- Quinoline
-
Quinoline 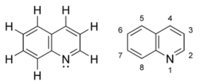
 QuinolineOther names1-benzazine, 1-azanaphthalene, benzo[b]pyridine
QuinolineOther names1-benzazine, 1-azanaphthalene, benzo[b]pyridineIdentifiers CAS number 91-22-5 
PubChem 7047 ChemSpider 6780 
UNII E66400VT9R 
KEGG C06413 
ChEBI CHEBI:17362 
ChEMBL CHEMBL14474 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - n1cccc2ccccc12
Properties Molecular formula C9H7N Molar mass 129.16 g/mol Density 1.093 g/ml Melting point −15 °C
Boiling point 237°C/760mm Hg, 108-110 °C/11mm Hg
Solubility in water Soluble Basicity (pKb) 4.85[1]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It has the formula C9H7N and is a colourless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odour. Aged samples, if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only slightly soluble in cold water but dissolves readily in hot water and most organic solvents.
Quinoline is mainly used as a building block to other specialty chemicals. Approximately 4 tonnes are produced annually according to a report published in 2005.[citation needed] Its principal use is as a precursor to 8-hydroxyquinoline, which is a versatile chelating agent and precursor to pesticides. Its 2- and 4-methyl derivatives are precursors to cyanine dyes. Oxidation of quinoline affords quinolinic acid (pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid), a precursor to the herbicide sold under the name "Assert".[2]
Like other nitrogen heterocylic compounds, such as pyridine derivatives, quinoline is often reported as an environmental contaminant associated with facilities processing oil shale or coal, and has also been found at legacy wood treatment sites. Owing to high water solubility quinoline has significant potential for mobility in the environment, which may promote water contamination. Fortunately, quinoline is readily degradable by certain microorganisms, such as Rhodococcus species Strain Q1, which was isolated from soil and paper mill sludge. [3]
Contents
Isolation and synthesis
Quinoline was first extracted from coal tar in 1834 by Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge.[4] Coal tar remains the principal source of commercial quinoline. It can be synthesized using various methods:
- Combes quinoline synthesis using anilines and β-diketones.
- Conrad-Limpach synthesis using anilines and β-ketoesters.
- Doebner-Miller reaction using anilines and α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
- Friedländer synthesis using 2-aminobenzaldehyde and acetaldehyde.
- Skraup synthesis using ferrous sulfate, glycerol, aniline, nitrobenzene, and sulfuric acid.
- Povarov reaction using an aniline, a benzaldehyde and an activated alkene.
- Camps quinoline synthesis utilizing an o-acylaminoacetophenone and hydroxide
- Knorr quinoline synthesis, using a β-ketoanilide and sulfuric acid.
- Gould-Jacobs reaction starting from an aniline and ethyl ethoxymethylenemalonate
- Niementowski quinoline synthesis, using anthranilic acid and ketones.
Applications
In manufacturing of dyes, preparation of hydroxyquinoline sulfate and niacin. Solvent for resins and terpenes.
See also
- Isoquinoline, an analog with the nitrogen atom in position 2.
- Pyridine, an analog without the fused benzene ring.
- Naphthalene, an analog without the nitrogen atom.
- Indole, an analog with only a five-membered nitrogen ring.
- Simple aromatic rings
- Niementowski quinoline synthesis, quinoline derivative synthesis
- Lindlar catalyst, quinoline prevents formation of alkanes
References
- ^ Brown, H.C., et al., in Baude, E.A. and Nachod, F.C., Determination of Organic Structures by Physical Methods, Academic Press, New York, 1955.
- ^ Gerd Collin, Hartmut Höke "Quinoline and Isoquinoline" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; 2005 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_465
- ^ O'Loughlin, E.J., S.R. Kehrmeyer, and G.K. Sims. 1996. Isolation, characterization, and substrate utilization of a quinoline degrading bacterium. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation. 38(2):107-118. doi:10.1016/S0964-8305(96)00032-7
- ^ "Quinoline". Encyclopedia Britannica. 1911. http://www.1911encyclopedia.org/Quinoline.
External links
Categories:- Quinolines
- Hazardous air pollutants
- Amine solvents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
