- Betamethasone
-
Betamethasone 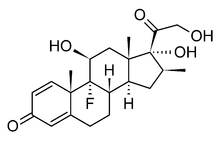
Systematic (IUPAC) name (8S,9R,10S,11S,13S,14S,16S,17R)-9-fluoro- 11,17-dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13,16-trimethyl- 6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro- 3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one Clinical data Trade names Celestone AHFS/Drugs.com monograph Pregnancy cat. C(US) Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes oral or topical Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability ? Metabolism hepatic CYP3A4 Half-life 5.6 hours Excretion Renal (in urine) Identifiers CAS number 378-44-9 ATC code A07EA04 C05AA05 D07AC01 D07XC01 H02AB01 R01AD06 R03BA04 S01BA06 S01CB04 S02BA07 S03BA03 PubChem CID 9782 DrugBank APRD00513 ChemSpider 9399 
UNII 9842X06Q6M 
KEGG D00244 
ChEBI CHEBI:3077 
ChEMBL CHEMBL632 
Chemical data Formula C22H29FO5 Mol. mass 392.461 SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Betamethasone is a potent glucocorticoid steroid with anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. Unlike other drugs with these effects, betamethasone does not cause water retention. It is applied as a topical cream, ointment, foam, lotion or gel to treat itching. Betamethasone sodium phosphate is sometimes prescribed as an intramuscular injection (I.M) for itching from various ailments including allergic reactions to poison ivy and similar plants.
Contents
Forms
Betamethasone is available in a number of compound forms: betamethasone dipropionate (branded as Diprosone, Diprolene, Celestamine, and others), sodium phosphate (branded as Bentelan in Italy[1]) and valerate (branded as Betnovate, Celestone and others). In the United States and Canada, betamethasone is mixed with clotrimazole and sold as Lotrisone and Lotriderm.
Indications
Betamethasone is a corticosteroid used as a topical cream to relieve skin irritation, such as itching and flaking from eczema. It is used as a treatment for local psoriasis, as Betamethasone dipropionate and salicylic acid, or as the combination betamethasone/calcipotriol. Betamethasone sodium phosphate is used orally and via injection with the same indications as other steroids.
A cream with 0.05% betamethasone appears effective in treating phimosis in boys, and often averts the need for circumcision. [2][3][4] It has replaced circumcision as the preferred treatment method for some physicians in the British National Health Service.[5][6]
Betamethasone is also used to stimulate fetal lung maturation (prevention of IRDS), and to decrease the incidence and mortality from intracranial hemorrhage in premature infants.
As it crosses the placenta, which is required for its beneficial effects, it may also be associated with complications, such as hypoglycemia and leukocytosis in newborns exposed in utero[citation needed].
References
- ^ http://farmaco.agenziafarmaco.it/index.php?SEARCH=yes&DESCR_SPECIALITA2=BENTELAN
- ^ Van Howe RS (1998). "Cost-effective treatment of phimosis". Pediatrics 102 (4): E43. doi:10.1542/peds.102.4.e43. PMID 9755280. http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/102/4/e43. A review of estimated costs and complications of 3 phimosis treatments.
- ^ Topical steroid application versus circumcision in pediatric patients with phimosis: a prospective randomized placebo controlled clinical trial, World Journal of Urology, 2008, 26, pp.187-190
- ^ Phimosis and topical steroids: new clinical findings, Pediatric Surgery International, 2007, 23, pp.331-335
- ^ Berdeu D, Sauze L, Ha-Vinh P, Blum-Boisgard C (2001). "Cost-effectiveness analysis of treatments for phimosis: a comparison of surgical and medicinal approaches and their economic effect". BJU Int. 87 (3): 239–44. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02033.x. PMID 11167650. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=1464-4096&date=2001&volume=87&issue=3&spage=239.
- ^ Chu CC, Chen KC, Diau GY (1999). "Topical steroid treatment of phimosis in boys". J. Urol. 162 (3 Pt 1): 861–3. doi:10.1097/00005392-199909010-00078. PMID 10458396.
External links
- "Betamethasone". safefetus.com. http://www.safefetus.com/DrugDetail.asp?DrugId=709&TradeName=Betaval&TradeId=775.
Vasoprotectives (C05) Antihemorrhoidals for topical use corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Betamethasone, Fluorometholone, Fluocortolone, Dexamethasone, Fluocinolone acetonide, Fluocinonide)
local anesthetics (Lidocaine, Tetracaine, Benzocaine, Cinchocaine, Procaine, Oxetacaine, Pramocaine)
other (Tribenoside)Antivaricose therapy heparins or heparinoids for topical use (Organo-heparinoid, Sodium apolate, Heparin, Pentosan polysulfate)
sclerosing agents for local injection (Monoethanolamine oleate, Polidocanol, Invert sugar, Sodium tetradecyl sulfate, Phenol)
other (Calcium dobesilate)Capillary stabilising agents bioflavonoids (Rutoside, Monoxerutin, Diosmin, Troxerutin, Hidrosmin) - other (Tribenoside, Etamsylate)Decongestants and other nasal preparations (R01) Topical Sympathomimetics, plainCyclopentamine • Ephedrine • Phenylephrine • Oxymetazoline • Tetryzoline • Xylometazoline • Naphazoline • Tramazoline • Metizoline • Tuaminoheptane • Fenoxazoline • Tymazoline • EpinephrineSpaglumic acid
histamine antagonists (Levocabastine, Antazoline, Thonzylamine)
mast cell stabilizer (some are also antihistamines) (Cromoglicic acid, Nedocromil, Azelastine, Olopatadine, Lodoxamide)Beclometasone • Prednisolone • Dexamethasone • Flunisolide • Budesonide • Betamethasone • Tixocortol • Fluticasone • Mometasone furoate • Triamcinolone • CiclesonideOther nasal preparationsCafaminol • Calcium hexamine thiocyanate • Retinol • Ipratropium bromide • Ritiometan • Mupirocin • Hexamidine • Framycetin • Hyaluronic acid • Eucalyptus oilSystemic use:
SympathomimeticsDrugs for obstructive airway diseases: asthma/COPD (R03) Adrenergics, inhalants Salbutamol#/Levosalbutamol • Fenoterol • Terbutaline • Pirbuterol • Procaterol • Bitolterol • Rimiterol • Carbuterol • Tulobuterol • ReproterolLong acting β2-agonists (LABA)otherGlucocorticoids Beclometasone# • Budesonide • Ciclesonide • Fluticasone • Mometasone • Flunisolide • Betamethasone • TriamcinoloneAnticholinergics/
muscarinic antagonistMast cell stabilizers Cromoglicate • NedocromilXanthines Eicosanoid inhibition Thromboxane receptor antagonistsCombination products Otologicals (S02) Anti-infectives Acetic acid • Aluminium acetotartrate • Boric acid • Chloramphenicol • Chlorhexidine • Ciprofloxacin • Clioquinol • Gentamicin • Hydrogen peroxide • Miconazole • Neomycin • Nitrofurazone • Ofloxacin • Polymyxin B • Rifamycin • TetracyclineCorticosteroids Analgesics and anesthetics M: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Steroids
- Organofluorides
- Otologicals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
