- Mixed inhibition
-
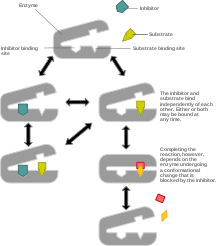
Mixed inhibition refers to a combination of two different types of reversible enzyme inhibition – competitive inhibition and uncompetitive inhibition. The term 'mixed' is used when the inhibitor can bind to either the free enzyme or the enzyme-substrate complex. In mixed inhibition, the inhibitor binds to a site different from the active site where the substrate binds. Mixed inhibition results in a decrease in the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate (
 ) and a decrease in the apparent maximum enzyme reaction rate (
) and a decrease in the apparent maximum enzyme reaction rate ( ).[1]
).[1]Mathematically, mixed inhibition occurs when the factors α and α’ (introduced into the Michaelis-Menten equation to account for competitive and uncompetitive inhibition, respectively) are both greater than 1.
In the special case where α = α’, noncompetitive inhibition occurs, in which case
 is reduced but Km is unaffected. This is very unusual in practice[1]
is reduced but Km is unaffected. This is very unusual in practice[1]References
Pharmacology: enzyme inhibition Class Competitive inhibition · Uncompetitive inhibition · Non-competitive inhibition · Suicide inhibition · Mixed inhibitionSubstrate Oxidoreductase (EC 1)1.1 Aldose reductase · HMG-CoA reductase
1.13 Lipoxygenase
1.17 Xanthine oxidase · Ribonucleotide reductaseTransferase (EC 2)2.1 COMT · Thymidylate synthase
2.4 PARP
2.5 Dihydropteroate synthetase · Farnesyltransferase
2.6 GABA transaminase
2.7 Nucleotidyltransferase (Integrase, Reverse transcriptase) · Protein kinase (Tyrosine-kinase (Janus kinase))Hydrolase (EC 3)3.1 Phosphodiesterase · Acetylcholinesterase · Ribonuclease
3.2 Polygalacturonase · Neuraminidase · Alpha-glucosidase
3.4 Protease: Exopeptidase (Dipeptidyl peptidase-4, ACE) · Endopeptidase (Trypsin, Renin, Matrix metalloproteinase)
3.5 Histone deacetylase · Beta-lactamaseLyase (EC 4)4.1 Dopa decarboxylase
4.2 Carbonic anhydraseCategories:- Biochemistry
- Biochemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.