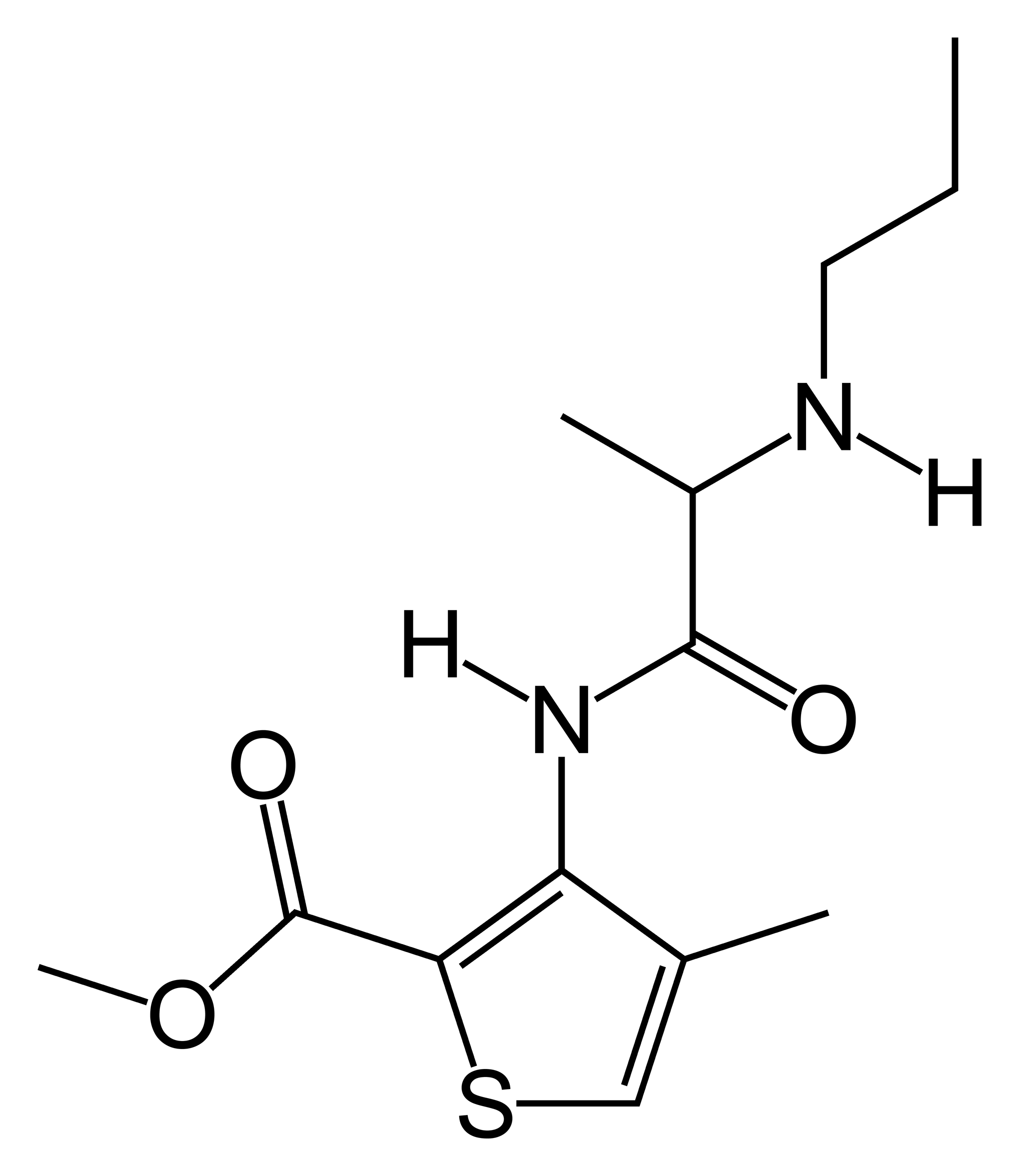
- Articaine
IUPAC_name = methyl 4-methyl-3-(2-propylaminopropanoylamino)thiophene-2-carboxylate hydrochloride
ATC_prefix= ?
ATC_suffix= ?
PubChem= ?
DrugBank= ?
CAS_number = 23964-57-0
C=13 | H=20 | N=2 | O=3 | S=1
molecular_weight = 320.836 g/mol
bioavailability = ?
metabolism =Liver , Plasma
elimination_half-life = ?
excretion = ?
pregnancy_category = ?
legal_status = ?
routes_of_administration =Subcutaneous , ?Articaine is a dental local anesthetic. It is manufactured and distributed by Septodont under the brand name Septocaine and under the name of Ultracaine by
Sanofi-Aventis , being Articaine hydrochloride 4% withepinephrine 1:100,000 or 1:200,000 injection. Septocaine was first approved for use in Germany in 1976 and throughout Europe shortly after. Canada approved usage in 1982, with the US FDA following in 2000. Qualities such as fast acting nature and strength of dosage have made it more appealing for use by dentists than other available anesthetics such asnovocaine andlidocaine .Structure and Metabolism
Articaine is unique among local anesthetics because it contains a
thiophene group, and also because it contains bothester andamide groups. Articaine is an amide anesthetic due to the amide intermediate chain, and undergoes hepatic metabolism. However, the associated ester group also allows plasma metabolism via pseudocholinesterase, purportedly increasing the rate of breakdown and reducing its toxicity. This difference in metabolism gives articaine the distinct advantage of having a 30 minute half life, as opposed to drugs such as lidocaine that have a 90 min. half life.Complications
Serious complications have been associated with Septocaine. Long-term or transient
paresthesia is among the worst of the reported side effects of Septocaine which occurs much more frequently than with lidocaine. Fact|date=August 2007It should be noted that almost all recorded cases of long term numbness or
parasthesia in a dental setting are associated with a mandibular nerve block type injection and simple infiltration injections are generally thought to be immune from such complications. For this reason many dentists have abandoned using articaine for mandibular nerve blocks.Clinical use
Articaine is often used by dentists for patients in whom lidocaine is not very effective. In people with
hypokalemic sensory overstimulation lidocaine is not very effective and articaine works well [cite journal |author= Segal MM, Rogers GF, Needleman HL, Chapman CA |title= Hypokalemic sensory overstimulation |journal= J Child Neurol |volume=22 |issue=12 |pages=1408–10 |year=2007 |doi=10.1177/0883073807307095 |pmid=18174562] .External links
* [http://www.septodont.com Septodont]
* [http://www.chemindustry.com/chemicals/810897.html Structure]
*cite journal |author=Haas DA |title=Articaine and paresthesia: epidemiological studies |journal=J Am Coll Dent |volume=73 |issue=3 |pages=5–10 |year=2006 |pmid=17477212 |doi= |url=References
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.