- Sulfasalazine
-
Sulfasalazine 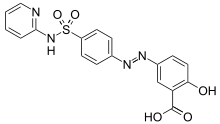
Systematic (IUPAC) name 2-hydroxy-5-[(E)-2-{4-[(pyridin-2-yl)sulfamoyl]phenyl}diazen-1-yl]benzoic acid Clinical data Trade names Azulfidine AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682204 Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability <15% Half-life 5-10 hours Identifiers CAS number 599-79-1 
ATC code A07EC01 PubChem CID 5384001 DrugBank APRD00152 ChemSpider 10481900 
UNII 3XC8GUZ6CB 
KEGG D00448 
ChEMBL CHEMBL421 
Chemical data Formula C18H14N4O5S Mol. mass 398.394 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Sulfasalazine (brand name Azulfidine in the U.S., Salazopyrin in Europe and Hong Kong) is a sulfa drug, a derivative of mesalazine (also called 5-aminosalicylic acid, or 5-ASA), used primarily as an anti-inflammatory agent in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease as well as for rheumatoid arthritis and enthesitis related arthritis like juvenile spondyloarthropathies. It may be abbreviated SSZ. It is not a pain killer, but a codrug or a mutual prodrug of sulfapyridine and 5-amino salicylic acid coupled with an azo linkage.
Contents
Indications
- See also Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for its role in rheumatoid arthritis
Sulfasalazine is used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is also indicated for use in rheumatoid arthritis and used in other types of inflammatory arthritis (e.g. psoriatic arthritis) where it has a beneficial affect. It is often well tolerated compared to other DMARDS.
In recent British research involving animal studies, and more recently, human trials for the treatment of chronic alcoholics, sulfasalazine has been found to reverse the scarring associated with cirrhosis of the liver. Cells called myofibroblasts, which contribute to scar tissue in a diseased liver, also appear to secrete proteins that prevent the breakdown of the scar tissue. Sulfasalazine appears to retard this secretion.
A study at University of Newcastle found that the drug may also act to aid the healing of cirrhosis of the liver.[1][2]
It is usually not given to children under 2 years of age.
The use of sulfasalazine in inflammatory bowel disease has declined due mainly to the fact that it yields the metabolite sulfapyridine which gives rise to side-effects such as agranulocytosis and hypospermia. However, the other metabolite of sulfasalazine, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) is attributed to the drug's therapeutic effect. Therefore, 5-ASA and other derivatives of 5-ASA, are now usually preferred and given alone (as mesalazine), despite their increased cost, due to their more favourable side-effect profile.
Sulfasalazine has also been used successfully to treat cases of idiopathic urticaria that do not respond to antihistamines.[3]
Mode of action
Sulfasalazine, and its metabolite 5-ASA, are poorly absorbed from the gut. Its main mode of action is therefore believed to be inside the intestine.
Bowel disease
In Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, it is thought to be an antinflammatory drug that is essentially providing topical relief inside the intestine. It does this via a number of mechanisms such as reducing the synthesis of inflammatory mediators known as eicosanoids and inflammatory cytokines. However, unlike glucocorticoids (another class of drug used in the treatment in inflammatory bowel disease), sulfasalazine has no immunosuppressant action.
Arthritis
When treatment for arthritis is successful, pain, joint swelling and stiffness will be reduced and this may slow down or stop the development of joint damage. The precise reasons why sulfasalazine are effective in various forms of arthritis is not clearly understood.
Because sulfasalazine and its metabolite 5-ASA are poorly absorbed into the bloodstream, it is surprising that the drug is effective against symptoms outside of the intestine. One possible explanation is that, given that ulcerative colitis produces arthritic symptoms, the arthritic symptoms are actually a product of unrecognized ulcerative colitis, which is effectively treated with sulfazalazine.
The other metabolite, sulfapyridine, is absorbed into the blood, and is believed to be the source of the side-effects discussed below. It is possible that the sulfapyridine is responsible for some of the anti-arthritic effects of sulfasalazine.
Side effects
Refer to external links for a full listing of known side effects.
In rare cases, Sulfasalazine can cause severe depression in young males. It can also cause temporary infertility. [4]
Sulfsalazine metabolizes to sulfapyridine. Serum levels should be monitored every three months, and more frequently at the outset. Serum levels above 50 μg/l are associated with side effects.
Immune thrombocytopenia has been reported.[5]
References
- ^ "Drug 'may reverse liver disease'". BBC News. 2006-09-26. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/5382172.stm. Retrieved 2010-05-24.
- ^ Fiona Oakley, Muriel Meso, John P. Iredale, Karen Green, Carylyn J. Marek, Xiaoying Zhou, Michael J. May, Harry Millward-Sadler, Matthew C. Wright, Derek A. Mann (Jan 2005). "Inhibition of inhibitor of κB kinases stimulates hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and accelerated recovery from rat liver fibrosis". Gastroenterology 128 (1): 108-120. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2004.10.003.
- ^ McGirt LY, Vasagar K, Gober LM, Saini SS, Beck LA (Oct 2006). "Successful treatment of recalcitrant chronic idiopathic urticaria with sulfasalazine". Arch Dermatol 142 (10): 1337–1342. doi:10.1001/archderm.142.10.1337. PMID 17043190.
- ^ http://www.medic8.com/medicines/Azulfidine.html
- ^ Cantarini L, Tinazzi I, Biasi D, Fioravanti A, Galeazzi M (June 2007). "Sulfasalazine-induced immune thrombocytopenia". Postgraduate medical journal 83 (980): e1. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2006.055194. PMC 2600053. PMID 17551063. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2600053.
External links
- Web MD
- Upjohn FDA Label
- Optimal Dosing of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid: 5 Decades of Choosing Between Politicians[dead link]
Specific antirheumatic products / DMARDs (M01C) Quinolines Gold preparations Other Penicillamine #/Bucillamine • Chloroquine #/Hydroxychloroquine • Leflunomide • Sulfasalazine # • antifolate (Methotrexate #) • thiopurine (Azathioprine) #M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Sulfonamides
- Antirheumatic products
- Drugs acting on the gastrointestinal system and metabolism
- Pyridines
- Azo compounds
- Salicylic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
