of Le Chatelier's Principle because the inhibitor binds to both the enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex equally so that the equilibrium is maintained. However, since some enzyme is always inhibited from converting the substrate to product, the effective enzyme concentration is lowered.
Mathematically,
Example: noncompetitive inhibitors of CYP2C9 enzyme
Noncompetitive inhibitors of CYP2C9 enzyme include nifedipine, tranylcypromine, phenethyl isothiocyanate, and 6-hydroxyflavone. Computer docking simulation and constructed mutants substituted indicate that the noncompetitive binding site of 6-hydroxyflavone is the reported allosteric binding site of CYP2C9 enzyme[2].
Citations
- ^ As opposed to competitive inhibition, where the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme. Berg, Tymoczko & Stryer 2007, p. 836
- ^ Si Dayong, Wang Y, Guo Y, Wang J, Zhou H, Zhou Y-H, Li Z-S, Fawcett JP (2008). Mechanism of CYP2C9 inhibition by flavones and flavonols. Drug Metabolism and Disposition. doi:10.1124/dmd.108.023416[1]
References
- Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, John L.; Stryer, Lubert (2007), Biochemistry (6 ed.), New York: WH Freeman & Co., ISBN 0-7167-6766-X
Pharmacology: enzyme inhibition Class Competitive inhibition · Uncompetitive inhibition · Non-competitive inhibition · Suicide inhibition · Mixed inhibitionSubstrate 1.1 Aldose reductase · HMG-CoA reductase
1.13 Lipoxygenase
1.17 Xanthine oxidase · Ribonucleotide reductase2.1 COMT · Thymidylate synthase
2.4 PARP
2.5 Dihydropteroate synthetase · Farnesyltransferase
2.6 GABA transaminase
2.7 Nucleotidyltransferase (Integrase, Reverse transcriptase) · Protein kinase (Tyrosine-kinase (Janus kinase))3.1 Phosphodiesterase · Acetylcholinesterase · Ribonuclease
3.2 Polygalacturonase · Neuraminidase · Alpha-glucosidase
3.4 Protease: Exopeptidase (Dipeptidyl peptidase-4, ACE) · Endopeptidase (Trypsin, Renin, Matrix metalloproteinase)
3.5 Histone deacetylase · Beta-lactamase4.1 Dopa decarboxylase
4.2 Carbonic anhydraseCategories:- Enzymes
- Metabolism
- Enzyme inhibitors
- Pharmacology
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


![V_{max}^{app} = \frac{V_{max}}{1+\frac{[I]}{K_I}}](1/0619dfdc799043de877316062528d8de.png)
![{apparent\ k}_2 = \frac{k_2}{1+\frac{[I]}{K_I}}](0/3d08549ff9644994a324ea81d1ae566e.png)