- Oxetacaine
-
Oxetacaine 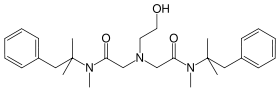
Systematic (IUPAC) name 2,2'-(2-hydroxyethylimino)bis [N-(1,1-dimethyl-2- phenylethyl)-N-methylacetamide] Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Routes Oral, topical Pharmacokinetic data Half-life 1 hour Identifiers CAS number 126-27-2 
ATC code C05AD06 PubChem CID 4621 ChemSpider 4460 
UNII IP8QT76V17 
KEGG D01152 
ChEMBL CHEMBL127592 
Chemical data Formula C28H41N3O3 Mol. mass 467.643 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Oxetacaine (INN, also known as oxethazaine) is a potent local anesthetic. It is administered orally (usually in combination with an antacid) for the relief of pain associated with peptic ulcer disease or esophagitis. It is also used topically in the management of hemorrhoid pain. Oral oxetacaine preparations are available in several countries, including India, South Africa, Japan and Brazil, but not the United States; oxetacaine was withdrawn from the UK market in 2002.
Unlike most local anesthetics, oxetacaine is active even in strongly acidic conditions.[1]
References
External links
Anesthetics: Local anesthetics - primarily sodium channel blockers (N01B) Esters Esters of aminobenzoic acidAmylocaine • Benzocaine • Butacaine • Butamben • Chloroprocaine • Dimethocaine • Meprylcaine • Metabutoxycaine • Orthocaine • Propoxycaine • Procaine (Novocaine) • Proxymetacaine • Risocaine • TetracaineEsters of benzoic acidAmides Articaine • Bupivacaine # /Levobupivacaine/Ropivacaine • Carticaine • Cinchocaine • Etidocaine • Lidocaine # • Mepivacaine • Prilocaine • TrimecaineCombinations Vasoprotectives (C05) Antihemorrhoidals for topical use corticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Betamethasone, Fluorometholone, Fluocortolone, Dexamethasone, Fluocinolone acetonide, Fluocinonide)
local anesthetics (Lidocaine, Tetracaine, Benzocaine, Cinchocaine, Procaine, Oxetacaine, Pramocaine)
other (Tribenoside)Antivaricose therapy heparins or heparinoids for topical use (Organo-heparinoid, Sodium apolate, Heparin, Pentosan polysulfate)
sclerosing agents for local injection (Monoethanolamine oleate, Polidocanol, Invert sugar, Sodium tetradecyl sulfate, Phenol)
other (Calcium dobesilate)Capillary stabilising agents bioflavonoids (Rutoside, Monoxerutin, Diosmin, Troxerutin, Hidrosmin) - other (Tribenoside, Etamsylate)
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This drug article relating to the nervous system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
